本试题 “短文改错。此题要求改正所给短文的错误。对标有题号的每一行做出判断:如无错误,在该行右边横线上划一个勾(√);如有错误(每行只有一个错误),则按下列情...” 主要考查您对可数名词及其单复数
定冠词
物主代词
形容词
并列连词
动词的过去式
动词
动名词
it的用法
主谓一致
等考点的理解。关于这些考点您可以点击下面的选项卡查看详细档案。
- 可数名词及其单复数
- 定冠词
- 物主代词
- 形容词
- 并列连词
- 动词的过去式
- 动词
- 动名词
- it的用法
- 主谓一致
可数名词:
是指能以数目来计算,可以分成个体的人或东西;因此它有复数形式,当它的复数形式在句子中作主语时,句子的谓语也应用复数形式。
可数名词复数的规则变化:
| 情况 | 构成方法 | 读音 | 例词 |
| 一般情况 | 加 –s | 1.清辅音后读/s/; 2.浊辅音和元音后读/z/; |
map-maps bag-bags car-cars |
| 以s,sh,ch,x等结尾的词 | 加 -es | 读 /iz/ | bus-buses watch-watches |
| 以ce,se,ze,(d)ge等结尾 的词 |
加 -s | 读 /iz/ | license-licenses |
| 以辅音字母+y结尾的词 | 变y 为i再加es | 读 /z/ | baby-babies |
1)以y 结尾的专有名词,或元音字母+y结尾的名词变复数时,直接加s变复数:
如:two Marys the Henrys monkey---monkeys holiday---holidays
比较:层楼:storey---storeys story---stories
2)以o 结尾的名词,变复数时:
a. 加s,如: photo---photos piano---pianos
b. 加es,如:potato--potatoes tomato--tomatoes
c. 均可,如:zero---zeros / zeroes
3)以f或fe 结尾的名词变复数时:
a. 加s,如: belief---beliefs roof---roofs safe---safes gulf---gulfs;
b. 去f, fe 加ves,如:half---halves knife---knives leaf---leaves wolf---wolves wife---wives life---lives thief---thieves;
c. 均可,如:handkerchief: handkerchiefs / handkerchieves
可数名词复数的不规则变化:
1)child---children foot---feet tooth---teeth mouse---mice man---men woman---women
注意:与 man 和 woman构成的合成词,其复数形式也是 -men 和-women。
如:an Englishman,two Englishmen. 但German不是合成词,故复数形式为Germans;Bowman是姓,其复数是the Bowmans。
2)单复同形 如:
deer,sheep,fish,Chinese,Japanese
li,jin,yuan,two li,three mu,four jin
但除人民币元、角、分外,美元、英镑、法郎等都有复数形式。如:
a dollar, two dollars; a meter, two meters
3)集体名词,以单数形式出现,但实为复数。
如:staff people police cattle 等本身就是复数,不能说a staff a people,a police,a cattle,
但可以说a person,a policeman,a head of cattle, the English,the British,the French,the Chinese,the
Japanese, the Swiss 等名词,表示国民总称时,作复数用。
如:The Chinese are industries and brave. 中国人民是勤劳勇敢的。
4)以s 结尾,仍为单数的名词,如:
a. maths,politics,physics等学科名词,为不可数名词,是单数。
b. news 是不可数名词。
c. the United States,the United Nations 应视为单数。
The United Nations was organized in 1945. 联合国是1945年组建起来的。
d. 以复数形式出现的书名,剧名,报纸,杂志名,也可视为单数。
"The Arabian Nights" is a very interesting story-book.
<<一千零一夜>>是一本非常有趣的故事书。
5) 表示由两部分构成的东西,如:glasses (眼镜) trousers, clothes ;
若表达具体数目,要借助数量词 pair(对,双); suit(套); a pair of glasses; two pairs of trousers
6)另外还有一些名词,其复数形式有时可表示特别意思,如:goods货物,waters水域,fishes(各种)鱼
复合名词的复数形式:
名词作定语名词作定语一般用单数,但也有以下例外。
1)用复数作定语。
如:sports meeting 运动会
students reading-room 学生阅览室
talks table 谈判桌
the foreign languages department 外语系
2)man, woman, gentleman等作定语时,其单复数以所修饰的名词的单复数而定。
如:men workers
women teachers
gentlemen officials
3)有些原有s结尾的名词,作定语时,s保留。
如:goods train (货车)
arms produce 武器生产
customs papers 海关文件
clothes brush衣刷
4)数词+名词作定语时,这个名词一般保留单数形式。
如:two-dozen eggs 两打/(二十四个鸡蛋)
a ten-mile walk 十里路
two-hundred trees 两百棵树
a five-year plan 一个五年计划
可数名词单复数知识体系:

不同国籍人的单复数:
国籍
总称(谓语用复数)
单数
复数
中国人
the Chinese
a Chinese
two Chinese
瑞士人
the Swiss
a Swiss
two Swiss
澳大利亚人
the Australians
an Australian
two Australians
俄国人
the Russians
a Russian
two Russians
意大利人
the Italians
an Italian
two Italians
希腊人
the Greek
a Greek
two Greeks
法国人
the French
a Frenchman
two Frenchmen
日本人
the Japanese
a Japanese
two Japanese
美国人
the Americans
an American
two Americans
印度人
the Indians
an Indian
two Indians
加拿大人
the Canadians
a Canadian
two Canadians
德国人
the Germans
a German
two Germans
英国人
the English
an Englishman
two Englishmen
瑞典人
the Swedish
a Swede
two Swedes
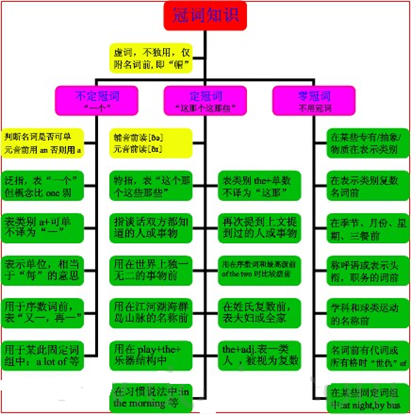
定冠词的定义:
定冠词the 有this,that,these,those等意义,但较弱,用于单数或复数名词前,主要用来特指,使一个或几个事物区别于所有其他同名的事物。
定冠词通常位于名词或名词修饰语前,但放在both、all、double、half、twice等词之后。
如:All the students in the class went out.班里所有的学生都出去了。
定冠词的用法:
1、表示特指:
如:Look! A car has stopped there. The car is beautiful. 瞧,有辆汽车在那儿停下了。那辆汽车可真漂亮。
Why not ask the teacher? 为什么不问问老师?
