本试题 “_________is known to us all,America is a developed country__________the first world.[ ]A. Which; belonging toB. Which; belonged toC. As; belonging ...” 主要考查您对关系代词
现在分词
非限制性定语从句
等考点的理解。关于这些考点您可以点击下面的选项卡查看详细档案。
- 关系代词
- 现在分词
- 非限制性定语从句
关系代词的概念:
英语中的关系代词有who, whom, whose, that, which, 它们是用来引导定语从句的。关系代词既代表定语从句所修饰的词,又在其所引导的从句中承担一个成分,如主语、宾语、表语、或定语。
如:This is the man who saved your son. (who在从句中作主语,先行词是man)
The man whom I met yesterday is Jim.
A child whose parents are dead is an orphan.
He wants a room whose window looks out over the sea.
关系代词用法:
1、that与which的用法区别:
两者都可指物,常可互换。其区别主要在于:
(1)引导非限制性定语从句时,通常要用which:
如:She received an invitation from her boss, which came as a surprise. 她收到了老板的邀请,这是她意想不到的。
(2)直接放在介词后作宾语时,通常要用which:
如:The tool with which he is working is called a hammer. 他干活用的那个工具叫做锤子。
(3)当先行词是下列不定代词或被它们修饰时much, little, none, all, few, every(thing), any(thing), no(thing)等时,通常用that:
如:There was little that the enemy could do but surrender. 敌人无法,只有投降了。
All[Everything] that can be done must be done. 凡能做的事都必须做。
(4)当先行词有the very, the only, the same等修饰时,通常用that:
如:This is the only example that I know. 我知道的例子只有这一个。
Those are the very words that he used. 那是他的原话。
(5)当先行词有形容词最高级或序数词(包括last, next等)等修饰时,通常用that:
如:This is the best dictionary that I've ever used. 这是我用过的最好的词典。
The first thing that you should do is to work out a plan. 你应该做的第一件事是订个计划。
(6)当关系代词在定语从句中用作表语时,通常用that:
如:China is not the country(that) it was. 中国已不是过去的中国了。
(7)当先行词是一个既指人又指物的并列词组时,通常用that:
如:They talked about the persons and things that most impressed them. 他们谈论了使他们印象最深的人和事。
(8)当要避免重复时:
如:Which is the course that we are to take? 我们选哪门课程?
2、that与who的用法区别:
(1)两者均可指人,有时可互换:
如:All that[who] heard him were delighted. 所有听了他讲话的人都很高兴。
Have you met anybody that[who] has been to Paris? 你遇见过到过巴黎的人吗?
He is the only one among us that[who] knows Russian. 他是我们中间唯一懂俄语的人。
(2)但是在下列情况,通常要用that:
①当先行词是一个既指人又指物的并列词组时:
如:I made a speech on the men and things that I had seen abroad. 我就我在国外所见到的人和事作了报告。
②当先行词是who时(为避免重复):
如:Who was it that won the World Cup in1982? 谁赢得了1982年的世界杯?
③当关系代词在定语从句中作表语时(可省略):
如:Tom is not the boy(that) he was. 汤姆这孩子已不是以前那个样子了。
关系代词知识体系:
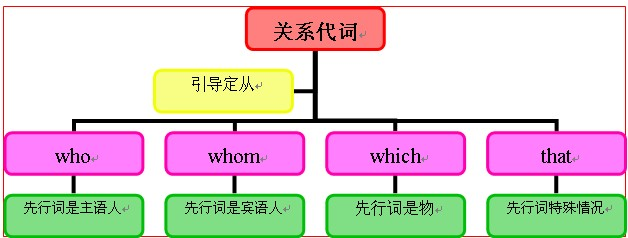
关系代词用法拓展:
1、as与which的用法区别:
(1)引导限制性定语从句时,在such,as,thesame后只能用as,其他情况用which:
如:I never heard such stories as he tells. 我从未听过他讲那样的故事。
It's the same story as I heard yesterday. 这故事跟我昨天听到的一样。
This is the photo which shows my house. 这张照片拍的是我的住宅。
(2)引导非限制性定语从句时,有时两者可互换:
如:I live a long way from work, as [which] you know. 我住得离工作单位很远,这你是知道的。
(3)但在,在以下情况引导非限制性定语从句时,两者不可换用:
①当从句位于主句前面时,只用as:
如:As is known to everybody, the moon travels round the earth once every month. 月球每月绕地球转一周,这是每个人都清楚的。
②as引导的非限制性定语从句应与主句在意义上和谐一致,which无此限制:
如:He went abroad, as[which] was expected. 他出国了,这是大家预料到的。
He went abroad, which was unexpected. 他出国了,这让大家感到很意外。(不用as)
③as引导非限制性定语从句时,先行词通常不能是主句中某个具体的词,而应是整个句子、整个短语或某个短语推断出来的概念,而which则无此限制:
如:The river, which flows through London, is called the Thames. 这条流经伦敦的河叫泰晤士河。(不用as)
④当as引导非限制性定语从句作主语时,其谓语通常应是连系动词,而不宜是其他动词,而which则无此限制:
如:She has married again, as[which] seemed natural. 她又结婚了,这似乎很自常。
She has married again, which delighted us.她又结婚了,这使我们很高兴。(不用as)
2、who与whom的用法区别:
两者均只用于人,从理论上说,who为主格,whom为宾格:
如:Where's the girl who sells the tickets? 卖票的女孩在哪里?
