本试题 “It came to the world _____ that more than 10 prisoners were buried _____ by the terrorists.[ ]A. as shocking; aliveB. a shock; livingC. shocked; li...” 主要考查您对不定冠词
副词
介词和介词短语
等考点的理解。关于这些考点您可以点击下面的选项卡查看详细档案。
- 不定冠词
- 副词
- 介词和介词短语
不定冠词的概念:
冠词是置于名词前,说明各词所表示的人或事物的一种虚词,它不能离开名词而单独存在。冠词有两种,一种是定冠词,一种是不定冠词。定冠词是the,不定冠词有两种形式,一是a,另一是an。不定冠词a用于辅音音素起首的单词前,an用于元音音素起首的单词前。如:a bike, a dog, an egg, an elephant
不定冠词的特殊用法:
(1)用于序数词之前,表示数量或序数的增加:
如:Soon I saw a second plane.不久我又看到了另一架飞机。
"This is the second time that I've read the book." “这是我第二次看这本书。”
"Do you want to read it a third time?"“你还想看第三次吗?”
(2)用于表示“非常”、“很”等意义的most前:
如:This is a most interesting story. 这是一个非常有趣的故事。
(3)用于物质名词前,使之转化为具体名词,表示“一种”、“一杯之量”等:
如:A coffee, please. 请给我来杯咖啡。
I'd like a tea, please. 我要来杯茶。
(4)用于抽象名词前,使之具体化,表示与该之相关的具体的人或事:
如:He was a success in business. 他事业成功。
It's a pleasure to talk with you. 同你谈话是件令人愉快的事。
(5)用于指人的专有名词前,指某人、某人的作品或艺术品、…似(式)的人等:
如:A Mr Smith wants to see you. 一位名叫史密斯先生的人想见你。
He bought a complete Lu Hsun. 他买了一套鲁迅全集。
He thought he was a Zhu Geliang. 他自以为是诸葛亮。
(6)用于某些由动词转化来或具有动作意味的名词前,表示一次、一番等义(通常与have,take,make,give等动词连用):
如:Let's go out for a walk. 我们出去走走吧。
如:Do you care for as moke? 抽烟吗?
Would you like a drink? 要喝一杯吗?
(7)有的不可数名词或本来带有定冠词the的名词,由于受定语的修饰,其前可用不定冠词,表示某种状态。此时的不定冠词含有类似akindof的意思:
如:have breakfast 吃早餐─have a quick breakfast 吃快餐
the world 世界─a world like ours 像我们这样的世界
(8)构成短语表示数量:
如:a few apples 几个苹果
a little money 一点点钱
a lot of time 许多时间
a great many friends 许多朋友
不定冠词与one的用法解析:
1、两者均可表示“一”的意思,有时可互换。
如:About a[one] thousand students attended the meeting. 大约有1000学生参加了会议。
注:在数字开头时,两者均可用;但若不是数字开头,则应用one,如不可说three thousand a hundred,而说three thousand one hundred
如:A [One]Mr Smith wants to see you. 一个名叫史密斯先生的人想见你。(a Mr...与one Mr...同义,也可说a certain Mr...,但如果没有Mr这样的词,两者则不宜随便互换,否则含意会发生变化。
2、尽管两者均可表示“一”,有时也可换用,但毕竟由于两者的词性不同,用法不同,在多数情况下是不能互换的:
(1)从词性上看:a(an)是不定冠词,主要表示类别,即着重表示其后的名词是某物,而不是其他物;而one表示“一(个)”时是数词,主要表示数量,即强调在数量上是一个,而不是两个或多个。
比较:Give me a dictionary. 给我一本字典。
Give me one dictionary. 给我一本字典。
前者强调的是,我要的是一本字典,而不是一本教材,也不是一本小说等;而后者强调的是,我要的是一本字典,而不是两本字典或多本字典)。
再比较以下一组表达在意义上的区别:
more than a year一年多 (如一年零三个月等)
more than one year 不止一年 (如两年或三年等)
(2)由于one是数词,着重数量意义,所以当要强调数量、进行数量对比或回答how many的提问时,均应用one,而不能用a(an)。
如:He has only one pen, but I have two. 他只有一枝钢笔,但我有两枝。
I want one box, not five. 我想要一个盒子,不是要五个。
—How many friends do you have here? 你在这儿有多少个朋友?
