本试题 “短文改错。增加:在缺词处加一个漏字符号(∧)。并在其下面写出修改后的词。删除:把多余的词用斜线(/)划掉。修改:在错词后划一横线并在该词下面写出修改...” 主要考查您对人称代词
不定代词
形容词
地点副词
从属连词
动词短语
动词
过去分词
一般过去时
等考点的理解。关于这些考点您可以点击下面的选项卡查看详细档案。
- 人称代词
- 不定代词
- 形容词
- 地点副词
- 从属连词
- 动词短语
- 动词
- 过去分词
- 一般过去时
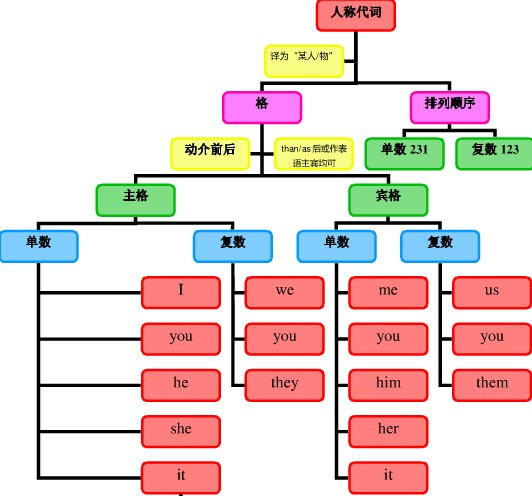
人称代词的概念:
人称代词是替代我、你、他、她、它、我们、你们、他们、她们、它们等人称的词。
人称代词分为主格和宾格形式,并有人称的单复数形式。按所替代人称的不同分为第一人称、第二人称和第三人称。
人称代词的用法:
人称代词在句中可以用作主语(用主格,如:I,you,he,she,we,they,等)和宾语(用宾格,如 me,you,him,her,us,them等)
如:He loves her, but she hates him. 他爱她,但她却讨厌他。
注:(1)在口语中,当人称代词用作表语、用于than, as之后或用于强调句中被强调时,可以用语。 例如:
"Who is it?" "It's me."“是谁呀?”“是我。”
He sings better than me. 他比我唱得好。
He is as tall as her. 他和她一样高。
It's me who did it. 这是我干的。但是,若than,as后的人称代词后跟有动词,则必须用主格。例如:
He sings better than I do./ He is as tall as she is.
(2)单独使用的人称代词通常用宾格。
"I' m tired.""Me too."“我累了。”“我也累了。”
"Who wants this?" "Me."“谁要这个?”“我要。”
(3)有时用主格或宾格会导致意思的变化。
I like you better than he. 我比他更喜欢你。为 I like you better than he likes you. 之略。
I like you better than him. 我喜欢你胜过喜欢他。为 I like you better than he likes him. 之略。
人称代词主格、宾格、人称、单复数对比:
|
人称代词 |
单数 |
复数 | ||
|
主格 |
宾格 |
主格 |
宾格 | |
|
第一人称 |
I |
me |
we |
us |
|
第二人称 |
you |
you |
you |
you |
|
第三人称 |
he |
him |
they |
them |
|
she |
her |
them | ||
|
it |
it | |||
人称代词的排序:
人称代词的排列顺序为:单数人称代词通常按“二三一”排列,即you, he and I;复数人称代词通常按“一二三”排列,即we, you and they:
You, he and I are of the same age. 你,他和我都是同一年龄。
We, you and they are all good citizens. 我们,你们和他们都是好公民。
但若是用于承担责任或错误等场合,则可把第一人称I置于其他人称代词之前:
I and Tom are to blame. 我和汤姆该受批评。
比较:Tom and I hope to go there. 汤姆和我想去那儿。
注意:you and I 是固定结构,语序通常不宜颠倒。
人称代词知识体系:
人称代词用法拓展:
1、在通常情况下,人称代词在句子中出现在它所代替的名词之后,即先出现名词,再出现相应的代词。但是,在书面语中,有时也可出现代词,后出现代词所代替的名词。
As soon as it had hopped off, the plane picked up speed.飞机刚一起飞,就加了速。
(比较:As soon as the plane had hopped off, it picked up speed.)
2、人称代词后跟名词同位语。有些人称代词后有时可跟同位语。
These small desks are forus students.这些小课桌是给我们学生的。
We girls often go to the movies together.我们女孩子常一起去看电影。
He asked you boys to be quiet.他要你们男孩子安静些。
不定代词概说:
英语的不定代词有all, each, both, either, neither, one, none, little, few, many, much, other, another, some, any, no, few, little, both, enough, every等,以及由some,any,no和every构成的合成代词(即somebody, anyone, nothing等)。在这些不定代词中,多数都能作主语、宾语、表语或定语,但是代词none以及由some, any, no和every构成的合成代词只能作主语、宾语或表语,不能作定语,而no和every则只用作定语。
不定代词用法对比:
1、so little与such little的区别:
用so little还是such little取决于little的意思:若表示数量方面的“少”,则用so little;若表示形状体积的“小”,则用such little:
如:He has so little time for reading. 他读书的时间少得可怜。
I've never seen such little boxes. 我从未见过那样小的盒子。
2、some与any的用法区别:
一般说来,some用于肯定句中,any用于否定句和疑问句中。但是,在表示请求、邀请或征求意见的句子中,通常要用some而不用any:
如:Would you like some cake? 吃点蛋糕吗?
Why not buy some bread? 为什么不买些面包呢?
Shall I get some chalk for you? 要我帮你拿些粉笔来吗?
注:any有时也用于肯定句中,此时表示“任何”:
如:Any colour will do. 任何颜色都行。
Come any day you like. 随便哪天来都可以。
3、many与much的用法区别:
两者都表示“许多”,但many修饰或代替可数名词(复数),与few(少数)相对;
而much用来修饰或代替不可数名词(单数),与little(少量)相对。在口语中两者主要用于非肯定句中:
如:Did you see many people there? 你在那儿看见许多人了吗?