2、与单数可数名词连用表类别:
如:I hate the telephone. 我讨厌电话。
The cobra is dangerous. 眼镜蛇是危险的。
3、与某些形容词连用表示类别:
如:The rich are not always happier than the poor. 富人并不总是比穷人过得开心。
Theoldaremorelikelytocatchcoldthantheyoung.老年人比年轻人容易感冒。
4、用于独一无二的事物名词前:
如:The earth goes around the sun. 地球绕着太阳转。
The sky was blue and clear. 天空清澈湛蓝。
5、用于方向或方位等名词前:
如:He looked towards the east. 他朝东望。
Turn to the right at the second crossing. 在第二十字路口向右拐。
6、用于序数词或形容词的最高级前:
如:You will be the second to speak. 你第二个发言。
Autumn is the best season here. 秋季是这里最好的季节。
7、用于乐器名词前表示演奏:
如:He plays the piano very well. 他的钢琴弹得很好。
注:若不是从演奏角度来考虑,而是考虑乐器的实体,则不一定用定冠词:
He bought a piano for his son. 他为儿子买了部钢琴。
定冠词与不定冠词互换用法比较:
1、在形容词最高级前一般加定冠词。但有时却用不定冠词,这时它不表示“最”的意思,而表示“非常”“很”的意思。
如:This is the most important question of all. 这是所有问题中最重要的一个。
This is a most important question. 这时一个非常重要的问题。
2、在序数词前加定冠词,表示“第几”;加不定冠词则表示“又”“再”。
如:Will you be the firse to read the text? 你第一个读课文好吗?
Will you have a second try? 你再试一次好吗?
3、在有些短语中,用定冠词和不定冠词一样。
如:The number of our school students is about 1500. 我校学生人数约为1500人。
定冠词的用法口诀:
特指双熟悉,上文已提及;
世上独无二,序数最高级;
某些专有名,习语及乐器。
以上口诀归纳了用定冠词的一般情况,即:
①特指某些人或物
②谈话双方都熟悉的人或事
③上文已经提到的人或事
④世界上独一无二的事物前
⑤序数词回形容词最高级前
⑥某些专有名词前
⑦一些习惯短语(如:intheday等)中和乐器前(如:playtheviolin/piano)。
定冠词知识体系:
定冠词用法拓展:
1、用于姓氏的复数前,表示全家人或全家中两个或两个以上的人:
如:The Browns live next to us. 布朗一家就住在我们隔壁。
The Greens have no Children. 格林夫妇没有小孩。
2、用来代替前面已提到的人的身体部位或衣着等的一部分:
如:He hit me in the face. 他打我的脸。
He caught the thief by the collar. 他抓住小偷的衣领。
3、用于逢整十数词的复数名词前,指世纪中的年代或人的约略年岁:
如:He began to learn French in his fifties. 他五十多岁开始学习法语。
He went to Japan with his family in the sixties. 他在60年代带家人去了日本。
4、用于某些单数可数名词前,使意义抽象化,指其属性或功能等:
如:This colour is pleasant to the eye. 这颜色悦目。
He is fond of the bottle. 他喜欢喝酒。
5、表示计算单位,含有a, each, per 之类的意义:
如:He is paid by the hour (piece). 他拿计时(件)工资。
It sells at two dollars the pound. 这东西每磅卖两美元。
6、用于人名前,或特指、或比喻、或指其作品等;用于某些产品的名称前,指产品:
如:He likes the Picasso. 他喜欢毕加索的画。
Lu Xun has been known as the Gorky of China. 鲁迅人称中国的高尔基。
7、用于江、(运)河、海、洋以及山脉、群岛、半岛、海岛、海峡、沙漠等名称的前:
如:the Chang jiang River 长江
the Pacific(Ocean) 太平洋
the Suez(Canal) 苏伊士运河
①关于湖名前是否用冠词通常要分两种情况:
中国的湖名在英译时,其前通常加定冠词:
the West Lake 西湖,the Dong ting Lake洞庭湖。
而外国的湖名前,多数不加定冠词,少数加定冠词,视习惯而定:
Lake Success 成功湖,the Lake of Geneva日内瓦湖
②山名的构成有两种方式:
若用于“山名+Mountains”,其前常用定冠词:the Jing gang Mountains 井冈山;
若用于“Mount/Mt+山名”,则通常不用冠词:Mount Tai 泰山。
另外,若不出现mountain一词时,则通常要用冠词:theAlps阿尔卑斯山。
8、用于由普通名词或含有普通名词构成的专有名词 (如国名、地名、政党、团体、组织机构以及旅馆、商店、学校、医院、文娱场所、建筑物等)前:
如:the United Nations 联合国
the People's Republic of China 中华人民共和国
the National People's Congress 全国人民代表大会
注:大学名称的构成要注意以下情况:
①对于以地名命名的大学,通常有两种形式 (注意冠词的有无):
如:the University of London / London University 伦敦大学
②对于以人名命名的大学,通常只有一种表达(不用冠词):
如:Yale University 耶鲁大学
Brown University 布朗大学
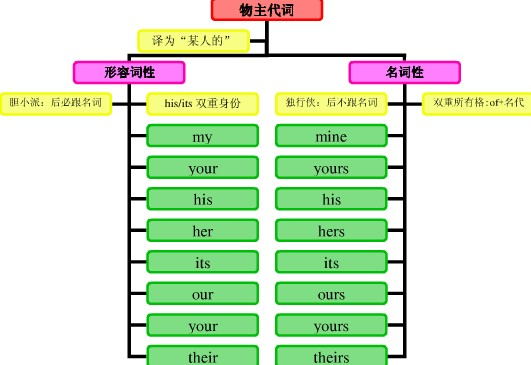
物主代词的概念:
表示所有关系的代词叫物主代词。
物主代词有两种形式:一种是形容词性物主代词,在句中只能充当定语;另一种是名词性物主代词,和名词用法相同,在句中作主语、宾语、表语等。
物主代词的特性:
1、物主代词既有表示所属的作用又有指代作用。
例如:John had cut his finger;约翰割破了手指。
物主代词有形容词性(my,your等)和名词性(mine,yours等)两种,形容词性的物主代词属于限定词。
名词性的物主代词在用法上相当于省略了中心名词的“'s”属格结构,
如:Jack's cap 意为 The cap is Jack's.
His cap 意为 The cap is his.
2、名词性物主代词的句法功能:
a.作主语,例如:May I use your pen? Yours works better.
b.作宾语,例如:I love my motherland as much as you love yours.
c.作介词宾语,例如:Your should interpret what I said in my sense of the word,not in yours.
d.作主语补语,例如:The life I have is yours. It's yours. It's yours. 我的生命属于你,属于你,属于你。
物主代词的基本形式:
|
第一人称 |
第二人称 |
第三人称 | ||||
|
|
|
名词性 |
形容词性 |
名词性 |
形容词性 |
名词性 |
|
单数 |
my |
mine |
your |
yours |
his |
his |
|
复数 |
our |
ours |
your |
yours |
theirs | |
形容词性物主代词的用法:
1、形容词性物主代词通常修饰名词,作定语。
如:We should treat her mother very well.
2、与own连用表示强调。
如:I saw it with my own eyes.