—Only one. 只有一个。
(3)在某些表达中,两者均可用,但含义不同:at a time 每次,同时 at one time 一度,曾经 as a man 就一个人的性格而论 as one man一起,同时,全体一致地
在某些表达中,两者均可用,虽含义相同,但表达不同:
on a hot summe rafternoon 一个炎热的夏日的下午(注意用介词on)
one hot summer afternoon 一个炎热的夏日的下午(注意不用介词on)
an hour and a half一个半小时(通常不说one hour and a half)
one and a half hours 一个半小时
a minute or two一两分钟(通常不说one minute or two)
one or two minutes 一两分种
在绝大多数习语中,两者是不能换用的。如:
in a hurry 匆忙 once up on a time 从前 as a result 结果 all of a sudden突然 oneday 一天
one by one一个一个地 one and all 全部,每个人 one and the same 完全相同的
英语不定冠词(a/an)的用法:
1、用a还是an:一般说来,辅音或半元音[j, w]开头的词要前用a。
如:He has a computer (watch). 他有一台电脑(一块手表)。
He's a university student (European). 他是大学生(欧洲人)。
元音开头的词前要用an。
如:This is an egg (hones tboy). 这是一只鸡蛋(诚实的男孩)。
注意:有的字母(如a,e,f,h,i等) 或缩略词,若第一个音是元音也应用an。
如:He missed an "n" in the word. 他写的这个单词漏了一个n。
2、不要从汉语习惯出发,漏掉必用的a/an。
如:他父亲是著名诗人。
误:His father is famous poet.
正:His father is a famous poet.
3、用于转化为普通名词的专有名词前,表示某某人或某某人的一部作品、艺术品等。
如:A Mr Smith wants to see you. 一位叫史密斯先生的人想见你。
He bought a complete Lu Hsun. 他买了一套鲁迅全集。
4、用于转化为普通名词的物质名词前,表示相应的产品或种类,有时表示数量关系。
如:It’sagoodwine.这是(一种)好酒。 Twocoffeesandatea,please.请来两杯咖啡和一杯茶。
5、用于具体化的抽象名词前,表示与该抽象名词意义相关的人或事等。
如:The party was a great success. 晚会开得非常成功。
It's a pleasure to talk with you. 同你谈话是件愉快的事。
6、用于某些由动词转化来或具有动作意味的名词前,表示一次、一番等意义。
如:Let me have a look. 让我看看吧。
I'll give the car a good wash. 我要把车好好洗一洗。
7、用于序数词前表示数量或序数的增加。
如:He bought a second computer. 他又买了一台(即第二台)电脑。
Later she borne a third son. 后来她又生了第三个儿子。
8、有的不可数名词或本来应该带定冠词(the)的名词,由于受定语(尤其是形容词)的修饰,其前一般要用不定冠词或改用不定冠词,表示某种状态,此时的不定冠词通常含有a kind of的意思。
如:have breakfast 吃早餐→have a quick breakfast 吃快餐
the world 世界→a world like ours 像我们这样的世界
注:有些不可数名词即使受形容词的修饰也不能用不定冠词,容易弄错的有:news(消息),advice(忠告),luck(运气),fortune(运气),work(工作),fun(娱乐,有趣的事),weather(天气),homework(家庭作业),housework(家务活),information(情报),behavior(行为),harm(伤害),damage(损害),progress(进步),furniture(家具),baggage(行李),luggage(行李),poetry(诗),scenery(风景)等。
9、两个单数可数名词连用表示一个整体时,只用一个不定冠词。
如:He is a teacher and poet. 他既是老师又是诗人。
There's a horse and cart on the road. 路上有一辆马车。
10、不定冠词可用来表示“类属”,这是其基本用法,它表明的是某一类属中的每一个人和东西都能说明该类属的整体情况(有类似汉语的“举一反三”或“以此类推”的含义)。此时也可用定冠词或名词复数形式来表示。
如:马是有用的动物。
正:A horse is a useful animal.
正:The horse is a useful animal.
正:Horses are useful animals.
