本试题 “短文改错。英语课上,老师要求同桌同学相互修改作文。假设以下短文为你同桌所写,请你对其进行修改。文中共有10处错误,每句中最多有两处。错误涉及一个单词的...” 主要考查您对定冠词
不定代词
形容词
副词
介词和介词短语
并列连词
系动词
情态动词
动词
一般过去时
等考点的理解。关于这些考点您可以点击下面的选项卡查看详细档案。
- 定冠词
- 不定代词
- 形容词
- 副词
- 介词和介词短语
- 并列连词
- 系动词
- 情态动词
- 动词
- 一般过去时
定冠词的定义:
定冠词the 有this,that,these,those等意义,但较弱,用于单数或复数名词前,主要用来特指,使一个或几个事物区别于所有其他同名的事物。
定冠词通常位于名词或名词修饰语前,但放在both、all、double、half、twice等词之后。
如:All the students in the class went out.班里所有的学生都出去了。
定冠词的用法:
1、表示特指:
如:Look! A car has stopped there. The car is beautiful. 瞧,有辆汽车在那儿停下了。那辆汽车可真漂亮。
Why not ask the teacher? 为什么不问问老师?
2、与单数可数名词连用表类别:
如:I hate the telephone. 我讨厌电话。
The cobra is dangerous. 眼镜蛇是危险的。
3、与某些形容词连用表示类别:
如:The rich are not always happier than the poor. 富人并不总是比穷人过得开心。
Theoldaremorelikelytocatchcoldthantheyoung.老年人比年轻人容易感冒。
4、用于独一无二的事物名词前:
如:The earth goes around the sun. 地球绕着太阳转。
The sky was blue and clear. 天空清澈湛蓝。
5、用于方向或方位等名词前:
如:He looked towards the east. 他朝东望。
Turn to the right at the second crossing. 在第二十字路口向右拐。
6、用于序数词或形容词的最高级前:
如:You will be the second to speak. 你第二个发言。
Autumn is the best season here. 秋季是这里最好的季节。
7、用于乐器名词前表示演奏:
如:He plays the piano very well. 他的钢琴弹得很好。
注:若不是从演奏角度来考虑,而是考虑乐器的实体,则不一定用定冠词:
He bought a piano for his son. 他为儿子买了部钢琴。
定冠词与不定冠词互换用法比较:
1、在形容词最高级前一般加定冠词。但有时却用不定冠词,这时它不表示“最”的意思,而表示“非常”“很”的意思。
如:This is the most important question of all. 这是所有问题中最重要的一个。
This is a most important question. 这时一个非常重要的问题。
2、在序数词前加定冠词,表示“第几”;加不定冠词则表示“又”“再”。
如:Will you be the firse to read the text? 你第一个读课文好吗?
Will you have a second try? 你再试一次好吗?
3、在有些短语中,用定冠词和不定冠词一样。
如:The number of our school students is about 1500. 我校学生人数约为1500人。
定冠词的用法口诀:
特指双熟悉,上文已提及;
世上独无二,序数最高级;
某些专有名,习语及乐器。
以上口诀归纳了用定冠词的一般情况,即:
①特指某些人或物
②谈话双方都熟悉的人或事
③上文已经提到的人或事
④世界上独一无二的事物前
⑤序数词回形容词最高级前
⑥某些专有名词前
⑦一些习惯短语(如:intheday等)中和乐器前(如:playtheviolin/piano)。
定冠词知识体系:
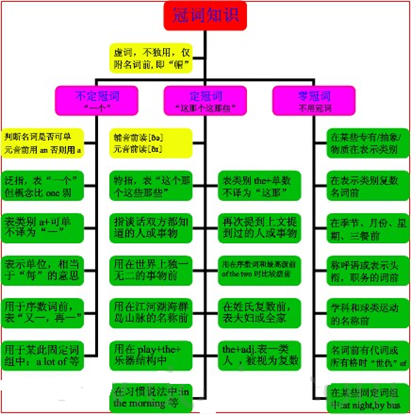
定冠词用法拓展:
1、用于姓氏的复数前,表示全家人或全家中两个或两个以上的人:
如:The Browns live next to us. 布朗一家就住在我们隔壁。
The Greens have no Children. 格林夫妇没有小孩。
2、用来代替前面已提到的人的身体部位或衣着等的一部分:
如:He hit me in the face. 他打我的脸。
He caught the thief by the collar. 他抓住小偷的衣领。
3、用于逢整十数词的复数名词前,指世纪中的年代或人的约略年岁:
如:He began to learn French in his fifties. 他五十多岁开始学习法语。
He went to Japan with his family in the sixties. 他在60年代带家人去了日本。
4、用于某些单数可数名词前,使意义抽象化,指其属性或功能等:
如:This colour is pleasant to the eye. 这颜色悦目。
He is fond of the bottle. 他喜欢喝酒。
5、表示计算单位,含有a, each, per 之类的意义:
如:He is paid by the hour (piece). 他拿计时(件)工资。
It sells at two dollars the pound. 这东西每磅卖两美元。
6、用于人名前,或特指、或比喻、或指其作品等;用于某些产品的名称前,指产品:
如:He likes the Picasso. 他喜欢毕加索的画。
Lu Xun has been known as the Gorky of China. 鲁迅人称中国的高尔基。
7、用于江、(运)河、海、洋以及山脉、群岛、半岛、海岛、海峡、沙漠等名称的前:
如:the Chang jiang River 长江
the Pacific(Ocean) 太平洋
the Suez(Canal) 苏伊士运河
①关于湖名前是否用冠词通常要分两种情况:
