本试题 “He must be helping the old man to water the flowers,________?A.is heB.isn't heC.must beD.mustn't he” 主要考查您对一般疑问句
特殊疑问句
反意疑问句
等考点的理解。关于这些考点您可以点击下面的选项卡查看详细档案。
- 一般疑问句
- 特殊疑问句
- 反意疑问句
一般疑问句的概念:
就全句提出问题,希望对方给予肯定或否定答复的问句,叫做一般疑问句。回答时要用Yes或No来开头,句末用问号,朗读时用升调。其结构是:系动词be/助动词/情态动词+主语+其他成分?
一般疑问句用法要点:
一、一般疑问句的基本结构:
1、如果谓语中有情态动词、助动词或be,将这些词移到主语之前。
如:Can you dance? 你会跳舞吗?
Will he go there tomorrow? 他明天去那里?
Are you a student? 你是学生吗?
2、如果谓语中没有情态动词、助动词或be,就在主语前加助动词do(does、did),原来的动词都用原形。
如:Do you like English? 你喜欢英语吗?
Does your brother like English? 你的兄弟喜欢英语吗?
Did you sleep well last night? 你昨晚睡得好吗?
注:have做助动词时,将其移至主语前;作“有”解时也可以将其移至主语前;不是作“有”解的为行为动词时,其疑问式和其他行为动词一样要在主语前加do(does、did)。
如:Has he gone to England? 他到英国去了?
Have you(=Do you have)a car? 你有汽车吗?
Do you have lunch at school? 你是在学校吃中饭的吗?
二、一般疑问句的简略回答:
如:—Can you swim? 你会游泳吗?
—Yes, I can.(No, I can't)会。(不会)
—Have you finished your work? 你工作做完了吗?
—Yes, I have.(No, I haven't.)做完了。(还没有。)
—Is this your pen? 这是你的钢笔吗??
—Yes, it is. (No, it isn't)是的。(不是。)
三、一般疑问句的否定形式:
当说话人或是期待肯定的回答或是不期待对方的回答时用否定式。其结构,在口语里,总是把not与情态动词、助动词或be缩略成一个词;有时也将not放在主语后。
如:Can't you see the kite? 难道你看不到那个风筝?
Don't you like playing football? 难道你不喜欢踢足球?
Aren't you(=Are you not)aYoung Pioneer?难道你不是少先队员?
四、注意否定疑问句的回答:
英语的yes和no是对答语的肯定或否定,而不是对问句的肯定或否定,所以只要答语是肯定的,就用“Yes+肯定结构”,答语是否定的,就用“No+否定结构”。这与汉语的习惯不同。
如:—Won't he go to the hospital? 难道他不去医院了?
—Yes, he will. (No, he won't.)不,他去。(是的,他不去。)
—Can't you speak English? 你难道不会讲英语吗?
—Yes, I can. (No, I can't.)不,我会。(是的,我不会)
五、陈述句语序的一般问句:
这种疑问句指望对方作出肯定的答复,其疑问意思由句末的升调来表达。
如:You want to see him? 你想见他?
I think they have asked for better pay again? 我想他们又要求加工资了吧?
不用yes或者no回答的一般疑问句:
用yes或no回答的疑问句叫做一般疑问句。但一般疑问句并不一定都用yes或no来回答,请看下面几种情况。
一、对别人的问话表示同意时,用yes回答固然可以,但如果更直截了当地回答时,可以不用yes。
1:Jim:Do you want a go?
Ling:OK, thanks.
2:Teacher:Could you take it to the classroom?
Liu Ming:Certainly.
3:Meimei:May I come then?
Ann:Sure!Work must come first!
注:ctrtainly多用于英国英语,而sure多用于美国英语。
如:Ann:May I go with you?
WeiHua:Why not?His home isn't far from here. Let's go.
二、对于别人提问的情况似乎知道,但回答时又没有多大把握时,可以用提问的方式、商量的口气或其他方式回答对方。
1、Meimei:Where's Wuhan?Do you know?
Lily:Er, is it in Hebei?
2、A:Is it in the box?
B:Let me have a look. Oh, here it is.
3、WeiHua:Is it ready now?
UncleWant:Come and look.
三、有些问题的答语不宜模棱两可,需要准确具体,否则,可能会引起别人的误解。
如:Wang:Can you speak Chinese?
Jim:Only a little.
注:若用yes回答,别人会认为你的汉语不错。
四、为了使回答显得委婉、客气、往往不采用yes来十分肯定自己的看法,也不用no来断然否定别人的意见,说话往往留有余地而礼貌谦恭。
1、A:Can you mend it?
B:I think so. Let me see.
2、A:Do you have a big piece, please?
B:Sorry, I don't.
3、Kate:Isthekitebroken?
Jim:I don't think so.