名词性物主代词的用法:
1、名词性物主代词可作主语、表语和宾语。
如:This is my desk. Yours is over there.
2、名词性物主代词常用于双重属格,于of连用。
如:This girl is a friend of mine.
物主代词知识体系:
物主代词特别用法:
1、名词性和形容词性物主代词不能混用。
如:Jack has a low opinion of Sue.
2、物主代词的单复数必须和它所指代的名词一致。
如:His idea is to do more practice every day.
3、对于anyone,anybody,everyone,everybody,应根据上下文来判断his或her,有时也可用their。
如:Has everyone finished their work?
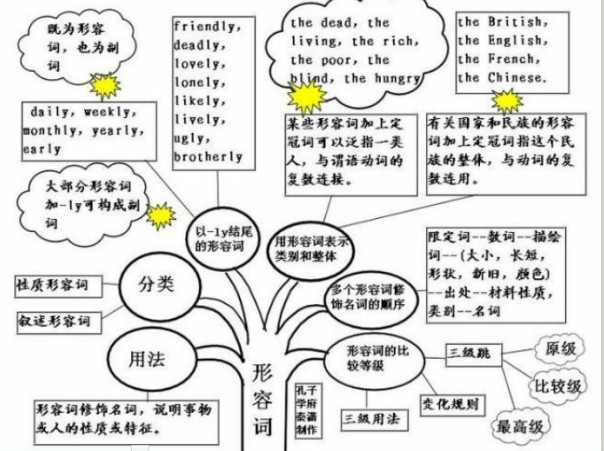
形容词的概念:
形容词(adjective),简称adj.或a,形容词用来修饰名词或代词,表示人或事物的性质、状态,和特征的程度好坏与否,形容词在句中作定语、表语、宾语补足语。通常,可将形容词分成性质形容词和叙述形容词两类,其位置不一定都放在名词前面。
形容词的作用与位置:
形容词是用来修饰名词的,常被放在名词前作定语,或放在系动词后面作表语。以下属几种特殊情况,须牢记;
(1)形容词短语作定语,定语后置。
如:a language difficult to master,
a leaning tower about 180 feet high
(2)表语形容词(afraid、alike、alone、asleep、awake、alive等)作定语,定语后置。如a man alive。有些表身体健康状况的形容词如well、faint、ill只作表语。sick既可作表语又可作定语,ill如作定语意为“bad”。
(3)用作定语,修饰由不定代词one、no、any、some和every构成的复合词如anything、something等时,通常后置。
如:I have something important to tell you.
(4)else常用作疑问代词和不定代词的后置定语。
(5)enough、nearby修饰名词前置或后置,程度副词一般位于形容词、副词前面,enough修饰形容词、副词时,必须后置。
(6)几个并列的形容词作定语,其语序通常为:限定语(The、A)+描绘性形容词+size(大小)+shape(形状)+age(年龄、时间)+color(颜色)+origin(国籍、来源)+material(材料)+purpose(目的)+名词。
口诀:
限定描绘大长高,形状年龄和新老;颜色国籍跟材料,作用类别往后靠。
如:a heavy black Chinese steel umbrella,
the man's first tow interesting little red French oil paintings
形容词的用法:
1、形容词修饰名词,说明事物或人的性质或特征。通常,可将形容词分成性质形容词和叙述形容词两类,其位置不一定都放在名词前面:
1)直接说明事物的性质或特征的形容词是性质形容词,它有级的变化,可以用程度副词修饰,在句中可作定语、表语和补语。例如:hot热的。
2)叙述形容词只能作表语,所以又称为表语形容词。这类形容词没有级的变化,也不可用程度副词修饰。
大多数以a开头的形容词都属于这一类。例如:
afraid害怕的。(错)Heisanillman. (对)Themanisill. (错)Sheisanafraidgirl. (对)Thegirlisafraid.
这类词还有:well,unwell,ill,faint,afraid,alike,alive,alone,asleep,awake等。
3)形容词作定语修饰名词时,要放在名词的前边。但是如果形容词修饰以-thing为字尾的词语时,要放在这些词之后。例如:somethingnice
2、用形容词表示类别和整体:
1)某些形容词加上定冠词可以泛指一类人,与谓语动词的复数连接。如:the dead,the living,the rich,the poor,the blind,the hungry The poorarelosinghope.穷人失去了希望。
2)有关国家和民族的形容词加上定冠词指这个民族的整体,与动词的复数连用。如:the British,the English,the French,the Chinese. The English have wonderful senseofhumor.
以-ly结尾的形容词:
1)大部分形容词加-ly可构成副词。但friendly,deadly,lovely,lonely,likely,lively,ugly,brotherly,仍为形容词。改错:
如:(错)She sang lovely.
(错)He spoke to me very friendly.
(对)Her singing was lovely.
(对)He spoke to me in a very friendly way.
2)有些以-ly结尾既为形容词,也为副词。 daily,weekly,monthly,yearly,early .
如:The Times is a daily paper.
The Times is published daily.
形容词知识体系:
复合形容词的构成:
(1)形容词+名词+ed:
如:kind-hearted 好心的,white-haired 白发的
(2)形容词+形容词:
如:red-hot 炽热的,dark-blue 深蓝的
(3)形容词+现在分词:
如:good-looking 好看的,easy-going 随和的
(4)副词+现在分词:
如:hard-working 勤劳的,fast-moving 快速转动的
(5)副词+过去分词:
如:hard-won 得来不易的,newly-made 新建的
(6)名词+形容词:
如:life-long 终生的,world-famous 世界闻名的
(7)名词+现在分词:
如:peace-loving 爱好和平的,fun-loving 爱开玩笑的
(8)名词+过去分词:
如:snow-covered 白雪覆盖的,hand-made 手工的
(9)数词+名词+ed:
如:four-storeyed 4层楼的,three-legged 3条腿的
(10)数词+名词(名词用单数):
如:ten-year 10年的, two-man 两人的
并列连词的概念:
连词是一种虚词,它不能独立担任句子成分而只起连接词与词,短语与短语以及句与句的作用。连词主要可分为两类:并列连词和从属连词。并列连词用来连接平行的词、词组和分句。如:and, but, or, nor, so, therefore, yet, however, for, hence, as well as, both...and, notonly...butalso, either...or, neither...nor, (and)then 等等。
并列连词与并列结构:
并列连词引导两个并列的句子。
1)and与or:
判断改错:
(错) They sat down and talk about something.
(错) They started to dance and sang.
(错) I saw two men sitting behind and whisper there.
(对) They sat down and talked about something.
(对) They started to dance and sing.
(对) I saw two men sitting behind and whispering there.
解析:第一句:and连接两个并列的谓语,所以talk应改为talked。
第二句:and连接两个并列的动词不定式,第二个不定式往往省略to,因此sang应改为sing。
第三句:and连接感观动词saw后面的用作的宾补的两个并列分词结构,因此whisper应改为whispering。
注意:and还可以和祈使句或名词词组连用表示条件。(or也有此用法)
如:Make up your mind, and you'll get the chance.=If you make up your mind, you'll get the chance.