The author whom you criticized in your view has written a letter in reply. 你在评论中批评的那个作者已写了一封回信。
但实际上,除非在正式文体中,宾格关系代词whom往往省略不用,或用who或that代之:
如:The man(that, who, whom) you met just now is called Jim. 你刚遇见的那个人叫吉姆。
不过,在以下几种情况值得注意:
(1)直接跟在介词后面作宾语时,只能用whom,而且不能省略:
如:She brought with her three friends, none of whom I had ever met before. 她带了3个朋友来,我以前都没见过。
(2)引导非限制性定语从句且作宾语时,who和whom均可用,但以用whom为佳,此时也不能省略:
如:This is Jack, who[whom] you haven't met before. 这是杰克,你以前没见过。
现在分词的概念:
现在分词(PresentParticiple)(又称-ing形式),是分词的一种,是非限定动词,即在句子里面不能单独充当谓语,但能充当其它的一些成分(定语,表语,补语和状语)。一般式:doing;一般被动式:being done;完成式:having done;完成被动式:having been done。所有否定式都是在-ing前面加not。
现在分词的用法:
1)做表语:
如:He was very amusing.
That book was rather boring.
很多动词的现在分词都可以作表语:exciting, interesting, encouraging, disappointing, confusing, touching, puzzling.
2)作定语:
上面所出现的现在分词都可以用作定语,修饰一个名词:
如:That must have been a terrifying experience.
I found him a charming person.
现在分词短语还可以放在名词的后面修饰名词,相当于一个定语从句:
如:There are a few boys swimming in the river.
There is a car waiting outside.
3)作状语:
现在分词短语可以表示一个同时发生的次要的或伴随的动作:
如:Following Tom, we started to climb the mountain.
Opening the drawer, he took out a box.
Taking a key out of his pocket, he opened the door.
现在分词短语还可以表示原因,相当于一个原因状语从句:
如:Not knowing her address, we couldn't get in touch with her.
Being unemployed, he hasn't got much money.
现在分词短语还可以表示时间,相当于一个时间状语从句:
如:Hearing the news, they all jumped with joy.
Returning home, he began to do his homework.
Jim hurt his arm while playing tennis.
Be careful when crossing the road.
Having found a hotel, we looked for some where to have dinner.
Having finished her work, she went home.
4)作宾补:
现在分词在一些动词之后可以做宾语的补语:
例如:see, hear, catch, find, keep, have等。
如:I see him passing my house every day.
I caught him stealing things in that shop.
I smelt something burning.
She kept him working all day.
现在分词其他用法解析:
1、现在分词一般式的用法:
现在分词的一般式所表示的动作与主语动作同时发生:
如:When we arrived, we found him sleeping. 我们到达时发现他在睡觉。
Living in the 示的动作也可略早于或迟于谓语动作,但两者之间没有时间间隔:
如:Seeing nobody at home, he decided to leave a note. 发现没有在家,他决定留个字条。
He went home, finding the door locked. 他回到家,发现门是锁着的。当现在分词所表示的动作略迟于谓语动作时,现在分词通常位于句末。
2、现在分词完成式的用法:
现在分词的完成式主要表示发生在谓语动作之前的动作:
如:Having been there once, she knew the place quite well. 由于去过那儿一次,她对那地方很熟悉。
Having failed twice, he didn't want to try again. 他已经失败了两次,不想再试了。
注:(1)现在分词的一般式和完成式均可表示已完成或先于谓语的动作,但有区别:现在分词所表示的动作虽然可以先于谓语动作,但两者之间没有时间间隔,而现在分词的完成式所表示先于谓语的动作则与谓语动作有一定的时间间隔:
如:Locking the door, he went out. 锁好门之后,他就出去了。
Having invited him here to speak, we'd better go to his lecture. 既然我们请了他来作报告,我们最好去听一下。
有时即使是分词动作与谓语动作几乎同时发生,但如果要强调分词动作的完成性,也应用现在分词的完成式:
如:Having bought our tickets, we went into the theatre. 我们买好票后就走进剧场。
(2)现在分词的完成式一般不用作定语:
误:Do you know anyone having lost a cat? 你知道有谁丢了一只猫吗?