若不是说明每一个人和东西的情况,而是说整个类属,则不能用不定冠词,而要用定冠词。
如:The tiger is indanger of becoming extinct.老虎面临绝种的危险。
Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone in 1876.亚历山大·格雷汉母·贝尔于1876年发明了电话。
不定冠词知识体系:
| 不定冠词 | a | 1、辅音音素开头的单词前用a,否则用an。 2、泛指,表“一个”但概念比one弱。 3、表类别 a+可数名词单数,不译为“一”。 4、表示单位,相当于“每”的意思。 5、用于序数词前,表“又一,再一”。 6、用于某些固定词组中,a lot of等。 |
| an |
使用不定冠词和不用不定冠词的差异:
1、英语中的某些名词即可用作不可数名词,又可用作可数名词,但是含义不同,用法也不一样。
如:iron 铁;an iron 一个熨斗
kindness 和善; a kindness 一件善事
2、“with+抽象名词”使用时相当于副词,抽象名词前不用不定冠词。
如:with pleasure 乐意地
with kindness 亲切地
with joy 高兴地
with diffculty 吃力地
with angry 生气地
但在“with+a+名词”结构中虽有不定冠词,却没有实际意义。
如:with a smile 微笑地
with an effort 努力地
with a light heart 愉快地
因汉语习惯用错不定冠词的几种情形:
(1)单数可数名词若泛指,其前需加a/an,不要按汉语习惯漏掉此不定冠词:
如:他是著名影星。
正:Heisafamousfilmstar.
误:Heisfamousfilmstar.
(2)不定冠词不能与指示代词、物主代词、所有格等连用:
如:我在公园遇到了我的一位朋友。
正:Imetafriendofmineinthepark.
误:Imetmyafriendinthepark.
(3)不要受汉语影响而用错不定冠词位置:
如:我从未读过如此有趣的书。
正:Ihaveneverreadsuchaninterestingbook.
误:Ihaveneverreadasuchinterestingbook.
误:Ihaveneverreadasointerestingbook.
不定冠词的省略与重复:
(1)在不引起误会的情况下,两个并列名词中的后一个名词前的不定冠词可以省略:
如:The noun is the name of a person or thing. 名词是人和物的名称。
(2)当两个并列名词指的是同一个人时,后一名词前的不定冠词通常省略:
如:His father is a teacher and poet. 他父亲是位教师兼诗人。
但如果要强调这两种身份,也可后一个不定冠词:
His father is a teacher and a poet. 他父亲既是教师,又是诗人。
有时,由于两个并列的名词关系比较紧密、被视为一个整体,也可只用一个冠词:
A man and woman are walking arm-in-arm.一对男女手挽着手走着。
(3)两个形容词并列同时修饰一个名词时,若该名词指的是两个事物,则通常应分别使用两个冠词:
如:We have a black and a white cat. 我们养了一只黑猫和一只白猫。
(比较:We have a black and white cat. 我们养了一只黑白花猫。)
但是,有时两个并列的名词只一个事物,为了加强语气,也有了两个冠词:
如:It was a cold and a dark night. 那是一个又冷又黑的夜晚。
(4)有些由两样东西构成的“自然成对”使用的事物,通常只在其前使用一个冠词:
如:a knife and fork一副刀叉
a cup and saucer 一副茶杯与茶托
a horse and cart 一辆马车
a needle and thread 一根带线的针
hire a car and driver 租一辆配有司机的汽车
有时连第一个冠词也省略(尤其是与介词连用时):
如:with knife and fork 用刀叉
(5)当要对两个并列的名词进行选择和比较方面的强调时,通常应重复两个冠词:
如:Give me a pen, not a pencil. 给我一支钢笔,不是铅笔。
Do you want a novel or a dictionary? 你是想要本小说,还是想要本字典?