One more effort, and you'll succeed.=If you make one more effort, you'll succeed.
2)both...and 两者都
如:She plays(both) the piano and the guitar.
3)not only...but(also), as well as 不但…而且
如:She plays not only the piano, but(also) the guitar.
注意:not only…but also关联两个分句时,一个分句因有否定词not而必须倒装。
如:Not only does he like reading stories, but also he can even write some.
4)neither...nor 意思为“既不……也不……”谓语动词采用就近原则,与nor后的词保持一致。
如:Neither you nor he is to blame.
比较so和such :
so与such的用法由不同词性决定。such是形容词,修饰名词或名词词组,so是副词,只能修饰形容词或副词。so还可与表示数量的形容词many,few,much,little连用,形成固定搭配。
构成:so+adj.
such+a(n)+n.
so+adj.+a(n)+n.
such+n.(pl.)
so+adj.+n.(pl.)
such+n.(pl.)
so+adj.+n.[不可数]
such+n.[不可数]
如:so foolish
such a fool
so nice a flower
such a nice flower
so many/few flowers
such nice flowers
so much/ little money.
such rapid progress
so many people
such a lot of people
注:so many 已成固定搭配,a lot of 虽相当于many,但a lot of为名词性的,只能用such搭配。 so...that与such...that之间的转换既为so与such之间的转换。
并列连词用法点拨:
1、表示并列关系:
1)or意思为“否则”。
如:I must work hard, or I'll fail in the exam.
2)either...or意思为“或者……或者……”。注意谓语动词采用就近原则。
如:Either you or I am right.
2、表示转折或对比关系:
1)but表示转折,while表示对比。
如:Some people love cats, while others hate them.
典型例题:
—Would you like to come to dinner tonight?
—I'd like to, ___ I'm too busy.
A. and
B. so
C. as
D. but
答案:D。but与前面形成转折,符合语意。而表并列的and,结果的so,原因的as都不符合句意。
2)not...but...意思为“不是……而是……” not和but后面的用词要遵循一致原则。
如:They were not the bones of an animal, but(the bones) of a human being.
3、表示原因关系:
1)for 判断改错:
(错)For he is ill, he is absent today.
(对)He is absent today, for he is ill. for是并列连词,不能置于含两个并列分句的句子的句首,只能将其放在两个分句中间。
并列连词知识体系:
| 种类 | 用法 | 举例 |
| 并列连词 | 表示转折关系 | yet, but等 |
| 表示并列关系 | and, or, either...or..., as welll as等 | |
| 表示因果关系 | for, so等 |
比较and和or的用法:
1)并列结构中,or通常用于否定句,and用于肯定句。
2)但有时and也可用于否定句。请注意其不同特点:
如:There is no air or water in the moon.
There is no air and no water on the moon.
在否定中并列结构用or连接,但含有两个否定词的句子实际被看作是肯定结构,因此要用and。
典型例题:
—I don't like chicken___fish.
—I don't like chicken, ___I like fish very much.
A. and;and
B. and;but
C. or;but
D. or;and
答案:C。否定句中表并列用or,but表转折。
判断改错:
(错)We will die without air and water.
(错)We can't live without air or water.
(对)We will die without air or water.
(对)We can't live without air and water.
动词过去式的概念:
用来表示动词过去时的动词形式,规则变化加是动词后加-ed,不规则的要单独记。
动词过去式变化规则及其读音规则:
一、规则动词的过去式变化如下:
1、一般情况下,动词词尾加-ed:
如:work-worked play-played wanted-wanted act-acted
2、以不发音的-e结尾动词,动词词尾加-d:
如:live-lived move-moved taste-tasted hope-hoped
3、以辅音字母+y结尾的动词,把-y变为-i再加-ed:
如:study-studied copy-copied cry-cried carry-carried
4、以一个辅音字母结尾的重读闭音节动词,双写词尾辅音字母,再加-ed:
如:stop-stopped
5、不规则动词的过去式变化规律性不强,须多加记忆。
如:go-went make-made get-got buy-bought come-came fly-flew
二、不规则动词的过去式的构成:
1、把动词原形中的i改为a,变成过去式。
如:begin—began,drink—drank,give—gave,ring—rang,sing—sang,sit—sat,swim—swam
2、把重读开音节中的i改为o,变成过去式。
如:drive—drove,ride—rode,write—wrote
3、改动词原形中的aw/ow为ew,变成过去式。
如:draw—drew,grow—grew,know—knew,throw—threw(动词show除外,show—showed)
4、动词原形中的e改为o,变成过去式。
如:get—got,forget—forgot
5、动词原形中的ee改为e,变成过去式。
如:feed—fed,meet—met
6、动词原形中的eep改为ept,变成过去式。
如keep—kept,sleep—slept,sweep—swept
7、动词原形中的eak改为oke,变成过去式。
如:break—broke,speak—spoke
8、动词原形中的ell改为old,变成过去式。
如:sell—sold,tell—told
9、动词原形中的an改为oo,变成过去式。
如:stand—stood,understand—understood
10、以ought和aught结尾,且读音是〔:t〕的过去式。
如:bring—brought,buy—bought,think—thought,catch—caught,teach—taught
11、以ould结尾且读音为〔ud〕的情态动词过去式。
如:can—could,shall—should,will—would
12、把动词原形中的o改为a,变成过去式。
如:come—came,become—became
13、在动词原形后加d或t变成过去式,并且发生音变。
如:hear〔hi〕—heard〔h:d〕,say〔sei〕—said〔sed〕,mean〔mi:n〕—meant〔ment〕
14、动词的过去式与动词原形一样。
如: let—let,must—must,put—put,read—read〔red〕
15、不符合上述规律的动词过去式。
如:am,is—was,are—were,build—built,do—did,eat—ate,fall—fell,feel—felt,find—found,fly—flew,
go—went,have/has—had,hold—held,leave—left,make—made,may—might,run—ran,see—saw,take—took
三:过去式“-ed”的发音规则:
(1)动词词尾为“t,d”时,发/id/音。
如:want→wanted(要)need→needed(需要)
(2)动词词尾为清辅音时,发/t/音。
如:help→helped(帮助)laugh→laughed(笑)look→looked(看) kiss→kissed(吻)wash→washed(洗)watch→watched(注视)
(3)动词词尾为t,d以外之浊辅音或元音时,发/d/音。
如:call→called(叫)stay→stayed(停留)cry→cried(哭)
be动词的过去式:
在没有实义动词的句子中使用be动词,am,is的过去式为was;are的过去式为were.请看如下句型的构成:
1、肯定句:主语+was(were)+宾语
例:I was late yesterday.(昨天我迟到了。)
2、否定句:主语+was(were)+not+宾语
例:We weren't late yesterday. (我们昨天没迟到)
3、疑问句:Was(Were)+主语+宾语
例:Were you ill yesterday?(你昨天病了吗?)