We don't have much time. 我们没有许多时间。
在肯定句中,一般用a lot of, lots of, plenty of 等代之。但在正式文体中有时也用于肯定句中;
另外,若用作主语或主语的定语,或其前有how, too, as, so, a good, a great等修饰,也可用于肯定句中:
如:Many of us left early. 我们有许多人离开得很早。
Much work has been done. 许多工作都已经做了。
You've given me too much. 你已给我太多了。
Take as many(much) as you want. 你要多少拿多少。
I asked her a great many questions. 我问了她许多问题。
4、few, a few与little, a little的用法区别:
(1)few和a few后接可数名词的复数形式。few表示数量很少或几乎没有,强调“少”,含有否定意义;
a few表示数量虽然少但毕竟还有,强调“有”,含有肯定意义:
如:It is very difficult, and few people understand it. 它很难,没有几个人能懂。
It is very difficult, but a few people understand it. 他虽难,但是有些人懂。
(2)little和alittle之后接不可数名词,其区别跟few和a few之间的区别相似:
如:Unfortunately, I had little money on me. 很不巧,我身上没带什么钱。
Fortunately, I had a little money on me. 幸好我身上带着一点钱。
5、other, the other, another与others的用法区别:
这些不定代词不仅在含义上有单复数之分,而且在用法上有泛指(无the)和特指(有the)之别。其用法区别可归纳如下:
(1)指单数时,若泛指用another,若特指用the other:
如:Give me another(one). 另外给我一个。
Shut the other eye, please. 请把另一只眼睛也闭上。
(2)指复数时,若泛指用other(后接复数名词),若特指用the other(后接复数名词):
如:There are other ways of doing it. 做这事还有其他的办法。
Where have the other students gone? 其他学生都到哪里去了?
(3)others永远表示复数意义(且其后不能再接名词)。其用法大致相当于“other+复数名词”,同样地the others大致相当于“the other+复数名词”:
如:Other people[Others] may not think that way. 别的人可能不这样想。
He is cleverer than the others[the other students] in her class. 他比班上其他学生聪明。
(4)another一般只能表单数,且其后接名词也只能接单数名词。但是若其后有数词或few修饰时,则也可接复数名词:
如:We need another few chairs. 我们还需要几把椅子。
In another two weeks it'll be finished. 再过两个星期就可做完了。
(5)与some对比使用时,用others(此时与some同义):
如:Some say yes, and others say no. 有人说对,有人说不对。
不定代词用法点拨:
1、指两者和三者的不定代词:
有些不定代词用于指两者(如both, either, neither),有的不定代词用于指三者(如all, any, none, every),注意不要弄混:
如:Both of my parents are doctors. 我的父母都是医生。
All of the students are interested in it. 所有的学生对此都很感兴趣。
There are trees on any side of the square. 广场的每一边都种有树。
He has two sons, neither of whom is rich. 他有两个儿子,都不富有。
He has three sons, none of whom is rich. 他有三个儿子,都不富有。
注:each可用于两者、三者或三者以上,而every只用于三者或三者以上,因此用于两者时只能用each,不能用every。
2、复合不定代词的用法特点:
复合不定代词包括something, somebody, someone, anything, anybody, anyone, nothing, nobody, noone, everything, everybody, everyone等。它们在句中可用作主语、宾语或表语,但不能用作定语。something, someone等和anything, anyone等的区别与some和any的区别一样,前者一般用于肯定句,后者一般用于否定句、疑问句或条件句。具体使用时应注意以下几点:
(1)复合不定代词受定语修饰时,定语应放在它们后面:
如:There is nothing wrong with the radio. 这收音机没有毛病。
Have you seen anyone[anybody] famous? 你见过名人吗?
(2)指人的复合不定代词若用作主语,其谓语动词一般用单数,相应的人称代词和物主代词也用单数he, him, his(不一定指男性)。但在非正式文体中常用复数代词they, them, their:
如:Everyone knows this, doesn't he[don't they]? 人人都知道这一点,不是吗?
If anybody[anyone] comes, ask him[them] to wait. 要是有人来,让他等着。
(3)指事物的复合不定代词若用作主语,谓语动词只能用单数,相应的人称代词也只能用it,而不用they:
如:Everything is ready, isn't it? 一切都准备好了,是吗?
(4)anyone, everyone等只能指人,不能指物,且其后一般不接of 短语。若是指物或后接of 短语,可用any one, every one(分开写):
如:any one of the boys(books) 孩子们(书)当中的任何一个(本)
every one of the students(schools) 每一个学生(一所学校)
3、是any not还是not any:
按英语习惯,any以及含有any的复合不定代词用于否定句时,它只能出现在否定词之后,而不能在否定词之前:
误:Anyone doesn't know how to do it.
正:No one knows how to do it.任何人都不知道如何做它。
误:Anybody[Anyone] can not do it.
正:Nobody[Noone] can do it.这事谁也干不了。
误:Anything can not prevent me from going.
正:Nothing can prevent me from going. 什么也不能阻挡我去。
4、不定代词与部分否定:
不定代词all, both, every等与not连用时构成部分否定;若要表示完全否定,则需换用none, neither, no one等。
比较:All of the students like the novel. 所有这些学生都喜欢这本小说。
Not all of the students like the novel. 并不是所有这些学生都喜欢这本小说。
All of the students don't like the novel. 并不是所有这些学生都喜欢这本小说。
None of the students like the novel. 这些学生当中没有一个喜欢这本小说。
5、all, both, each等用作同位语:
若用作主语同位语,主语可以是名词或代词;若用作宾语等其他成分的同位语,则宾语等成分必须是人称代词,而不能是名词:
如:We have all read it. 我们都读过他。(all修饰的主语是代词)
The villages have all been destroyed. 村庄都被毁了。(all修饰的主语是名词)
They told us all to wait there. 他叫我们都在那儿等。(all修饰的宾语是代词)
但不能说:They told the men all to wait there. (all修饰的宾语是名词不是代词)
不定代词知识体系:

不定代词与语境考题:
不定代词是高考的常考考点,有的不定代词考题出得比较灵活,不能死套规则,要注意结合语境来理解:
例1:—Is____here?