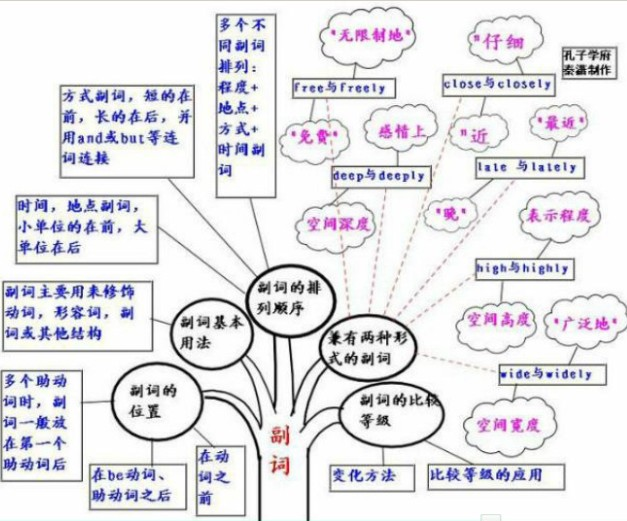
副词的概念:
副词是指在句子中表示行为或状态特征的词,用来修饰动词、形容词、其他副词、介词短语、非谓语动词乃至整个句子,表示时间、地点、程度、方式等概念。
副词的位置:
1)在动词之前。
2)在be动词、助动词之后。
3)多个助动词时,副词一般放在第一个助动词后。
注意:
a. 大多数方式副词位于句尾,但宾语过长,副词可以提前,以使句子平衡。
如:We could see very clearly a strange light ahead of us.
b. 方式副词well,badly糟、坏,hard等只放在句尾。
如:He speaks English well.
副词的排列顺序:
1)时间,地点副词,小单位的在前,大单位在后。
2)方式副词,短的在前,长的在后,并用and或but等连词连接。
如:Please write slowly and carefully.
3)多个不同副词排列:程度+地点+方式+时间副词。
注意:副词very可以修饰形容词,但不能修饰动词。
改错:(错)I very like English.
(对)I like English very much.
注意:副词enough要放在形容词的后面,形容词enough放在名词前后都可。
如:I don't know him well enough.
There is enough food for everyone to eat.
There is food enough for everyone to eat.
兼有两种形式的副词:
1)close与closely:
close意思是“近”;closely意思是“仔细地”。
如: He is sitting close to me.
Watch him closely.
2)late与lately:
late意思是"晚";lately意思是“最近” 。
如:You have come too late.
What have you been doing lately?
3)deep与deeply:
deep意思是“深”,表示空间深度;deeply时常表示感情上的深度,“深深地” 。
如:He pushed the stick deep into the mud.
Even father was deeply moved by the film.
4)high与highly:
high表示空间高度;highly表示程度,相当于much。
如:The plane was flying high.
I think highly of your opinion.
5)wide与widely:
wide表示空间宽度;widely意思是“广泛地”,“在许多地方”。
如:He opened the door wide.
English is widely used in the world.
6)free与freely:
free的意思是“免费”;freely的意思是“无限制地”。
如:You can eat free in my restaurant whenever you like.
You may speak freely, say what you like.
副词知识体系:
介词和介词短语的概念:
介词是一种用来表示词与词、词与句之间的关系的虚词,在句中不能单独作句子成分。介词后面一般有名词、代词或相当于名词的其他词类,短语或从句作它的宾语。介词和它的宾语构成介词词组,在句中作状语,表语,补语或介词宾语。介词可以分为时间介词、地点介词、方式介词和其他介词。
误用介词的三种情况:
1、多用介词:
多用介词可能是受汉语意思的影响将及物动词误用作不及物动词,也可能是受相关结构的影响而用错:
误:We discussed about the plan.
正:We discussed the plan. 我们讨论了计划。
误:Did he mention about the accident?
正:Did he mention the accident? 他提到那次事故了吗?
误:I saw her enter into the bank.
正:I saw her enter the bank. 我看见她进了银行。
误:He married with[to] a nurse.
正:He married a nurse. 他同一位护士结了婚。
误:How can contact with you?
正:How can contact you? 我怎么与你联系?
误:We should serve for the people heart and soul.
正:We should serve the people heart and soul. 我们应该全心全意地为人民服务。
误:Who controls over the factory? (但名词control可接over)
正:Who controls the factory? 谁管理这个工厂?
误:He has a great many of friends here. (比较a great number of)
正:He has a great many friends here. 他在这儿有很多朋友。
2、漏用介词:
漏用介词可能是受汉语意思的影响将不及物动词误用作及物动词,或是受相关结构的影响的影响而用错等:
误:This matter is difficult to deal. (deal with=处理)
正:This matter is difficult to deal with. 这事很难处理。
误:He is not a man to be depended.
正:He is not a man to be depended on. 他不是个可靠的人。
误:He took a cup of tea, and went on the story.