4、肯定回答:Yes, I was. (是的,我病了。)
否定回答:No, I wasn't. (不,我没病。)
5、特殊疑问句:特殊疑问词+was(were)+主语+宾语
例:When were you born? 你是什么时候出生的?
【方法窍门】
be的过去式有四巧:
一是时间状语巧:表示过去的短语要记牢;
二是形式巧:单数was,复数were;
三是否定句结构巧:not紧跟was/were;
四是疑问句式巧:was/were向前跑(提前)。
【思路分析】
『一巧』 时间状语巧。一般过去时表示过去发生的动作或存在的状态,恰巧与表示过去的一些时间状语连用。
例如:yesterday, last night/week/month/year, last Saturday, the day beforey esterday, in 1998, five years ago等。
『二巧』 形式巧。它与一般现在时一样,形式多样:当主语是第一人称单数或第三人称单数时,谓语动词用was;主语是第二人称或其他人称复数时,谓语动词用were。
例如:I was in the classroom yesterday morning. 昨天早上我在教室里。
He was at school last Tuesday. 上周二他在学校。
They were over there a moment ago. 刚才他们在那边。
『三巧』 否定句结构巧。与动词be的一般现在时一样,它在动词后面加not即可变成否定句,并且was, were与not可以缩写成wasn't, weren't。即:主语+wasn’t/weren’t+表语+其他。
例如:I was not(=wasn't)here yesterday. 昨天我不在这儿。
My parents were not(=weren't)at home last Sunday. 上周日我父母不在家。
『四巧』 疑问句式巧。把was, were提到句首,句末用问号即可变为一般疑问句。即:Was(Were)+主语+表语+其他?这恰巧与动词be的一般现在时的疑问句式相似。
例如:Were you at home the day before yesterday? 前天你在家吗?
Was she late this morning? 今天早上她迟到了吗?
更巧的是疑问句的答语也相似,肯定回答用“Yes, 主语+was/were.”;否定回答用“No, 主语+wasn't/weren't.”。
例如:—Were Wei Hua and Han Mei here just now? —刚才魏华和韩梅在这儿吗?
—Yes, they were./No, they weren't.是的,在这了。
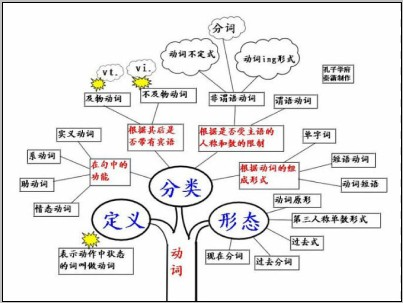
动词的定义:
表示动作中状态的词叫做动词。根据其在句中的功能,动词可分为行为动词、系动词、助动词和情态动词四类,有些动词是兼类词。
例如:We have lunch at 12. (have是行为动词)
We have been to NewYork. (have是助动词)
I am hungry. (am是系动词)
You need not have waited for me. (need是情态动词)
The door needs painting. (need是兼类词)
动词的分类:
1)表示动作中状态的词叫做动词。
2)根据其在句中的功能,动词可分为四类,分别是:
实义动词(Notional Verb)、系动词(Link Verb)、助动词(Auxiliary Verb)、情态动词(Modal Verb)。
说明:有些情况下,有些动词是兼类词。
例如:We are having a meeting. 我们正在开会。(having是实义动词。)
He has gone to NewYork.他已去纽约。(has是助动词。)
3)动词根据其后是否带有宾语,可分为两类,分别是:
及物动词(Transitive Verb)、不及物动词(Intransitive Verb),缩写形式分别为vt.和vi.。
说明:同一动词有时可用作及物动词,有时可用作不及物动词。
例如:She can dance and sing. 她能唱歌又能跳舞。(sing在此用作不及物动词。)
She can sing many English songs. 她能唱好多首英文歌曲。(sing用作及物动词。)
4)根据是否受主语的人称和数的限制,可分两类,分别是:
限定动词(Finite Verb)、非限定动词(Non-finite Verb)。
例如:She sings very well. 她唱得很好。(sing受主语she的限制,故用第三人称单数形式sings。)
She wants to learn English well. 她想学好英语。(to learn不受主语she的限制,没有词形变化,是非限定动词。
说明:英语中共有三种非限定动词,分别是:动词不定式(Infinitive)、动名词(Gerund)、分词(Participle)。
5)根据动词的组成形式,可分为三类,分别是:
单字词(One-Word Verb)、短语动词(Phrasal Verb)、动词短语(Verbal Phrase)
例如:The English language contains many phrasal verbs and verbal phrases. 英语里有许多短语动词和动词短语。(contains是单字动词。)
Students should learn to look up new words in dictionaries. 学生们学会查字典。(look up是短语动词。)
The young ought to take care of the old. 年轻人应照料老人。(takecareof是动词短语。)
6)动词有五种形态,分别是:
原形(OriginalForm)、第三人称单数形式(Singular From in Third Personal)、过去式(Past Form)、过去分词(Past Participle)、现在分词(Present Participle)。
动词知识体系:
动名词概念:
动名词是一种兼有动词和名词特征的非限定动词。它可以支配宾语,也能被副词修饰,动名词有时态和语态的变化。
现在分词和动名词用法比较:
动词的-ing形式包括现在分词和动名词两种形式。他们的句法功能如下:
动词的-ing形式如果作句子的主语或者宾语时,应该是动名词形式;如果作补语或者状语时,应该是现在分词形式。那么作表语或者定语的动名词和现在分词又该怎样区分呢?
1、动名词与现在分词作表语时的比较:
(1)动名词作表语说明主语的内容,回答what的问题;现在分词作表语相当于形容词作表语,说明主语的性质、特征等,回答how的问题。
如:One of the best exercises is swimming. 游泳是最好的运动项目之一。
What pleases him most is bathing in the sea. 最使他高兴的事是在海中沐浴。
The situation both at home and abroad is very in-spiring. 国内外的形势都很鼓舞人心。
The color is pleasing to the eye. 颜色悦目。
(2)动名词作表语,表语和主语几乎处于同等地位,可以互换位置,其句意不变;现在分词作表语,表语和主语则不能互换位置。
如:Our work is serving the people.