五、乐意或拒绝接受对方的邀请或要求时,不用yes或no,当拒绝或有不同的看法时,要婉言谢绝或提出自己的看法。
1、Ann:Would you like to come to supper?
Meimei:Oh, thank you!I would love to!But I must ask my parents first.
2、Jim:Shall we go to the park?
LinTao:Good idea!When shall we meet?
3、LiLei:Could I speak to Jim, please?
Kate:I'm afraid he's out at the moment.
4、LiLei:Oh!Is that a ball?Aren't all balls round?
Sam:Not in the USA.
5、A:Shall we meet at half past two?
B:All right.
六、在回答有些问题时,若回答者不愿或不便表明自己的态度,也往往不用yes或no作正面的回答。
1、A:Do you like doing housework?
B:I don't know.
2、A:Where're Lucy's pencils?Are they on her desk?
B:I can't see.
特殊疑问句的概念:
就句中某一部分进行提问的疑问句叫做特殊疑问句。特殊疑问句的基本结构是“疑问词+一般疑问句”,其回答应当是具体的。特殊疑问句句末一般用降调。
例如:How do I get there?
Why not?
What about the sports news?
特殊疑问句的使用:
1、特殊疑问句的概念: 所谓特殊疑问句就是指以疑问词开头的疑问句。
如:What are you laughing at? 你们笑什么? 句中的what就是疑问词,它的意思是“什么”。
英语中的疑问词不多,常见的有what, who, whose, when, where, why, how等;
以how开头的how many, how much, how old等,以及以what开头的what colour, what year, what class等,也都可视为疑问句。
如:How many do you need? 你们需要多少?
What colour are your curtains? 你的窗帘是什么颜色的?
2、特殊疑问句的两种句型:
特殊疑问句有两种句型结构,一种是“疑问词+一般疑问句”。
如:When did you see him? 你什么时候见到他的?
Why are you late again? 你怎么又迟到了。
第一句中的when为疑问词,其后的did you see him为一般疑问句形式;
第二句中的why为疑问词,are you late again是一个一般疑问句。
另一种是“疑问词+陈述句语序”,此时的疑问词在句中用作主语,或是修饰主语。
如:Who can answer this question? 谁能回答这个问题?
Which book is more cheap? 哪本书更便宜些?
第一句中的who为疑问词,在句中用作主语,整个句子为陈述句词序;
第二句中的which为疑问词,在句中修饰主语book,整个句子也是陈述句词序。
3、特殊疑问句的回答:
特殊疑问句与一般疑问句不同,它不能直接用Yes或No来回答,而应根据具体情况作出相应的回答。
如:—Who sings best? 谁唱得最好?
—(误)Yes, he does.
—(正)Tom does. 汤姆唱得最好。
4、特殊疑问句的省略形式:
特殊疑问句有时可用省略形式,尤其是省略与前面相同的句子结构。
如:—He won't come. 他不来了。
—Why? 为什么?
—There's someone coming. 有人要来。
—Who? 谁?
有些省略形式已成为约定成俗的固定表达,请大家要引起注意噢!
如:Why not use both? 为什么不两者都用?
What about having a rest? 休息一会儿怎么样?
Why not…后接动词原形,表示建议,意为“为什么不……呢”;
What about…后接名词或动名词,也表示建议,意为“……怎么样”。
使用特殊疑问句特别提示:
1、疑问词的选用:
特殊疑问句是以what, who, when, where, how等开头的疑问句。这些表示疑问的词叫做疑问词。当然提问的内容的不同,我们使用的疑问词也不同。问物或做什么事用what,问电话号码也用what;问人的用who;问谁的用whose;问哪里用where;问何时用when;问年龄用how old;问身高用how tall;问颜色用what colour等。
例如:—What colour is your sweater? 你的毛衣是什么颜色的?
—It's blue. 蓝色。
—Whereisyourfather? 你的爸爸在哪?
—He's in the kitchen. 他在厨房。
2、语序:
想知道对方是谁,汉语中可问“你是谁?”译成英语时语序变了,成了“Who are you?”而不能是“You are who?”所以,在英语中,我们特殊疑问句一般用倒装的语序,即用“特殊疑问词+一般疑问句的语序”构成。
小贴士:如果疑问词在句中作主语,则其后直接跟动词,语序不变。
例如:Who is going to the park tomorrow? 明天谁要去公园?
3、回答:
回答一般疑问句用yes和no来回答。但回答我们特殊疑问句时不可以用yes或no来回答,而应根据所提问的内容直接做出回答。
例如:—How tall are you? 你多高?
—I'm 1.7 meters tall. 我1.7米高。
—How is your brother? 你弟弟好吗?