正:He took a cup of tea, and wentonwiththestory.他喝了一口茶,又接着讲故事。
误:My mother still regards me a child. (比较consider…as中的as可省略)
正:My mother still regards me as a child. 我母亲还把我当小孩看。
误:They insisted sending a car over to fetch us.
正:They insisted on sending a car over to fetch us.他们坚持要派车来接我们。
误:What he says is worth listening.
正:What he said is worth listening to.他的话值得一听。
3、错用介词:
错用介词的情况比较复杂,可能是因受汉语意思的而错,也可能是因弄不清搭配关系而错,可能是混淆用法而错,也可能是受相关结构的影响而错,可能是忽略语境而错,也可能是想当然的用错:
误:She called on his office yesterday. (call on+人,call at+地点)
正:She called at his office yesterday. 她昨天去了他办公室拜访。
误:He is engaged with a nurse.
正:He is engaged to a nurse.他与一位护士订了婚。
误:The sun rises from the east.
正:The sun rises in the east.太阳从东方升起。
误:Under his help, I finished it in time.
正:With his help, I finished it in time. 在他的帮助下,我及时做完了。
误:During he was in Japan, he visited many places.
正:During his stay in Japan, he visited many places.他在日本期间,参观过许多地方。
误:We are familiar to his character.
正:We are familiar with his character.我们了解他的性格。
误:Help yourself with the fruit.
正:Help yourself to the fruit.吃点水果吧。
介词的宾语:
1、名词或代词作介词宾语:
如:Are you interested in history? 你对历史感兴趣吗?
Don't worry about it. 别为它担心。
注:若是人称代词用作介词宾语,要注意用宾格。
如:No one can sing like her. 没有人能像她那样唱歌。(不能用like she)
2、动名词作介词宾语:
如:He is good at telling stories. 他善于讲故事。
In crossing the street he was run over. 他在穿过马路时被汽车撞倒。
3、过去分词作介词宾语:
如:We can't regard the matter as settled. 我们不能认为这事已经解决。
I take it for granted you have read the book. 我以为你读过这本书。
注:过去分词用作介词宾语通常只见于某些固定结构中,如上面第1句涉及regard…as(认为…是)结构,第2句涉及take sth for granted(认为某事属实)。在其他情况下,介词后通常不直接跟过去分词作宾语,若语义上需要接过去分词(表被动),可换用“being+过去分词”:
如:He went out without being seen by the others.他出去了,没有被其他人看见。
4、从句作介词宾语:
如:He was not satisfied with what she said. 他对她说的不满意。
I'm worried about where he is. 我担心他上哪儿去了。
注:介词后通常不接that从句,遇此情况需考虑用其他结构:
误:He paid no attention to that she was poor.
正:He paid no attention to the fact that she was poor. 他根本不注意她很穷这一事实。
但有个别介词(如except)可接that从句。
比较:I know nothing about him except that he lives next door./I know nothing about him except for the fact that he lives next door. 我只知道他住在隔壁,其它的就不知道了。
5、不定式作介词宾语:
如:I had no choice but to wait. 除了等,我没有别的选择。
He wanted nothing but to stay there. 他只想留在那儿。
They did nothing but complain. 他们老是一个劲地抱怨。
He never did anything but watch TV. 除了看电视,他从不干任何事。
注:(1)介词后接不定式的情形通常只见于but, except等极个别个词。该不定式有时带to,有时不带to,其区别是:若其前出现了动词do,其后的不定式通常不带to;
若其前没有出现动词do,则其后的不定式通常带to。
(2)介词后虽然通常不直接跟不定式作宾语,但却可接“连接代词(副词)+不定式”结构:
如:He gave me some advice on how to do it. 对于如何做这事他给我提了些建议。
6、形容词作介词宾语:
如:Her pronunciation is far from perfect. 她的语音远不是完美的。
In short, we must be prepared. 总而言之,我们要有准备。
Things have gone from bad to worse. 事情越来越糟。
注:(1)有些形容词用作介词宾语可视为其前省略了动名词being:
如:He regarded the situationas(being) serious. 他认为形势严重。
His work is far from(being) satisfactory. 他的工作丝毫不令人满意。
(2)有些“介词+形容词”的结构已构成固定搭配:in full全部地,全面地,无省略地; in private私下地,秘密地; in particular特别地;in general一般地,通常地,概括地; in brief 简言之;in short总之,简言之; in vain徒然地,徒劳无益地;for fee免费地,无偿地; for certain肯定地,确切地;for sure肯定地,确切地; for short为了简短,简称;atl arge自由自在地,逍遥法外; by far…得多