—No, Bob and Tim have asked for leave.
A. anybody
B. everybody
C. somebody
D. nobody
解析:
若只是从表面来看,填空句是个疑问句,可能会误选A。但其实此题最佳答案应选B,因为下文的答句说“只有Bob和Tim请假了”,这说明问句是在查人数,故用Is everybody here? (大家都到齐了吗?)
例2:I agree with most of what you said, but I don't agree with_____.
A. everything
B. anything
C. something
D. nothing
解析:
此句若从表面看,有可能误选B,因为填空句为否定句。但实际上最佳答案为A,因为上文说“我同意他说的大部分内容”,这与下文的but I don't agree with everything (但并不是同意他说的所有内容)完全相符。
例3:—Doyouhave_____athomenow,Mary?
—No, we still have to get some fruit and tea.
A. something
B. anything
C. everything
D. nothing
解析:答案:C,句意为“玛丽,现在家里东西都准备齐了吗?”“还没有,我们还要买些水果和茶。”
例4:—If you want a necklace, I'll buy one for you at once.
—Oh, no. A necklace is not_____that I need most.
A. anything
B. something
C. nothing
D. everything
解析:
此题容易误选A,机械地认为:something用于肯定句,anything用于否定句或疑问句。但是,此题的最佳答案是B,something在此的意思不是“某种东西”,而是指“那种东西”或“这种东西”,即心中最想要的那种东西(相当于the thing)。
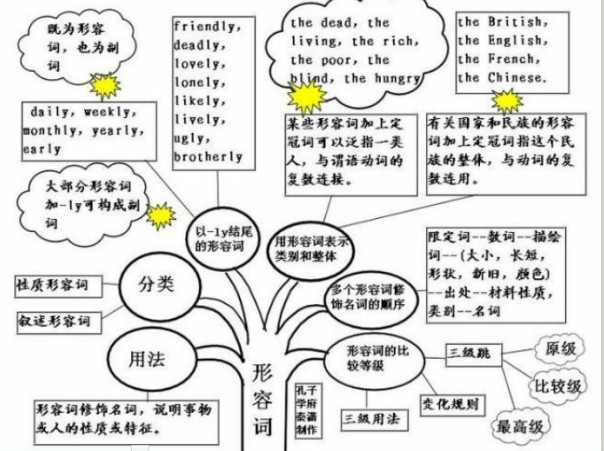
形容词的概念:
形容词(adjective),简称adj.或a,形容词用来修饰名词或代词,表示人或事物的性质、状态,和特征的程度好坏与否,形容词在句中作定语、表语、宾语补足语。通常,可将形容词分成性质形容词和叙述形容词两类,其位置不一定都放在名词前面。
形容词的作用与位置:
形容词是用来修饰名词的,常被放在名词前作定语,或放在系动词后面作表语。以下属几种特殊情况,须牢记;
(1)形容词短语作定语,定语后置。
如:a language difficult to master,
a leaning tower about 180 feet high
(2)表语形容词(afraid、alike、alone、asleep、awake、alive等)作定语,定语后置。如a man alive。有些表身体健康状况的形容词如well、faint、ill只作表语。sick既可作表语又可作定语,ill如作定语意为“bad”。
(3)用作定语,修饰由不定代词one、no、any、some和every构成的复合词如anything、something等时,通常后置。
如:I have something important to tell you.
(4)else常用作疑问代词和不定代词的后置定语。
(5)enough、nearby修饰名词前置或后置,程度副词一般位于形容词、副词前面,enough修饰形容词、副词时,必须后置。
(6)几个并列的形容词作定语,其语序通常为:限定语(The、A)+描绘性形容词+size(大小)+shape(形状)+age(年龄、时间)+color(颜色)+origin(国籍、来源)+material(材料)+purpose(目的)+名词。
口诀:
限定描绘大长高,形状年龄和新老;颜色国籍跟材料,作用类别往后靠。
如:a heavy black Chinese steel umbrella,
the man's first tow interesting little red French oil paintings
形容词的用法:
1、形容词修饰名词,说明事物或人的性质或特征。通常,可将形容词分成性质形容词和叙述形容词两类,其位置不一定都放在名词前面:
1)直接说明事物的性质或特征的形容词是性质形容词,它有级的变化,可以用程度副词修饰,在句中可作定语、表语和补语。例如:hot热的。
2)叙述形容词只能作表语,所以又称为表语形容词。这类形容词没有级的变化,也不可用程度副词修饰。
大多数以a开头的形容词都属于这一类。例如:
afraid害怕的。(错)Heisanillman. (对)Themanisill. (错)Sheisanafraidgirl. (对)Thegirlisafraid.
这类词还有:well,unwell,ill,faint,afraid,alike,alive,alone,asleep,awake等。
3)形容词作定语修饰名词时,要放在名词的前边。但是如果形容词修饰以-thing为字尾的词语时,要放在这些词之后。例如:somethingnice
2、用形容词表示类别和整体:
1)某些形容词加上定冠词可以泛指一类人,与谓语动词的复数连接。如:the dead,the living,the rich,the poor,the blind,the hungry The poorarelosinghope.穷人失去了希望。
2)有关国家和民族的形容词加上定冠词指这个民族的整体,与动词的复数连用。如:the British,the English,the French,the Chinese. The English have wonderful senseofhumor.
以-ly结尾的形容词:
1)大部分形容词加-ly可构成副词。但friendly,deadly,lovely,lonely,likely,lively,ugly,brotherly,仍为形容词。改错:
如:(错)She sang lovely.
(错)He spoke to me very friendly.
(对)Her singing was lovely.
(对)He spoke to me in a very friendly way.
2)有些以-ly结尾既为形容词,也为副词。 daily,weekly,monthly,yearly,early .