(=Serving the people is our work.)我们的工作是为人民服务。
The news was disappointing. 那消息令人失望。
(3)作表语的现在分词前可以用very,quite,rather,greatly等副词修饰,而动名词则不可以。
如:What he said was very encouraging. 他的话很鼓舞人心。
Our goal is realizing the four modernizations in the near future. 我们的目标是在不久的将来实现四个现代化。
(4)现在分词与形容词一样可以和more,the most构成形容词的比较级和最高级,而动名词则不可以。
如:The story is the most fascinating. 那个故事最迷人。
(5)作表语用的现在分词除了和be连用以外,还可以和其它的系动词连用;而作表语的动名词则通常只能和be连用。
如:His speech seems inspiring.他的演讲似乎很鼓舞人心。
His interest is writing for the news papers. 他的爱好是给报社写文章。
(6)有些用作表语的现在分词已经形容词化了。常见的有:exciting,moving,inspiring,missing,interesting,disappointing等。
2、动名词与现在分词作定语时的比较:
(1)动名词作定语时,表示它所修饰的名词的性能和用途,和它所修饰的名词在逻辑上没有主谓关系;
现在分词作定语时,表示它所修饰的名词正在进行的动作,和它所修饰的名词在逻辑上有主谓关系,常可以扩展成一个定语从句。
如:a swimming girl=a girl who is swimming 一个在游泳的姑娘
a walking stick=a stick that is used for walking 一根拐杖
(2)现在分词作定语有时可以后置,而动名词则通常只能放在它所修饰的名词之前。
如:The girl wearing glasses is one of his students. 戴眼镜的那个女孩是他的一个学生。
I bought some reading materials. 我买了一些阅读材料。
动名词的用法:
1、作主语:
例如:Fighting broke out between the South and the North. 南方与北方开战了。
2、作宾语:
a. 有些动词可以用动名词作宾语。
例如:admit承认 appreciate感激 avoid避免 complete完成 consider认为 delay耽误 deny否认 detest讨厌 endure忍受 enjoy喜欢 escape逃脱 fancy想象 finish完成 imagine想象 mind介意 miss想念 postpone推迟 practice训练 recall回忆 resent讨厌 resume继续 resist抵抗 risk冒险 suggest建议 face面对 include包括 stand忍受 understand理解 forgive宽恕 keep继续
例如:Would you mind turning down your radio a little, please? 你把收音机音量调小一点,好吗?
The squirrel was lucky that it just missed being caught. 这松鼠幸运得很,刚逃避了被逮住的厄运。
b. 有些结构后面可以用动名词作宾语或其他成分。
例如:admit to prefer...to burst out keep on insist on count on set about put off be good at take up give up be successful in be used to lead to devote oneself to object to stick to no good no use be fond of look forward to be proud of be busy can't help be tired of be capable of be afraid of think of
3、作表语,对主语说明、解释:
例如:Her job is washing, cleaning and taking care of the children. 她的工作是洗刷、清扫和照顾孩子。
比较:She is washing, cleaning and taking care of the children.
4、作定语,一般表示所修饰名词事物的用途:
例如:a writing desk=a desk for writing 写字台
a swimming pool=a pool swimming 游泳池
有些动名词作定语,与所修饰的名词关系比较复杂。
例如:boiling point=a temperature point at which something begins to boil 沸点
a walking tractor=a tractor which a driver can operate while he or she is walking behind it 手扶拖拉机
动名词知识体系:

动名词与不定式用法对比:
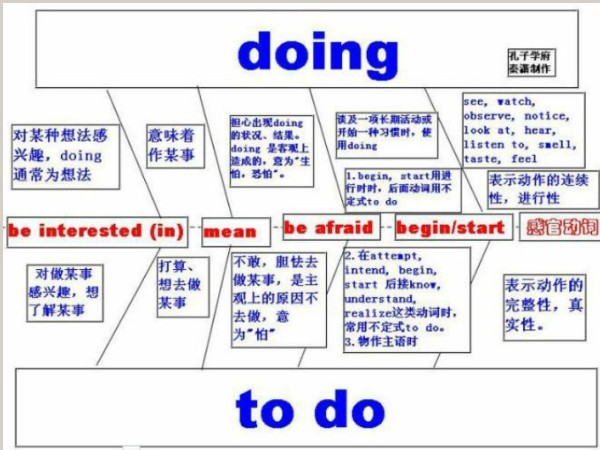
it的概念:
it可用作人称代词、指示代词、先行词及引导词等。
it 的用法:
1、it可指天气、温度、时间、距离等 。
如:It is cold today, isn't it?
2、用作人称代词,代替前文提到过的事物。
如:The dog is not acold-blooded animals. It doesn't need to hibernate.
3、为避免重复,it可用来代替前面说过的短语或句子。
如:I tried to persuade my father to give up smoking, but found it impossible. (it=to persuade my father to give up smoking)
4、代替指示代词this,that。
如:—What's this?
—It's an album.
—Whose new bike is that?
—It's Mary's.
注:it与one,that的区别:
it=the(this, that)+名词,特指并且代替前面所提到的某特定事物。
如:He's bought a new car, so he drives it everywhere to show ito ff.
one=a+名词,one指前面提到的同类事物中的不同的另一个。
如:He needs a computer, but he can't afford one.
that=the+名词,that指代的名词与前面的名词属于同一类,但不属同一个。
如:The population of China is larger than that of Japan. that指代population,但其后有一个of短语作定语,以区别于the population of China。
注:it与that的异同:
it指同一事物,that指同类但并不是同一事物。
如:I like the climate of Kunming more than that of Beijing.
The climate of Kunming is mild, and I like it.
5、It/This/That+be+the first(second, third...) time+that-clause 这个句型表示截止到说话时为止的某人的一种经历,关键是注意time前有序数词,主句是一般现在时is时,从句要用现在完成时;如果主句用一般过去时was时,则从句须相应地用过去完成时。
如:This is the first time(that) these Europeans have visited the Great Wall.
It was the fifth time(that) I had paid a friendly visit to America.
6、在一些相对固定的词组中,没有特殊含义,经常不翻译。
如:He's never really made it as an actor. 作为演员,他从未获得过真正的成功。
It is my turn. 轮到我了。
强调句中的it:
可以用来改变句子结构,使句子的某一成分得到强调:
1)强调句的基本句型it's/was+被强调成分+that/who+其他成分
原句:I told Jim the news in our office yesterday.
强调主语:It was I that/who told Jim the news in our office yesterday.
强调宾语:It was Jim that I told the news in our office yesterday.
或:It was the news that I told Jim in our office yesterday.
强调地点状语:It was in our office that I told Jim the news yesterday.
强调时间状语:It was yesterday that I told Jim the news in our office.
2)强调句的一般疑问句型Is/Was+it+所强调部分+that/who...?
如:Was it you that told Jim the news in your office yesterday?
3)强调句的特殊疑问句型疑问词+is/was+it+that/who...?
如:Who was it that told Jim the news in your office yesterday?
【注】强调句与主语从句虽然在形式上很相似,即都含有it is(was)...that。但,区别在于:强调句去掉it is(was)…that之后,句子结构仍然完整,而主语从句却不能这样。
如:(It is)our hope(that) the two sides will work towards peace.
解析:去掉It is…that之后,句子是不成立的。由此得出该句不是强调句,而是一个简单的主语从句,it是形式主语,从句是真正的主语。
“it”的用法:
1、it 作形式主语:
it 在句中可作形式主语,而真正作主语的主语从句需要放在句子的末尾。主语从句后置常用以下几种结构:
1)It is/was+adj.+subject-clause可用于此句型的形容词有:
clear, certain, funny, good, impossible, likely, natural, obvious, possible, probable, strange, surprising, true, unusual, wonderful等。
如:It is obvious that going for sports will do a lot of good to your health.