7、副词作介词宾语:
如:I can't stay for long. 我不能久呆。
It's too hot in here. 这里面太热了。
I looked every where except there. 除了那儿,我到处都看过了。
8、数词作介词宾语:
如:The city has a population of four million. 这座城市有四百万人口。
He was among the first to arrive. 他是第一批到的。
9、介词短语作介词宾语:
如:Choose a book from among these. 从这些书中选一本吧。
I saw her from across the street. 我从街的对面望见了她。
注:通常可后接介词短语作宾语的介词是from, till, until, since, except, instead of等。
比较:I took it from the bed. 我从床那儿(或床上)拿的。
I took it from under the bed. 我从床下拿的。
10、复合结构用作介词宾语:
如:She had no objection to Mary marrying him. 她不反对玛丽与他结婚。
She came in with a book in her hand. 她手里拿着一本书走了进来。
All the afternoon he worked with the door locked. 整个下午他都锁着门在房里工作。
介词短语的句法功能:
1、表语:
如:He was with a friend. 他和一个朋友在一起。
Health is above wealth. 健康胜过财富。
This knife is for cutting bread. 这把小刀是用于切面包的。
注:有些介词(如because of)引出的短语通常只用作状语,不用作表语:
误:His absence is because of the rain.
正:His absence is due to the rain. 他因雨未来。
但是,若主语是代词(不是名词),becauseof引出的短语可用作表语:
如:It is because of hard work. 那是因为辛苦工作的原因。
2、状语:
如:Don't touch it with your hands. 别用手去摸它。
Did you do this by design or by accident? 你这样做是有意的还是无意的?
3、定语:
如:This is his reply to your letter. 这是他给你的回信。
This is the best way of doing it. 这是做此事最好的方法。
My love for you is deeper than the sea. 我对你的爱比海深。
4、宾语补足语:
如:I found everythingin good condition. 我发现一切正常。
Her illness kept her in bed for a week. 她因生病在床上躺了一星期。
注:用作宾语补足语的介词短语在相应的被动语态中则为主语补足语:
如:He was regarded as a hero. 他被看成是英雄。
5、宾语:
如:A man stepped out from behind the wall. 一个人从墙后走出来。
He cannot spare anytime except on Sunday. 除星期日外,他抽不出时间。
6、主语:
如:Between6 and 7 suits me. 六点到七点对我比较适合。
After the exams is the time to relax. 考试后是轻松一下的时间。
注:介词短语通常不用作主语,尽管有时也像上面这样用作主语,但通常可视为是在一定的上下文中有所省略:
如:—When are we going to have the next meeting? 我们下次什么时候见面?
—On Tuesday may be convenient. 星期二可能比较方便。
此句中onTuesday虽用作主语,但可视为是其前省略了meeting一词:
即:Meeting during the vacation may be convenient.
与“It came to the world _____ that more than 10 prisoners we...”考查相似的试题有:
- _______ old man in front of Tom is _______ artist. [ ]A. An, anB. A, theC. The, anD. The, a
- He’s so ill that his father has to send for _______ doctor.A.oneB.someC.aD.the
- It is ____ great pleasure for me to be praised in public.A./B.aC.anD.the
- The doctor will see you again next week. ____, you must rest as much as possible.A.MoreoverB.HoweverC.MeanwhileD....
- In my opinion, it is a good way for us to memorize new words by seeing them _______.[ ]A. properlyB. repeatedlyC. cle...
- John, who is seventeen this year, usually eats ____ his father does. No wonder he is growing taller.[ ]A. twice more ...
- 短文改错。文中共有10处语言错误,请在错误的地方增加、删除或修改某个单词。增加:在缺词处加一个漏字符号(∧),并在其下面写...
- .Gold is similar _________colour _______brass.A. in; in B. to; to C.in; to D at; to
- He finally won the general election because many of his promises were quite popular _____ the voters.[ ]A. forB. inC....
- 90. --- Who is that gentleman who talked to you just now?--- He is my uncle _____ marriage.A.atB.toC.byD.With