误:I want to talk to the person having broken the window. 我想同打破窗户的人谈谈。
若将以上现分词的完成式改为一般式也不可以(因为现在分词作后置定语时通常只表示与谓语动作同时或几乎同时发生的动作,而不能先于谓语动作而发生):
误:I want to talk to the person breaking the window.
3、现在分词被动式的用法:
当要表示一个被动动作时,现在分词就用被动形式。现在分词的一般式和完成式均有被动式形式:
(1)现在分词一般式的被动式:主要表示现在正在进行的动作,也可表示与谓语动作同时发生的动作:
如:Who is the woman being operated on? 正在动手术的女人是谁?
I saw him being taken away by the police. 我看见他被警察带走。
注:有时现在分词一般式的被动式所表示的动作也可发生在谓语动作之前(此时的现在分词通常用于表示原因,且多为状态动词):
如:Not having a car, he finds it difficult to get around. 由于没车,她感到行动很困难。
(2)现在分词完成式的被动式:主要表示发生在谓语动词之前且已经完成的动作。
如:The subject having been opened, he had to go on with it. 话题已经开始了,他不得不谈下去。
Having been written inhaste, the book has many mistakes. 这书因写得仓促,所以错误不少。
比较:Being so ill, she can't go to school. 由于病得那么严重,她不能去上学。
Having been ill for a long time, he needed time to recover. 由于病了很长时间,他需要一段恢复的时间。
非限制性定语从句的概念:
非限制性定语是对被修饰名词或代词的附加说明,它不是必需的,如果去掉,也不会影响句子的意思,它与被修饰名词之间通常用逗号分开。
如:The travellers, knowing about the floods, took another road. 游客们知道发了大水,都改道走了。
The boys, wanting to play football, were disappointed when it rained. 那些男孩子想踢足球,因为下雨感到失望。
非限制性定语从句用法:
1、引导非限定性定语从句时,只能用which(不用that)。
例如:Heat is another form of energy, which is as important as other kinds of energy.
热是另一种形式的能量,与其他形式的能量一样重要。 (从句表补充说明,而且关系代词which不能换成that。)
2、引导非限定性定语从句的which可以指代前面的先行词,也可以指前面整个句子的含义。
例如:That Peter will marry Alice, which has not been announced yet, has spread around.
彼特要娶爱丽斯这件事还没宣布,却已传得沸沸扬扬。(句子中的which指“彼特要娶爱丽斯”这整个句子的意思。)
3、除which外,还可用when,where,who等关系代、副词引导非限定性定语从句。
例如:After graduation, I decided to stay in Chongqing, where I spent my childhood and four years of college life.
毕业后,我决定留在重庆,在那里我曾度过了我的童年和四年大学生活。
Albert Einstein left Germany for the United States during World WarII, when Jews were badly treated in Germany.
第二次世界大战期间,爱因斯坦离开德国去了美国,那时犹太人在德国受到不好的对待。
4、在限定性定语从句中作宾语时,引导词可以省略,但引导非限定性定语从句的关联词不能省。
如:He was eager to go to the hospital to see his stepmother, whom he loved and respected as his own mother.
他急于想去医院看望他的继母,他把他的继母当作亲生母亲一样热爱和尊敬。
The American journalist(whom/who) the announcer mentioned in the news broadcast is said to have been killed by the gangsters.
播音员在新闻广播中提到的那位美国记者据说已经被匪徒杀害了。
两例中的关系代词都在从句中作宾语。由于第二例是限定性定语从句,可以省略关系代词;第一例中的引导词不能省略,因为它引导的是非限定性定语从句。
5、表示“正如”的含义时,通常用as引导非限定性定语从句,也可用which引导;但置于句首时,只能用as引导。
如:China has basically succeeded in defeating SARS, which/as we have expected.