如:The Times is a daily paper.
The Times is published daily.
形容词知识体系:
复合形容词的构成:
(1)形容词+名词+ed:
如:kind-hearted 好心的,white-haired 白发的
(2)形容词+形容词:
如:red-hot 炽热的,dark-blue 深蓝的
(3)形容词+现在分词:
如:good-looking 好看的,easy-going 随和的
(4)副词+现在分词:
如:hard-working 勤劳的,fast-moving 快速转动的
(5)副词+过去分词:
如:hard-won 得来不易的,newly-made 新建的
(6)名词+形容词:
如:life-long 终生的,world-famous 世界闻名的
(7)名词+现在分词:
如:peace-loving 爱好和平的,fun-loving 爱开玩笑的
(8)名词+过去分词:
如:snow-covered 白雪覆盖的,hand-made 手工的
(9)数词+名词+ed:
如:four-storeyed 4层楼的,three-legged 3条腿的
(10)数词+名词(名词用单数):
如:ten-year 10年的, two-man 两人的
地点副词的概念:
表示地点的副词和表示位置关系的副词统称为地点副词。常见的地点副词有here, there, up, down, away, nearby, home, ahead, abroad, indoors, overseas, halfway, up, downstairs, upstairs等。
例如:Can you help to carry this table upstairs?
地点副词在句中的位置:
地点副词常放在动词后面,如果是及物动词,一般就放在宾语后面。
如:I remember having seen him somewhere.
Wuxia films are popular in China.
地点副词和时间副词并列使用时,一般要把地点副词放在时间副词之前。
如:We had a meeting here yesterday.
He did the work carefully here yesterday.
如果地点状语很长时,也可以放在时间状语之后。
如:He was born in 1940 in a small village at the foot of Mount Tai.
地点副词常可以用作表语:
副词可以用作表语,主要是地点副词,时间副词和其他副词有时也可以用作表语。
如:They are inside. 他们在里面。
How long will she be away? 她要离开多久?
When will you be back? 你什么时候回来?
You haven't been around much. 你很少到这边来。
He'll be round in an hour. 他一个小时内就到。
Now autumn is in. 秋天来了。
I must be off now. 我得走了。
We are behind in our plan. 我们落在计划后面了。
注:在表示位置关系的副词中,有些副词也可用作介词(如:above, over, beyond, around, below, down, up, in, along, near, off, on, past等),在没有宾语时就是副词,有宾语时就是介词:
如:Comein, please. (副词)
They live in the next room.(介词)
Let's take along. (副词)
Let's walk along this street. (介词)
She looked around.(副词)
They sat around the table. (介词)
Let's go on with the work.(副词)
What subject will you speak on? (介词)
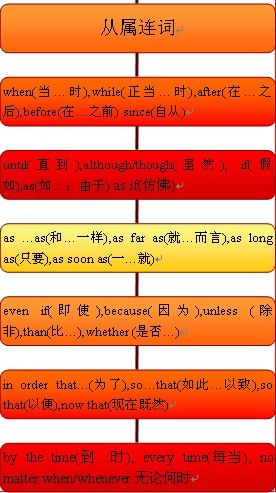
从属连词的概念:
连词用于引导从句以形成句子的一部分或修饰句子的构成要素的叫作从属连词。
英语从属连词用法分类详解:
1、引导时间状语从句的从属连词:
(1)表示“当…时候”或“每当”的时间连词。主要的when, while, as, whenever:
如:He jumped up when the phone rang. 电话铃响时他吓了一跳。
We listened while the teacher read. 老师朗读时我们听着。
The phone rang just as I was leaving. 我正要离开,电话铃就响了起来。
(2)表示“在…之前(或之后)”的时间连词。主要的有before, after:
如:Turn the lights off before you leave. 离开前请关灯。
He started the job soon after he left the university. 他大学毕业后就开始做这份工作。
(3)表示“自从”或“直到”的时间连词。主要的有since, until, till:
如:He has lived here since he got married. 他结婚后就一直住在这儿。
Most men worked until[till] they're 65. 大多数男人工作到65岁。
(4)表示“一…就”的时间连词。主要的有as soon as, the moment, the minute, the second, the instant, immediately, directly, instantly, once, no sooner…than, hardly…when等:
如:Tell him the news as soon as you see him. 你一见到他就把这消息告诉他。
I recognized her the moment(that) I saw her. 我一看到她就认出她来了。
I want to see him the minute(that) he arrives. 他一到来我就要见他。
I went home directly I had finished work. 我一干完活就回家了。
Once he arrives, we can start. 他一来我们就可以开始。
(5)表示“上次”、“下次”、“每次”等的时间连词。主要的有every time(每次),each time(每次),(the) next time(下次),any time(随时),(the) last time(上次),the first time(第一次):
如:Last time I saw him, he looked ill. 上次我见到他的时候,他好像有病。
Next time you're in London come and visit us. 你下次来伦敦过来探望我们。
Do look me up next time you're in London. 你下次到伦敦来,一定来找我。
Every time I call on him, he is out. 我每次去访问他,他都不在。
You can call me any time you want to. 你随时都可以给我打电话。
【注】every time,each time,any time前不用冠词,(the)next time, (the)last time中的冠词可以省略,而the first time中的冠词通常不能省略。
2、引导条件状语从句的从属连词:
这类连词主要有if, unless, as[so] long as, incase等:
如:If anyone calls tell them I'm not at home. 要是有人打电话来,就说我不在家。
You will fail unless you work hard. 你若不努力就会失败。
As[So] long as you need me, I'll stay. 只要你需要我,我就留下。
In case I forget, please remind me about it. 万一我忘记,请提醒我一下。
【注】在条件状语从句中,通常要用一般现在时表示将来意义,而不能直接使用将来时态。不过,有时表示条件的if之后可能用will,但那不是将来时态,而是表示意愿或委婉的请求(will为情态动词):
如:If you will wait a moment, I'll fetch the money. 请等一下,我就去拿钱。
3、引导目的状语从句的从属连词:
主要有in order that, so that, in case, for fear等:
如:We used the computer in order that we might save time. 我们使用计算机是为了节约时间。
Speak clearly so that they may understand you. 说清楚,以便让他们能明白你的意思。