中国的湖名在英译时,其前通常加定冠词:
the West Lake 西湖,the Dong ting Lake洞庭湖。
而外国的湖名前,多数不加定冠词,少数加定冠词,视习惯而定:
Lake Success 成功湖,the Lake of Geneva日内瓦湖
②山名的构成有两种方式:
若用于“山名+Mountains”,其前常用定冠词:the Jing gang Mountains 井冈山;
若用于“Mount/Mt+山名”,则通常不用冠词:Mount Tai 泰山。
另外,若不出现mountain一词时,则通常要用冠词:theAlps阿尔卑斯山。
8、用于由普通名词或含有普通名词构成的专有名词 (如国名、地名、政党、团体、组织机构以及旅馆、商店、学校、医院、文娱场所、建筑物等)前:
如:the United Nations 联合国
the People's Republic of China 中华人民共和国
the National People's Congress 全国人民代表大会
注:大学名称的构成要注意以下情况:
①对于以地名命名的大学,通常有两种形式 (注意冠词的有无):
如:the University of London / London University 伦敦大学
②对于以人名命名的大学,通常只有一种表达(不用冠词):
如:Yale University 耶鲁大学
Brown University 布朗大学
不定代词概说:
英语的不定代词有all, each, both, either, neither, one, none, little, few, many, much, other, another, some, any, no, few, little, both, enough, every等,以及由some,any,no和every构成的合成代词(即somebody, anyone, nothing等)。在这些不定代词中,多数都能作主语、宾语、表语或定语,但是代词none以及由some, any, no和every构成的合成代词只能作主语、宾语或表语,不能作定语,而no和every则只用作定语。
不定代词用法对比:
1、so little与such little的区别:
用so little还是such little取决于little的意思:若表示数量方面的“少”,则用so little;若表示形状体积的“小”,则用such little:
如:He has so little time for reading. 他读书的时间少得可怜。
I've never seen such little boxes. 我从未见过那样小的盒子。
2、some与any的用法区别:
一般说来,some用于肯定句中,any用于否定句和疑问句中。但是,在表示请求、邀请或征求意见的句子中,通常要用some而不用any:
如:Would you like some cake? 吃点蛋糕吗?
Why not buy some bread? 为什么不买些面包呢?
Shall I get some chalk for you? 要我帮你拿些粉笔来吗?
注:any有时也用于肯定句中,此时表示“任何”:
如:Any colour will do. 任何颜色都行。
Come any day you like. 随便哪天来都可以。
3、many与much的用法区别:
两者都表示“许多”,但many修饰或代替可数名词(复数),与few(少数)相对;
而much用来修饰或代替不可数名词(单数),与little(少量)相对。在口语中两者主要用于非肯定句中:
如:Did you see many people there? 你在那儿看见许多人了吗?
We don't have much time. 我们没有许多时间。
在肯定句中,一般用a lot of, lots of, plenty of 等代之。但在正式文体中有时也用于肯定句中;
另外,若用作主语或主语的定语,或其前有how, too, as, so, a good, a great等修饰,也可用于肯定句中:
如:Many of us left early. 我们有许多人离开得很早。
Much work has been done. 许多工作都已经做了。
You've given me too much. 你已给我太多了。
Take as many(much) as you want. 你要多少拿多少。
I asked her a great many questions. 我问了她许多问题。
4、few, a few与little, a little的用法区别:
(1)few和a few后接可数名词的复数形式。few表示数量很少或几乎没有,强调“少”,含有否定意义;
a few表示数量虽然少但毕竟还有,强调“有”,含有肯定意义:
如:It is very difficult, and few people understand it. 它很难,没有几个人能懂。
It is very difficult, but a few people understand it. 他虽难,但是有些人懂。
(2)little和alittle之后接不可数名词,其区别跟few和a few之间的区别相似:
如:Unfortunately, I had little money on me. 很不巧,我身上没带什么钱。
Fortunately, I had a little money on me. 幸好我身上带着一点钱。
5、other, the other, another与others的用法区别:
这些不定代词不仅在含义上有单复数之分,而且在用法上有泛指(无the)和特指(有the)之别。其用法区别可归纳如下:
(1)指单数时,若泛指用another,若特指用the other:
如:Give me another(one). 另外给我一个。
Shut the other eye, please. 请把另一只眼睛也闭上。
(2)指复数时,若泛指用other(后接复数名词),若特指用the other(后接复数名词):
如:There are other ways of doing it. 做这事还有其他的办法。
Where have the other students gone? 其他学生都到哪里去了?