—He's fine. 他很好。
—Thanks 谢谢。
小贴士:问句中的名词在答语中常用代词来代替,如上句中的yourbrother由he来代替。一般来说,this和that指物常用it来代替;these和those指物或人时可以用they代替。
如:What's this? It's a book.
What are these? They are books.
4、语调:
一般疑问句在朗读时应用升调,选择疑问句先升后降,而我们特殊疑问句在朗读时则用降调。
反意疑问句的概念:
表示提问人的看法,没有把握,需要对方证实。
反意疑问句由两部分组成:前一部分是一个陈述句,后一部分是一个简短的疑问句,两部分的人称时态应保持一致。
1、陈述部分肯定式+疑问部分否定式,可记为前肯后否。
2、陈述部分否定式+疑问部分肯定式,可记为前否后肯。
例如:This pencil is red, isn't it? Yes, it is. / No, it isn't.
This pencil isn't red, is it? Yes, it is. / No, it isn't.
反意疑问句类型:
1)陈述部分的主语是I,疑问部分要用aren't I.
如:I'm as tall as your sister, aren't I?
2)陈述部分的谓语是wish,疑问部分要用may+主语。
如:I wish to have a word with you, may I?
3)陈述部分用no, nothing, nobody, never, few, seldom, hardly, rarely, little等否定含义的词时,疑问部分用肯定含义。
如:The Swede made no answer, did he/she?
Some plants never blown(开花), do they?
4)含有oughtto的反意疑问句,陈述部分是肯定的,疑问部分用shouldn't/oughtn't+主语。
如:He ought to know what to do,oughtn't he?/shouldn't he?
5)陈述部分有have to+v.(had to+v.),疑问部分常用don't+主语(didn't+主语)。
如:We have to get there at eight tomorrow, don't we?
6)陈述部分的谓语是usedto时,疑问部分用didn't+主语或usedn't+主语。
如:He used to take pictures there, didn't he?/usedn't he?
7)陈述部分有had better+v. 疑问句部分用hadn't you?
如:You'd better read it by yourself, hadn't you?
8)陈述部分有would rather+v.,疑问部分多用wouldn't+主语。
如:He would rather read it ten times than recite it, wouldn't he?
9)陈述部分有You'd like to+v.疑问部分用wouldn't+主语。
如:You'd like to go with me, wouldn't you?
10)陈述部分有must的疑问句,疑问部分根据实际情况而定。
如:He must be a doctor, isn't he?
You must have studied English for three years, haven't you?/didn't you?
He must have finished it yesterday, didn't he?
反意疑问句用法总结:
| 陈述部分的谓语 | 疑问部分 |
| I' | aren’t I |
| wish | may + 主语 |
| no, nothing, nobody, never, few, seldom, hardly, rarely, little等否定含义的词 | 肯定含义 |
| ought to(肯定的) | shouldn't/ oughtn't +主语 |
| have to+v.(had to+v.) | don't +主语(didn't +主语) |
| used to | didn't +主语或 usedn't +主语 |
| had better + v. | hadn't you |
| would rather + v. | wouldn't +主语 |
| you'd like to + v. | wouldn't +主语 |
| must | 根据实际情况而定 |
| 感叹句中 | be +主语 |
| neither…nor, either…or 连接的并列主语 | 根据其实际逻辑意义而定 |
| 指示代词或不定代词everything, that, nothing, this | 主语用it |
| 并列复合句 | 谓语根据邻近从句的谓语而定 |
| 定语从句,宾语从句的主从复合句 | 根据主句的谓语而定 |
| think, believe, expect, suppose, imagine等引导 | 与宾语从句相对应的从句 |
| everybody, anyone, somebody, nobody, no one | 复数they, 单数he |
|
情态动词dare或need dare, need 为实义动词 |
need (dare ) +主语 do +主语 |
|
省去主语的祈使句 Let's 开头的祈使句 |
will you?shall we? |
| there be | 相应的谓语动词+there(省略主语代词) |
| 否定前缀不能视为否定词 | 仍用否定形式 |
| must表"推测" | 根据其推测的情况来确定反意疑问句 |
反意疑问句特殊用法点拨:
1、感叹句中,疑问部分用be+主语。
如:What colours, aren't they?
What a smell, isn't it?
2、陈述部分由neither...nor, either...or 连接的并列主语时,疑问部分根据其实际逻辑意义而定。
如:Neither you nor I am engineer, are we?
3、陈述部分主语是指示代词或不定代词everything, that, nothing, this,疑问部分主语用it。
如:Everything is ready, isn't it?
4、陈述部分为主语从句或并列复合句,疑问部分有三种情况:
a.并列复合句疑问部分,谓语动词根据邻近从句的谓语而定。
如:Mr. Smith had been to Bei jing for several times, he should have been in China now, shouldn't he?
b.带有定语从句,宾语从句的主从复合句,疑问部分谓语根据主句的谓语而定。
如:He is not the man who gave us a talk, is he?