Be quiet in case you should wake the baby. 安静些,免得把婴儿吵醒。
He is working hard for fear he should fail. 他努力工作以免会失败。
4、引导结果状语从句的从属连词:
主要的有so that, so…that, such…that等:
如:We're all here now, so that the meeting can begin at last. 我们现在都到齐了,终于能开会了。
It's so difficult a question that none of us can answer it. 那是一个很难的问题,我们没有一个人能回答。
He shut the window with such force that the glass broke. 他关窗户用力很大,结果玻璃震破了。
【注】so that中的that在口语中通常可以省略。
5、引导原因状语从句的从属连词:
主要的有because, as, since, seeing(that), now(that), considering(that)等:
如:He couldn't got to school because he had a cold. 他因患感冒而未能去上学。
Since everybody is here, let's begin our discussion. 大家都到了,我们就开始吧。
Seeing that it is 8o'clock, we'll wait no longer. 由于时间已到8点,我们将不再等了。
Now that you are here, you'd better stay. 你既然来了,最好还是留下吧。
6、引导让步状语从句的从属连词:
主要有although, though, eventhough, even if, while, however, whatever, whoever, whenever, wherever等:
如:Although[Though] he is poor, he is well contented. 他虽穷却能知足常乐。
Though[Even though] it's hard work, I enjoy it. 尽管是苦活,但我乐意干。
Even if you don't like wine, try a glass of this. 即使你不喜欢喝酒,也尝尝这杯吧。
7、引导方式状语从句的从属连词:
主要有as, like, as if, as though, the way等:
如:Do it as[like] he does. 像他那样做。
He behaved as if nothing had happened. 他装作若无其事的样子。
They treat me as though I were a stranger. 他们待我如陌生人。
Nobody else loves you the way(=as) I do.没有人像我这样爱你。
8、引导地点状语从句的从属连词:
主要有where, wherever, everywhere等:
如:There were lots of parks where I lived. 我住的地方有许多公园。
Sit wherever you like. 你想坐在那儿就坐在那儿。
Everywhere they went, they were warmly welcomed. 他们每到一个地方都受到热烈欢迎。
9、引导比较状语从句的从属连词:
主要有than和as…as:
如:It's easier than I thought. 这比我想像的要容易。
They are as often wrong as they are right. 他们错对各半。
10、引导名词性从句的从属连词:
主要有that, if, whether:
如:It is clear enough what he meant. 他是什么意思很清楚。
Your greatest fault is that you are careless. 你最大的缺点是粗心大意。
Whether it will do us harm remains to be seen.是否对我们有害还要看一看。
She didn't say if he was still alive. 她没说他是否还活着。
从属连词知识体系:
用作从属连词的六类名词结构:
英语中有些名词结构可用作从属连词,用以引导状语从句,且主要是时间状语从句。这类结构归纳起来有以下六类:
一、the+瞬间名词:
其中的瞬间名词主要包括moment, minute, instant, second等,其意为“一……就……”,相当于as soon as。
如:The minute he saw her he fell in love. 他对她一见倾心。
Telephone me the moment(that) you get the results. 你一有结果,马上给我打电话。
I was so tired that I fell asleep the instant I closed my eyes. 我很累,一合上眼就睡着了。
Sheputdownthereceiverthesecondsherecognizedmyvoice.她一听出是我的声音,马上就放下电话听筒。
注:其中的瞬间名词后可接that,也可省略。另外,有的个别副词(如directly/immediately等)也可表示类似意思。
如: Immediately the meal was over,he switchedon the radio.饭一吃完他就把收音机打开。
二、the+季节名词:
其中的季节名词包括spring,summer,autumn,winter,其意为“在……的那年春天、夏天、秋天、冬天。
如:His wife left him thes pring he went abroad.在他出国的那年春天,他的妻子离开了他。
He sold his house and went to the souththe summer he lost hisjob.在他失业的那年夏天,他卖掉房子去了南方。
He was sentto prison the winter his third daughter was born.在他第三个女儿出生的那年冬天,他被关进了监狱。
She got married the autumn she graduated from college.她大学毕业的那年秋天就结婚了。
三、the+时间名词:
其中的时间名词主要包括hour,day,night,week,month,season,year等,其意为“在……的时候、那天、那个晚上、那周、那个月、那个季节、那年”。
如: The hour he wa sin her office,he felt very sad.当他在她办公室的时候,他感到很伤心。
The day here turned home,his father was already dead.他回家的那一天,他的父亲已经死了。
The night I wenttoseeher,shehadleftforBeijingtoattendanimportantmeeting.就我去看她的那个晚上,她到北京去开一个重要的会议了。
Mr Smith didn't go to work the week his wife was ill.史密斯先生在他妻子生病的那个星期没去上班。
They ear helivedinthecountry,he learned alot.他在乡下呆的那一年,他学到了不少东西。
四、the+序数词+time
其中的序数词包括first,second,third,fourth等,其意为“当第几次……的时候”。
如: My girlfriend beat me at pokert he first time weplayed.我头一次和女朋友打扑克,她就把我赢了。
These cond time I saw her,she looked like an old woman.我第二次见到她时,她看上去像一个老太婆。
The third time I went there,I found all of them had left and the offices were all empty.我第三次去那儿时,我发现他们都离开了,所有的办公室都是空的。
注:
1.next,last也具有类似序数词的性质,因此也具有以上用法。
如: Nexttimeyoucomein,pleaseclosethedoor.下次你进来,请关门。
Thelasttimewetalkedhesaidheneededanothertwodays.上次我们谈话时他说他还需要两天。
2.thefirsttime,thesecondtime,thethirdtime等用作连词引导时间状语从句时,其前通常要有定冠词,而(the)nexttime,(the)lasttime引导状语从句时,其中的冠词可以省略,如下面这道上海高考题,其答案是C,不是A:
I though ther nice and honest______Imether.