2)It+be+adj./n.(forsb./ofsb.)+todosth. 该句型中的形容词通常表示事物的特点或特征的,如:
difficult, hard, easy, impossible, necessary, important等,此时用for;或表示人的性格特征或特点的,如:
nice, good, bad, kind, silly, foolish, wise, clever, careless, rude, brave, cruel, careful, grateful等,这时要用of 。
3)It is/was+名词词组+subject-clause可用于该结构的名词词组有:
a pity/duty, a good thing, no surprise, good news, an honor, a fact, a mystery, a shame, manners等。
如:It's a pity that I didn't attend the party.
4)It is/was+V-ed+subject-clause可用于该结构的动词的过去分词有:
said, reported, thought, supposed, believed, hoped, expected, known, decided, announced, arranged等。
如:It is said that something had been done to end the pollution.
注:本句还可改写为:Something is said to have been done to end the pollution.
5)It+vi.+subject-clause可用于该结构的动词有:appear, seem, happen, occur等。
如:It appeared to scientists that the stars had moved.
6)It doesn't matter(makes no difference,etc.) +连接代词或连接副词引起的从句作宾语。
如:It doesn't matter whether he'll join the army or not.
It makes no difference where we have the conference.
7)一些固定句型:
It takes sb. some time to do sth.
如:It will take you two days to get there on foot.
It costs sb. some money to do sth.
如:It costs 1,000 dollars to fly to America.
It is/was no use(useless) doing(做什么是没有用处的)
如:It's no use arguing with him.
It is/was no good doing(做什么是没有好处的)
8)以下句型结构中需要用虚拟语气
① It is/was important(necessary, strange) that...;
It is/was ordered(required, suggested, proposed) that...;
It is/was a pity(a shame) that...表示遗憾等感情的句子中,主语从句要用“should+动词原形”,should可以省略。
如:It's necessary that he(should) be operated on at once.
② It is (high)time that...结构中用should+动词原形(should不能省略)或动词过去式。
如:It is high time that you should make(made) full use of your time to go over your lessons.
2、it作形式宾语:
1)动词consider(feel, find, think等)+it+形容词(名词)+不定式(动词-ing形式,从句)。
如:She thinks it no use telling me.
2)主语+appreciate(enjoy,like,love,hate)+it+if(when)...结构
如:We would appreciate it if you could come to help us.
3)dependon, relyon, see to(负责/设法做到), takeforgranted(习以为常)等短语后跟that从句时,要以it作形式宾语。
如:We're depending on it that he will finish the job by Friday.
“it ”引起的几个易混淆的时间句型:
1)It be+时间+since-clause 这个句型表示从since从句谓语动作发生以后到现在或过去所经过的一段时间,意为“自从…以来已多久了”,主句多用一般现在时,从句用一般过去时,如果表示过去的情况,主句一般用过去时,从句用过去完成时,或主句用过去完成时,从句用一般过去时。
注:since引导时间状语从句时,从句若使用终止性动词,则表示该时间是主句时间段的终点(时间从现在算起);若从句使用延续性动词,则表示该动作状态的结束(时间从过去算起)。
如:It's five years since they got married. 他们结婚已经5年了。
It's five years since they were married. 他们离婚已经5年了。
It's ten years since his father was a worker. 他父亲不当工人已经10年了。
I haven't seen him since we were boys together. 我们长大以后再没有见过面。
2)It be+时间+before-clause 这个句型中的时间一般为表示一段时间的词语(如:long years, months, weeks, days, hours, minutes),主句中的谓语动词用肯定式,意为“过多长时间才…”。主句的谓语动词是否定式时,意为“没过多长时间就…”。主句的时态可用过去时was或将来时willbe;用was时,before从句的动词用一般过去时;用willbe时,before从句常用一般现在时。 如:It was not long before she learned those poems by heart. 她没过多久就背会了那些诗。
It was long before the police arrived. 过了很久警察才来。
It will be hours before he makes a decision. 要过好几个小时他才会作出决定。
It will not be hours before we meet again. 要不了几个小时我们还会再见面的
3)It be+时间+when-clause 这个句型中,it指时间,而且表示时间的词语前没有介词(时间一般是具体时间)。主句和从句中的谓语动词在时态上是一致的,主句是willbe,when从句用一般现在时代替将来时。
如:It was already 8 o'clock when we got home.
It will be late afternoon when they get there.
4)It be+时间+that-clause 这个句型是个强调句型。
如:It was at 5o'clock that he practiced playing the violin in the morning. (原句是:He practiced playing the violin at 5o'clock in the morning.)
比较:It was 5o'clock when he started in the morning.(5o'clock前没有介词,这个是定语从句)
5)It be+time+that-clause 这个句型属虚拟语气结构,不管主句中用的是is或was,that从句都须用动词的过去式或should+动词原形(但不及物动词通常用过去式),在time之前有时可以加上high 或about 以加强语气。
如:It is high time(that) he wrote a letter to his girl friend.
It is time(that) we made people's life a little easier.= It is time that we should make people's life a little easier.
主谓一致的概念:
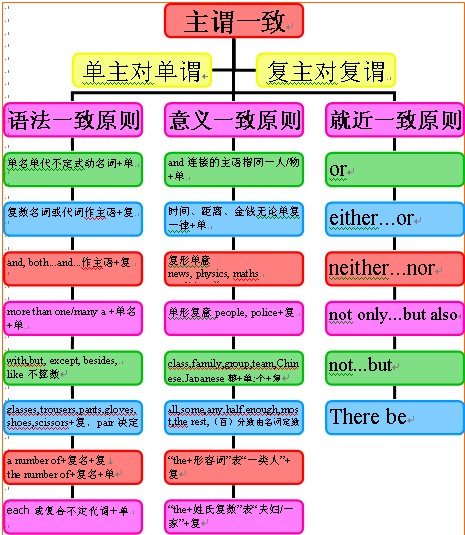
谓语的数必须和主语的人称和数保持一致,这就叫主谓一致。
主谓一致的基本原则:
1)语法一致原则,即在语法形式上取得一致。例如,主语是单数形式,谓语动词也采取单数形式;主语是复数形式,谓语动词也采取复数形式。
例如:The students are very young.
This picture looks beautiful.
2)意义一致原则,即从意义着眼处理一致关系。例如,主语形式虽是单数但意义是复数,谓语动词也采取复数形式;
而有些主语形式虽是复数但意义上看作单数,谓语动词也采取单数形式。
例如:The people in that country are fighting for independence.
The crowd deeply respect their leader.
Three years in a strange land seems a long time.
3)就近原则,即谓语动词的单数或复数形式取决于最靠近它的词语。
例如:Neither hen or I am going to see the film tonight because we are busy.
几对容易混淆词组的一致用法:
1、由“this/thatkind/typeof+名词”作主语,谓语动词用单数形式;而由"these/thosekind/typeof+复数名词”作主语,谓语动词用复数形式。
例如:This kind of apples is highly priced.