He said he wanted to visit Japan, didn't he?
c.上述部分主句谓语是think, believe, expect, suppose, imagine等引导的定语从句,疑问部分与宾语从句相对应构成反意疑问句。
如:I don't think he is bright, is he?
We believe she can do it better, can't she?
5、陈述部分主语是不定代词everybody, anyone, somebody, nobody, noone等,疑问部分常用复数they,有时也用单数he。
如:Everyone knows the answer, don't they?(doeshe?)
Nobody knows about it, do they?(doeshe?)
6、带情态动词dare或need的反意疑问句,疑问部分常用need(dare)+主语。
如:We need not do it again, need we?
He dare not say so,dare you? 当dare, need为实义动词时,疑问部分用助动词do+主语。
如:She doesn't dare to go home alone, does she?
7、省去主语的祈使句的反意疑问句,疑问部分用will you。
如:Don't do that again, will you?
Go with me, will you/won't you? 注意:Let's开头的祈使句,后用shall we? Let us开头的祈使句,后用will you?
如:Let's go and listen to the music, shall we?
Let us wait for you in the reading-room, will you?
8、陈述部分是"therebe"结构的,疑问部分用there省略主语代词。
如:There is something wrong with your watch, isn't there?
There will not be any trouble, will there?
9、否定前缀不能视为否定词,其反意疑问句仍用否定形式。
如:It is impossible, isn't it?
He is not unkind to his classmates, is he?
10、must在表"推测"时,根据其推测的情况来确定反意疑问句。
如:He must be there now, isn't he?
It must be going to rain tomorrow, won't it?
反意疑问句知识体系:
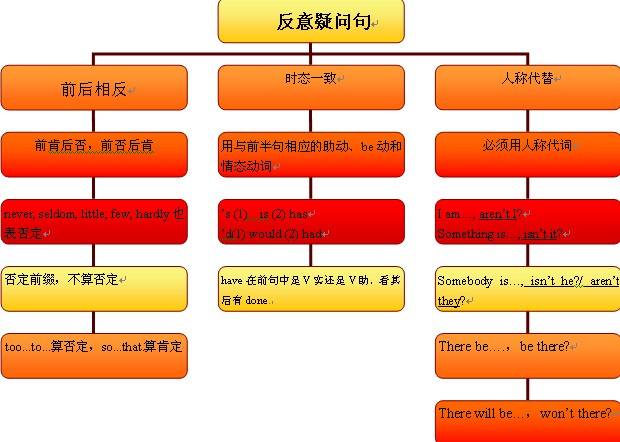
复合句的反意疑问句:
1、当陈述部分是一个(带that引导宾语从句的)主从复合句时,附加疑问句的主谓要和主句的主谓保持对应关系。但是,当陈述部分的主语是:I suppose, I think, I believe, I imagine, I expect等结构时,附加疑问句的主语和谓语要和从句的主语,谓语保持一致关系。而且要注意到否定的转移问题。
如:I think there is something wrong with the washer, isn't there?
We don't suppose he cares, does he?
2、当陈述部分是I'm sure that;we are sure;I'm afraid that;We are sure that;I feel sure that等后面跟宾语从句时,反意疑问句与后面的宾语从句一致。
3、当陈述部分是并列句时,附加疑问句的主谓语要和离它最近的句子的主谓保持对应关系。
如:We must redouble our efforts, or we'll not be able to catch up with the others, will we?
与“He must be helping the old man to water the flowers,____...”考查相似的试题有:
- — Did you know any Chinese before you arrived in Beijing?— Never ________ it, actually.A.had I learnedB.have I lear...
- — It's five years since I worked here.— ?A.Where do you work nowB. Have you worked here happilyC. How long will you w...
- Mary: This handbag isn’t yours, is it?Joan: __________.A.Yes, it’s not mineB.No, yours is biggerC.Yes, it’s my fri...
- —Are you going to the concert tonight?—I should have told you that I won’t, ______?A.haven’t youB.shouldn’t youC.a...
- —I don’t suppose Jimmy could have done well in the mid-term exam last week,______?--- ______ he almost failed in the ...
- Mr. Park, I know I am late, but please allow me to explain it to you, ________?A.don’t youB.do youC.won’t youD.w...
- I haven’t seen you since you came back from holiday. ________ a nice time?A.Do you haveB.Did you haveC.Have you ha...
- He knows so much about the story. He must have read the book, _______?A.mustn’t heB.doesn’t heC.hasn’t heD.didn’t he
- There has been a great increase in bicycle sales this year________?A.does thereB.isn’t thereC.hasn’t thereD.isn’t it
- Aunt Mary is crazy about shopping. She must be snapping up the bargains in the department store during such a sale, ?...