A.first time B.fo rthe first time C.the first timeD.by the first time
五、不定代词+time
其中的不定代词主要包括each,every,any等。
如:Every time I ringher,the phone is engaged.我每次给她打电话,电话都占线。
Every time I see him he either wants to tell me his trouble or borrow some money.每次我见到他,他不是向我诉苦,就是要向我借钱。
He felt nervous each times he spoke to him.每次她和他讲话,他都感到紧张。
AnytimeyoucometoLondondolookmeup.你无论什么时候到伦敦来,一定要来看我。
注意:everytime,eachtime,anytime用作连词引导状语从句时其前习惯上不用冠词,它与the first time,these cond time,the third time等引导时间状语从句时其前必须要用定冠词不同。
六、其他名词结构
以上归纳的名词结构均用于引导时间状语从句,有些其他结构还可引导其他性质的状语从句,如the way可用于引导方式状语从句,表示“像……一样”。如:
The didn’t do it the way we do now.那时他们不像我们现在这样行事。
Joyce looked at me the way alotof girls did.乔伊丝像许多姑娘那样瞧着我。
注:这样用的theway与as用法相似。
如:Hold itin both hands,the way(=as)Mummy does.用两只手捧住,像妈妈那样。
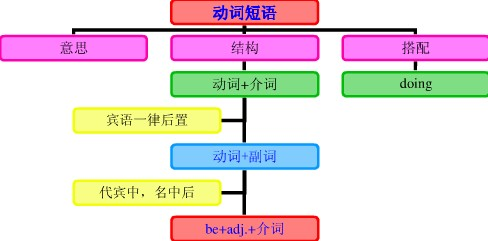
动词短语的概念:
动词常和某些其他词类用在一起,构成固定词组,形成所谓短语动词(phrasalverb)。和动词一样,短语动词也可分为及物和不及物两种。短语动词可以作为一个整体看待,同一般动词一样使用。
动词短语的搭配类型:
1)动词+介词:这类短语动词用作及物动词,后面须跟宾语。
如:The small boy insisted on going with his parents. 那男孩坚持要跟父母一起去。
Do you often listen to broadcasts in English? 你常听英语广播吗?
Look at the children. Aren't they lovely? 看着这些孩子们。他们多么可爱呀!
We stand for self-reliance. 我们是主张自力更生的。
这一类的短语动词还有很多,如depend on(upon)(依靠),wait on(服侍),look for(寻找),deal with(对待),look after(照料),wait for(等待)等。
2)动词+副词:
这类短语动词有的用作及物动词,有的用作不及物动词。
如:I always get up as soon as the bell rings. 我总是一打铃就起床。(不及物)
Look out, there's a car coming! 当心,来汽车了!(不及物)
Have you handed in your exercises already? 你已经交练习了吗?(及物)
Please don't forget to put on your coat, it's cold outside. 请不要忘记穿外衣,外面很冷。(及物)
这一类的短语动词还有很多,及物如put out(扑灭),eat up(吃光),put down(放下);不及物如set off(出发),come up(走近),go on(继续)。
注:"动词+副词"这类短语动词和上面第一类"动词+介词"的不同之处在于:"动词+介词"用作及物动词,后面须跟宾语。"动词+副词"则有的及物,有的不及物;用作及物动词而宾语为人称代词或自身代词时,副词往往放在宾语之后。
如:Please wake me up at five tomorrow. 请在明天早上五点唤醒我。
If you have done your exercises, please hand them in. 如果你们练习做完了请交来。
She doesn't normally behave like that, she's putting it on. 她通常并不如此表现,她是装出来的。
注:这类短语动词有不少可兼作及物和不及物动词用。
如:He took off his hat when he entered the office. 他进办公室后脱下帽子。(及物)
The plane took off at seven sharp. 飞机在七点整起飞。(不及物)
Charlie rang up Neil to ask about the time of the meeting. 查理打电话给尼尔问开会的时间。(及物)
If you can't come, please ring up and let us know. 你如来不了,请来电话告诉我们一声。(不及物)
3)动词+副词+介词:
"动词+副词"之后有的可以再加一个介词,形成另一种短语动词。这类短语动词用作及物动词。
如:Do not give up hope. We must go on with the experiment 不要失望。我们必须继续试验。(go on with继续)
He came up to me. 他走到我跟前。(come up to走近)
这类短语动词还有:look down upon(看不起),do away with(去掉),put up with(忍受)等。
4)动词+名词+介词:
这类短语动词也是及物的。
如:He shook hands with all the guests at the banquet. 他在宴会上和宾客一一握手。
Young pioneers often come to the Children's Palace to take part in after school activities.少先队员经常到少年宫来参加课外活动。
Pay attention to the temperature of the stored rice. 注意仓库里的稻谷的温度。
Her job is taking care of the babies. 她的工作是照顾婴儿。
这一类短语动词还有:put an end to(结束),take notice of(注意),catch hold of(抓住),lose sight of(看不见),make use of(利用)等。
动词短语知识体系:
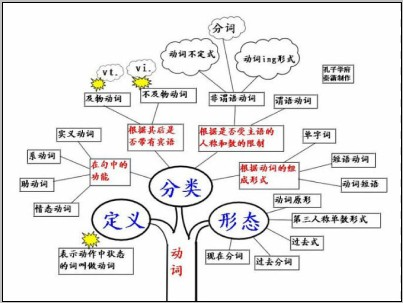
动词的定义:
表示动作中状态的词叫做动词。根据其在句中的功能,动词可分为行为动词、系动词、助动词和情态动词四类,有些动词是兼类词。
例如:We have lunch at 12. (have是行为动词)
We have been to NewYork. (have是助动词)
I am hungry. (am是系动词)
You need not have waited for me. (need是情态动词)
The door needs painting. (need是兼类词)
动词的分类:
1)表示动作中状态的词叫做动词。
2)根据其在句中的功能,动词可分为四类,分别是:
实义动词(Notional Verb)、系动词(Link Verb)、助动词(Auxiliary Verb)、情态动词(Modal Verb)。
说明:有些情况下,有些动词是兼类词。
例如:We are having a meeting. 我们正在开会。(having是实义动词。)
He has gone to NewYork.他已去纽约。(has是助动词。)
3)动词根据其后是否带有宾语,可分为两类,分别是:
及物动词(Transitive Verb)、不及物动词(Intransitive Verb),缩写形式分别为vt.和vi.。
说明:同一动词有时可用作及物动词,有时可用作不及物动词。
例如:She can dance and sing. 她能唱歌又能跳舞。(sing在此用作不及物动词。)
She can sing many English songs. 她能唱好多首英文歌曲。(sing用作及物动词。)
4)根据是否受主语的人称和数的限制,可分两类,分别是:
限定动词(Finite Verb)、非限定动词(Non-finite Verb)。
例如:She sings very well. 她唱得很好。(sing受主语she的限制,故用第三人称单数形式sings。)
She wants to learn English well. 她想学好英语。(to learn不受主语she的限制,没有词形变化,是非限定动词。
说明:英语中共有三种非限定动词,分别是:动词不定式(Infinitive)、动名词(Gerund)、分词(Participle)。