正如我们所预料的那样,中国已基本上战胜了“非典”。
As is well known to everybody, Tai wan is an inseparable part of China.
众所周知,台湾是中国不可分割的一部分。
但是当非限定性定语从句是否定含义时,就只能用which(而不用as)引导。
如:He didn't win the championship, which I hadn't expected.
他没获得冠军,这一点是我没预料到的。
非限制性定语丛句中as, which的区别:
1、which引导非限制性定语丛句代表前面的整个句子的时候,一般是对主句的结果的说明。
如: He grows too fast, which makes him taller than his classmates.
2、as引导非限制性丛句代表前面整个句子时一般来讲丛句的谓语动词有三种:
A. 含有be动词:
如:He failed the exam, as is natural.
B. 实意动词的被动形式:
如:As is reported, the fire caused a great loss.
C.感官动词和意识类动词如:
如:see, hear, notice, know, learn, realize 等。
As you know, I am a teacher.
3、as可翻译为正如,它引导的丛句可位于主句之前,也可位于主句之后;which引导的该丛句只能位于主句之后。
例1:__A___he realized, I was very useful to him.
例2:This elephant is like a snake, ___A__anybody can see.
例3:The sun gives us light and heat, __B___makes the plan tgrow well.
A. As(as)
B. which
C. that
D. who
限定性定语从句与非限定性定语从句的区别:
|
定 |
限制性定语从句 | 非限制性定语从句 |
| 1、不能省略,如果省略整个句子意思不完整。 | 可以省略,如果省略整个句子意思仍然完整。 | |
| 2、可以用that引导。 | 不可以用that引导。 | |
| 3、关联词有时可以省略。 | 关联词不可以省略。 | |
| 4、不用逗号把它和句子的其他部分隔开。 | 用逗号把它和句子的其他部分隔开。 | |
| 5、只能修饰先行词。 | 可以修饰先行词,也可以修饰整个句子或句子的一部分。 |
非限制性定语从句的关系词:
| 关系代词 | 指代对象 | 指代人 | 指代物 |
| 主格 | who | which, as | |
| 宾格 | whom | which, as | |
| 所有格 | of, whom, whose | which, of which, whose | |
| 关系副词:when, where | |||
非限定性定语从句的使用规则及注意事项:
1、which引导的非限定性定语从句是用来说明前面整个句子的情况或主句的某一部分。
2、在引导限定性定语从句时,that有时相当于in which, at which, for which或at which。其中,介词的选用,依据从句中的动词所需搭配的介词来选用。例句:
① Attitudes towards day dreaming are changing in much the same way that(inwhich)attitudes towards night dreaming have changed.
人们对白日做梦的态度正在改变,这与人们对夜间做梦的看法的变化有非常相似之处。
② I like the music for the very reason that(for which) he dislike it.
我出于某种原因喜欢这种音乐,而他恰恰与我相反。
③ We arrived the day that(on which) they left.
刚好我们到的那天他们走了。
3、as有时也可用作关系代词。
4、在非限定性定语从句中,关系词不能用that。
与“_________is known to us all,America is a developed countr...”考查相似的试题有:
- We asked John and Jerry,but ________ of them could offer a satisfactory explanation.A.eitherB.noneC.bothD.neither
- I spent the whole day repairing the motorbike.The work was ________ simple.A.nothing butB.anything butC.something ...
- _____is widely known that you value more what you haven’t rather than what you have .A.AsB.WhatC.ItD.Which
- We know such people are not ___.A.to rely onB.to be relied uponC.to be reliedD.to rely upon
- _____ the youth to the rising sun at 8 or 9 a. m. Mao Zedong expressed his great hope for the young men.[ ]A.Compare...
- All the citizens, young and old, walked and sang, beautifully ______ in new clothes of all kinds, ______ the success ...
- _____ from what he did, he isn't a person to depend on.[ ]A. JudgeB. JudgingC. JudgedD. Judges
- We still remember once__________round the famous tower when we were young.A.having takenB.to be takenC.having been...
- “Did he repair his bike all by himself that day?” “No, he ___.”A.hadn'tB.had had it repairingC.had it being repair...
- The police found that the house _______ and a lot of things _______.A.has broken into; has been stolenB.had broken ...