Those kind(s) of tests are good.
2、由“a number of,a totalo f,an average of+复数名词”作主语,谓语动词用复数形式;由“the number of,the total of,the average of+复数名词”作主语,谓语动词用单数形式。
例如:A number of students are waiting for the bus.
The number of the students in this university is increasing yearly.
3、one of,the(only) one of的一致用法
例如:This is one of the books that have been recommended.
This is the(only) one of the books that has been recommended.
主谓一致用法点拨:
1、并列结构作主语谓语用复数:
如:Reading and writing are very important.
注意:当主语由and连结时,如果它表示一个单一的概念,即指同一人或同一物时,谓语动词用单数,and此时连接的两个词前只有一个冠词。
如:The iron and steel industry is very important to our life.
典型例题:
The League secretary and monitor___asked to make a speech at the meeting.
A. is
B. was
C. are
D. were
答案:B.
注:先从时态上考虑。这是过去发生的事情应用过去时,先排除A、C本题易误选D,因为The League secretary and monitor 好象是两个人,但仔细辨别,monitor前没有the,在英语中,当一人兼数职时只在第一个职务前加定冠词。后面的职务用and相连。这样本题主语为一个人,所以应选B。
2、主谓一致中的靠近原则:
1)当there be句型的主语是一系列事物时,谓语应与最邻近的主语保持一致。
例如:There is a pen, a knife and several books on the desk.
There are twenty boy-students and twenty-three girl-students in the class.
2)当either…or…与neither…nor,连接两个主语时,谓语动词与最邻近的主语保持一致。
如果句子是由here, there引导,而主语又不止一个时,谓语通常也和最邻近的主语一致。
例如:Either you or she is to go.
Here is a pen, a few envelops and some paper for you.
3、谓语动词与前面的主语一致:
当主语后面跟有with, together with, like, except, but, no less than, as well as等词引起的短语时,谓语动词与前面的主语一致。
例如:The teacher together with some students is visiting the factory.
He as well as I wants to go boating.
4、谓语需用单数:
1)代词each和由every, some, no, any等构成的复合代词作主语,或主语中含有each,every,谓语需用单数。
例如:Each of us has a tape-recorder.
2)当主语是一本书或一条格言时,谓语动词常用单数。
例如:The Arabian Night is a book known to lovers of English.
3)表示金钱,时间,价格或度量衡的复合名词作主语时,通常把这些名词看作一个整体,谓语一般用单数。(用复数也可,意思不变。)
例如:Three weeks was allowed for making the necessary preparations.
Ten yuan is enough.
5、指代意义决定谓语的单复数:
1)在代词what, which, who, none, some, any, more, most, all等词的单复数由其指代的词的单复数决定。
例如:All is right. (一切顺利。)
All are present. (所有人都到齐了。)
2)集体名词作主语时,谓语的数要根据主语的意思来决定。
例如:family, audience, crew, crowd, class, company, committee等词后用复数形式时,意为这个集体中的各个成员,用单数时表示该个集体。
例如:His family isn't very large. 他家不是一个大家庭。
His family are music lovers. 他的家人都是音乐爱好者。
但集合名词people, police, cattle, poultry等在任何情况下都用复数形式。
例如:Are there any police around?
3)有些名词,如variety, number, population, proportion, majority等有时看作单数,有时看作复数。
A number of+名词复数+复数动词。 The number of+名词复数+单数动词。
例如:A number of books have lent out.
The majority of the students like English.
6、与后接名词或代词保持一致:
1)用half of, part of, most of, a portion of等词引起主语时,动词通常与of后面的名词,代词保持一致。
例如:Most of his money is spent on books.
Most of the students are taking an active part in sports.
2)在一些短语,如many a或more than one所修饰的词作主语时,谓语动词多用单数形式。
但由more than…of作主语时,动词应与其后的名词或代词保持一致。
例如:Many a person has read the novel. 许多人都读过这本书。
More than 60percent of the students are from the city. 百分之六十多的学生都来自这个城市
主谓一致知识体系:
主谓一致用法拓展:
1)当everyone,everybody,noone,nobody,anyone,anybody,someone,somebody,everything,anything,something,nothing等用作主语时,其相应的代词一般用单数形式。
例如:If anybody calls, tell him that I'm out.
Something strange happened, didn't it?
2)人称代词与名词的呼应:人称代词I(me),he(him),she(her),it(it) 都是代替前面的单数名词,而they(them),we(us)则是代替复数名词的,you既可以代表单数,也可以代表复数。但表示泛指的时候,用he或one来表示。
例如:If a young person enters a classical music field only for money, he is in the wrong profession.
3)物主代词与名词的呼应:my,our,his,her,its,their要与代替的名词在数上一致。
例如:The welfare department,as well as the other social services,will have its budget cut.
4)反身代词与其所代成分间的呼应。
例如:Many primitive people believed that by eating ananimal they could get some of the good qualities of that animal for themselves.
5)指示代词与所代名词间的呼应:this和that指代单数名词或不可数名词,these和those指代复数名词(those还可以用作先行词,引导定语从句,表示“那些人”)。
例如:She invited all those who had been her former colleagues.
6)much和muchof后接不可数名词,而many和manyof后接可数名词的复数。
例如:There is not much coal left.
A great many of the houses were knocked down by the earthquake.
7)表示量的词后面有的接可数名词,有的接不可数名词。
接可数名词的有:a number of,a rangeof,a series of十复数名词;
接不可数名词的有:a great deal of,an amount of十不可数名词;
既可接可数又可接不可数名词的有:a lot of,a variety of。
例如:1.The government attached a great deal of importance to education.
2.Quiteanumberofwomenappliedforthisjob.
3.The college library has avariety of books.
4.An apple is avariety off ruit.
与“短文改错。此题要求改正所给短文的错误。对标有题号的每一行...”考查相似的试题有:
- Today’s paper carries an exciting _______________ of the match.A.discountB.accountC.countD.accountant
- There was a _______ look on her face when she met with the _______ problem.A.confusing; confusingB.confused; confus...
- -Did you watch the football game on TV last night?-Yes,I did.It was________,and I enjoyed every minute of it.[ ]A.al...
- “Follow sb’s advice ” means ____.A.do as sb. doesB.say as sb. saysC.say as sb.doesD.do as sb.says
- It doesn’t matter what you wear—just ________ you come.A.as long asB.as far asC.as early asD.as soon as
- I don't believe we've met before, I must say you do look familiar.A.thereforeB.althoughC.sinceD.unless
- As I am not feeling too well, I really appreciate ___ to take my place.A.him offerB.for him to offerC.his offering...
- We did all that we could to________him________going abroad,but we failed.[ ]A.encourage;fromB.discourage;fromC....
- Parents and children should communicate more to ______ the gap between them so that they canunderstand each other bet...
- Soon after getting off his horse, the man appeared at the second storey windows, __ he could see nothing but trees.A...