5)根据动词的组成形式,可分为三类,分别是:
单字词(One-Word Verb)、短语动词(Phrasal Verb)、动词短语(Verbal Phrase)
例如:The English language contains many phrasal verbs and verbal phrases. 英语里有许多短语动词和动词短语。(contains是单字动词。)
Students should learn to look up new words in dictionaries. 学生们学会查字典。(look up是短语动词。)
The young ought to take care of the old. 年轻人应照料老人。(takecareof是动词短语。)
6)动词有五种形态,分别是:
原形(OriginalForm)、第三人称单数形式(Singular From in Third Personal)、过去式(Past Form)、过去分词(Past Participle)、现在分词(Present Participle)。
动词知识体系:
过去分词的概念:
过去分词一般表示完成和被动的动作,只有一种形式。即:动词原形加-ed构成。
如:fallen leaves 落叶
boiled water 开水
I heard the door closed. 我听见门被关上了。
过去分词与现在分词被动式的区别:
两者均可表示被动,其区别主要在于它们所表示的时间概念不同,但有时它们也可表示相同的意思。
如:Written in haste, the book has many mistakes. 这书因写得仓促,所以错误不少。
Being written in haste, the book has many mistakes. 这书因写得仓促,所以错误不少。
Having been written in haste, the book has many mistakes. 这书因写得仓促,所以错误不少。
有时虽然所表示的时间概念相同,但有细微区别:
如:Having been show the lab, we left. 被领着看了实验室后,我们就离开了。
过去分词的句法功能:
1、作定语:
如:I don't like the book written by Martin.
Our class went on an organized trip last Monday. 上周一我们班开展了一次有组织的旅行。
注意:当过去分词是单词时,一般用于名词前,如果是过去分词短语,就放在名词的后面。过去分词做定语相当于一个被动语态的定语从句。
2、过去分词作表语:
如:They were very excited at the news. 听到这个消息,他们非常激动。
The window is broken. 窗户破了。
They were frightened at the sad sight. 他们对眼前悲惨的景象感到很害怕。
注意:be+过去分词,如果表示状态是系表结构,如果表示被动的动作是被动语态。
区别:The window is broken.(系表)
The window was broken by the boy.(被动)
有些过去分词是不及物动词构成的,不表示被动,只表示完成。
如:boiled water(开水) fallen leaves(落叶) newly arrived goods(新到的货) the risen sun(升起的太阳) the changed world(变了的世界)
这类过去分词有:gone, come, fallen, risen, changed, arrived, returned, passed等。
3、过去分词作宾语补足语:
如:I heard the song sung several times last week. 上周我听见这首歌被唱了好几次。
有时过去分词做with短语中的宾语补足语:
如:With the work done, they went out to play. 工作做完了,他们出去玩去了。
4、过去分词作状语:
如:Praised by the neighbours, he became the pride of his parents. 受到邻居们的表扬,他成为父母的骄傲。(表示原因)
Onceseen, it can never be forgotten. 一旦它被看见,人们就忘不了。(表示时间)
Given more time, I'll be able to do it better. 如果给予更多的时间,我能做得更好。(表示条件)
Though told of the danger, he still risked his life to save the boy. 虽然被告之危险,他仍然冒生命危险去救那个孩子。(表示让步)
Filled with hopes and fears, he entered the cave. 心中充满了希望与恐惧,他走进山洞。
5、过去分词与逻辑主语构成独立主格:
如:All books returned at the end of the term, the library assistant was satisfied. 所有的书期末时都还了,图书管理员很高兴。
The field ploughed, he began to spread seed. 地耕好了,他开始撒种子。
现在分词与过去分词的区别:
1、分词作表语:
分词做表语有两种情况,一种是现在分词做表语,一种是过去分词做表语,这两者区别是考试中经常考到的地方。一般来说,表示心理状态的动词如excite,interest等都是及物动词,汉语意思不是“激动”,“高兴”,而是“使激动”、“使高兴”,因而现在分词应该是“令人激动的”、“令人高兴的”,过去分词则是“感到激动的”和“感到高兴的”。所以,凡表示“令人……的”都是-ing形式,凡是表示“感到……”都用-ed形式。换句话说,若人对……感兴趣,就是somebody is in terestedi n...,若人/物本身有兴趣时,就是说sb./sth. is interesting。这类词常见的有:
interesting 使人感到高兴—interested感到高兴的
exciting令人激动的—excited感到激动的
delighting令人高兴的—delighted感到高兴的
disappointing令人失望的—disappointed感到失望的
encouraging令人鼓舞的—encouraged感到鼓舞的
pleasing令人愉快的—pleased感到愉快的
puzzling令人费解的—puzzled感到费解的
satisfying令人满意的—satisfied感到满意的
surprising令人惊异的—surprised感到惊异的
worrying令人担心的—worried感到担心的
如:Travelling is interesting but tiring. 旅行是有趣的,但是使人疲劳。
The pupils will get confused if they are made to learn too much. 如果要学生学得太多,他们会感到糊涂的。
The game is exciting. (现在分词作表语)
We were excited at the news. (过去分词作表语)
2、分词作定语:
分词作定语时有下面几个特点:
1)现在分词表示主动意义,过去分词一般表示被动含意。
2)现在分词表示正在进行,过去分词表示状态或做完(完成)的事。
如:He rushed into the burning house. 他冲进了正在燃烧着的房子。
The child standing over there is my brother. 站在那儿的男孩子是我弟弟。
The room facing south is our classroom. 朝南的房间是我们的教室。
He is an advanced teacher. 他是个先进教师。
3)下列不及物动词也以过去分词形式做定语或表语,但不具有被动意义,这点要注意:
departed, elapsed, faded, fallen, gone, frown-up, retired, returned, risen, set, vanished, much-traveled, newly-arrived, recently-come
3、分词作状语:
现在分词做状语与过去分词做状语的最主要区别在于两者与所修饰的主语的主动与被动关系的区别。
1)现在分词作状语时,现在分词的动作就是句子主语的动作,它们之间的关系是主动关系。
如:He went out shutting the door behind him. 他出去后将门随手关上。
Not knowing what to do, he went to his parents for help. 由于不知如何办是好,他去找父母帮忙。
Smiling, they came in.
