本试题 “Directions: Read the following text and choose the most suitable heading from A—F for each paragraph. There is one extra heading which you do not n...” 主要考查您对序数词
等考点的理解。关于这些考点您可以点击下面的选项卡查看详细档案。
- 序数词
序数词的概念:
表示顺序的数称为序数词。如:first, second, third, fourth。
序数词的构成与用法:
1、序数词的构成:
①一般来说,是由相应的基数词加词尾th构成。
例:four+th→fourth
six+th→sixth
seven+th→seventh
ten+th→tenth
②下面这些基数词在变为序数词时,有特殊的变化。
例:one→first
two→second
three→third
five→fifth
eight→eighth
nine→ninth
twelve→twelfth
③十位整数序数词的构成方法是将基数词的词y变成i,然后再加eth。
例:twenty→twentieth
thirty→thirtieth
forty→fortieth
ninety→ninetieth
④两位或两位以上的基数词变成序数词时,仅将个位数变成序数词。
例:twenty-one→twenty-first
thirty-five→thirty-fifth
a hundred and fifty-three→a hundred and fifty-third
2、序数词的用法:
①序数词在使用时,一般加上定冠词。
例:the first book
the second floor
the third day
the fourth week.
②序数词在多数情况下都用作定语,有的也可以作表语、主语和宾语。
例:The may1st is Labour Day. 五月一日是劳动节。
My room is on the second floor. 我的房间在二楼。
The first is larger than the secon.(主语)第一个比第二个大。
Read the book from the first.(宾语)从开头读这本书。
You'll be the sixth to write.(表语)你将是第六个写的。
③序数词的前面可以加上不定冠词,用来表示“再一”,“又一”的意思。
例:You may have a third try. 你可以第三次尝试。
序数词知识体系:
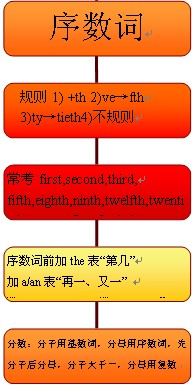
约数的表达方法:
用tens/dozens/scores/hundreds/thousands/millions of 表示“几十、几百、上千、成千上万”等。
如:The boy bought dozens of pencils.
Thousands of people died in the earthquake.
注意: (A):dozen, score, hundred, thousand, million等表示确切数量时,不用复数。
如:five dozen (of) eggs 五打鸡蛋
hree hundred people 三百个人
分数词的构成和用法:
1)分数词构成法:
分数词(FractionalNumerals)由基数词和序数词构成,基数词代表分子,序数词代表分母。除了分子为1的情况下,序数词都要用复数形式:
如:1/4:one-fourth
5/9:five-ninths
2/3:two-thirds
17/5:three and two-fifths
7/12:seven-twelfths
379/8:forty-seven and three-eighths
此外还有下面表示法:
如:1/2:a(one) half
1/4:a(one) quarter
3/4:three-quarters
9/4:two and a quarter
3/2:one and half
31/4:seven and three quarters
与“Directions: Read the following text and choose the most s...”考查相似的试题有:
- They havegiven upthe hope to save their friend from drowning.A.endedB.abandonedC.builtD.strengthen
- 根据短文内容,从短文后的选项中选出能填入空白处的最佳选项。选项中有两项为多于选项。Public Speaking Training·Get a coac...
- .第二节完型填空(共15小题;每小题1分,满分15分)Once upon a time,a man punished his 5-year-old daughter for 31 up th...
- 第二卷第四部分写作 (共两节,满分35分)第一节短文改错(共10小题;每小题1分, 满分10分)此题要求改正所给短文中的借误。对...
- 第二节:完成句子(共10小题;每小题1.5分,满分15分)阅读下列各小题,根据括号内的汉语提示,用句末括号内的英语单词完成句子,...
- —The exam was easy, wasn't it?—Yes, but I don't think ________ could pass it.A.somebodyB.anybodyC.nobodyD.everybody
- 根据短文内容, 从短文后的选项中选出能填入空白处的最佳选项, 选项中有两项为多余选项。Recently some American scientists h...
- 根据短文的内容,从短文后的选项中选出能填入空白处的最佳选项。选项中有两项为多余选项。Jealous of the kids at school who...
- Corruption is _______ problem in countries across the world, with developing countries often believed to be more seri...
- 根据句子意义选择方框内所给单词或短语的正确形式填空小题1:Those who suffer from headache will find they get from his me...