2)过去分词作状语时,过去分词表示的动作是句子主语承受的动作,它们之间的关系是被动关系。
如:Cleaned, the room looks nice.
Given more attention, the trees could have grown better. 如果对这些树多关心一些,它们本来会长得更好。
Faced with difficulties, we must try to overcome them. 在遇到困难的时候,我们必须设法克服。
一般过去时的概念:
一般过去时表示过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为;过去主语所具备的能力和性格。
一般过去时的用法:
1、表示过去发生的动作或存在的状态,常与表示过去时间的副词如:yesterday,last week,two hours ago等连用。
如:My family moved here five years ago. 我家五年前搬到了这里。
I was born in 1973. 我生于1973年。
2、表示过去一段时间经常或反复发生的动作。这时可与频度副词如:often,usually,always等连用。
如:He always worked in tonight those days. 那些日子他总是工作到深夜。
I often left on business in 1987. 1987年我经常出差。
注:表示“过去经常,而今不再”时,要用usedto.
如:I used to read newspaper after breakfast. 我过去经常早饭后看报纸。(意指现在已不是这样)
The children often swam in this river. 孩子们过去经常在这条河里游泳。
3、表示过去发生的一连串动作。
如:He put down the heavy box, took out the keys, and opened the door. 他放下这沉重的箱子,掏出钥匙开了房门。
注:过去发生的一连串动作,若用and,or,but等并列连词连接,则一律用过去式。
如:They moved the chairs to the table, sat down and began to have supper. 他们把椅子搬到桌边,坐下开始吃饭。
4、在时间和条件状语从句中,用一般过去时表示过去将来的动作。
如:He said that he would let me know as soon as he got the information. 他说他一得到消息就立即让我知道。
Mary told me that she would stay at home if it rained. 玛丽告诉我如果下雨她就呆在家里。
一般过去时的特别用法:
1、句型:It is time for sb. to do sth "到……时间了" "该……了"。
例如:It is time for you to go to bed.你该睡觉了。
It is time that sb.did sth. "时间已迟了" "早该……了"。
例如:It is time you went to bed. 你早该睡觉了。
2、would(had)rather sb.did sth. 表示'宁愿某人做某事'。
例如:I'd rather you came tomorrow. 还是明天来吧。
3、wish, wonder, think, hope等用过去时,作试探性的询问、请求、建议等,而一般过去时表示的动作或状态都已成为过去,现已不复存在。
例如:I thought you might have some. 我以为你想要一些。
比较:Christine was an invalid all her life.(含义:她已不在人间。)
Christine has been an invalid all her life.(含义:她现在还活着)
Mrs. Darby lived in Kentucky for seven years.(含义:达比太太已不再住在肯塔基州。)
Mrs. Darby has lived in Kentucky for seven years.(含义:现在还住在肯塔基州,有可能指刚离去)
注意:用过去时表示现在,表示委婉语气。
1)动词want, hope, wonder, think, intend等。
例如:Did you want any thing else? 您还要些什么吗?
I wondered if you could help me. 能不能帮我一下。
2)情态动词could, would。
例如:Could you lend me your bike? 你的自行车,能借用一些吗?
与“短文改错。增加:在缺词处加一个漏字符号(∧)。并在其下面写...”考查相似的试题有:
- 单词拼写 据下列句子所给汉语注释,在横线上写出空缺处各单词的正确形式。(每空只写一词)1. In the 1970s, may people in Chin...
- Crusoe ___ a boat, but he failed.A.meant to buildB.meant buildingC.had meant to buildD.had meant building
- (2014·山东省实验中学二模)He is no fool at all,________,he is the smartest boy I have ever seen.A.in addition B.i...
- She is being pleased about it: she is very angry.A.free fromB.free ofC.out ofD.far from
- — Can you understand the foreign speaker?— Almost.He ________ his speech with a lot of gestures.[ ]A. followedB. crea...
- Research shows that humans ______ from selfish to unselfish behavior when they are watched. [ ]A. tellB. switchC. ran...
- 265. Solids can usually be turned into liquids and liquids into gases if we _____ their temperatures high enough.A.r...
- I can understand _________ to live alone and be independent.A.she wantB.she wantingC.her to wantD.her wanting
- He was running hard to catch up with the rest of the his team when he fell over his own feet. When hestruggled up, he...
- Don't pretend ________ when you don't.A.knowingB.knowC.to knowD.to knowing