(3)others永远表示复数意义(且其后不能再接名词)。其用法大致相当于“other+复数名词”,同样地the others大致相当于“the other+复数名词”:
如:Other people[Others] may not think that way. 别的人可能不这样想。
He is cleverer than the others[the other students] in her class. 他比班上其他学生聪明。
(4)another一般只能表单数,且其后接名词也只能接单数名词。但是若其后有数词或few修饰时,则也可接复数名词:
如:We need another few chairs. 我们还需要几把椅子。
In another two weeks it'll be finished. 再过两个星期就可做完了。
(5)与some对比使用时,用others(此时与some同义):
如:Some say yes, and others say no. 有人说对,有人说不对。
不定代词用法点拨:
1、指两者和三者的不定代词:
有些不定代词用于指两者(如both, either, neither),有的不定代词用于指三者(如all, any, none, every),注意不要弄混:
如:Both of my parents are doctors. 我的父母都是医生。
All of the students are interested in it. 所有的学生对此都很感兴趣。
There are trees on any side of the square. 广场的每一边都种有树。
He has two sons, neither of whom is rich. 他有两个儿子,都不富有。
He has three sons, none of whom is rich. 他有三个儿子,都不富有。
注:each可用于两者、三者或三者以上,而every只用于三者或三者以上,因此用于两者时只能用each,不能用every。
2、复合不定代词的用法特点:
复合不定代词包括something, somebody, someone, anything, anybody, anyone, nothing, nobody, noone, everything, everybody, everyone等。它们在句中可用作主语、宾语或表语,但不能用作定语。something, someone等和anything, anyone等的区别与some和any的区别一样,前者一般用于肯定句,后者一般用于否定句、疑问句或条件句。具体使用时应注意以下几点:
(1)复合不定代词受定语修饰时,定语应放在它们后面:
如:There is nothing wrong with the radio. 这收音机没有毛病。
Have you seen anyone[anybody] famous? 你见过名人吗?
(2)指人的复合不定代词若用作主语,其谓语动词一般用单数,相应的人称代词和物主代词也用单数he, him, his(不一定指男性)。但在非正式文体中常用复数代词they, them, their:
如:Everyone knows this, doesn't he[don't they]? 人人都知道这一点,不是吗?
If anybody[anyone] comes, ask him[them] to wait. 要是有人来,让他等着。
(3)指事物的复合不定代词若用作主语,谓语动词只能用单数,相应的人称代词也只能用it,而不用they:
如:Everything is ready, isn't it? 一切都准备好了,是吗?
(4)anyone, everyone等只能指人,不能指物,且其后一般不接of 短语。若是指物或后接of 短语,可用any one, every one(分开写):
如:any one of the boys(books) 孩子们(书)当中的任何一个(本)
every one of the students(schools) 每一个学生(一所学校)
3、是any not还是not any:
按英语习惯,any以及含有any的复合不定代词用于否定句时,它只能出现在否定词之后,而不能在否定词之前:
误:Anyone doesn't know how to do it.
正:No one knows how to do it.任何人都不知道如何做它。
误:Anybody[Anyone] can not do it.
正:Nobody[Noone] can do it.这事谁也干不了。
误:Anything can not prevent me from going.
正:Nothing can prevent me from going. 什么也不能阻挡我去。
4、不定代词与部分否定:
不定代词all, both, every等与not连用时构成部分否定;若要表示完全否定,则需换用none, neither, no one等。
比较:All of the students like the novel. 所有这些学生都喜欢这本小说。
Not all of the students like the novel. 并不是所有这些学生都喜欢这本小说。
All of the students don't like the novel. 并不是所有这些学生都喜欢这本小说。
None of the students like the novel. 这些学生当中没有一个喜欢这本小说。
5、all, both, each等用作同位语:
若用作主语同位语,主语可以是名词或代词;若用作宾语等其他成分的同位语,则宾语等成分必须是人称代词,而不能是名词:
如:We have all read it. 我们都读过他。(all修饰的主语是代词)
The villages have all been destroyed. 村庄都被毁了。(all修饰的主语是名词)
They told us all to wait there. 他叫我们都在那儿等。(all修饰的宾语是代词)
但不能说:They told the men all to wait there. (all修饰的宾语是名词不是代词)
不定代词知识体系:

不定代词与语境考题:
不定代词是高考的常考考点,有的不定代词考题出得比较灵活,不能死套规则,要注意结合语境来理解:
例1:—Is____here?
—No, Bob and Tim have asked for leave.
A. anybody
B. everybody
C. somebody
D. nobody
解析:
若只是从表面来看,填空句是个疑问句,可能会误选A。但其实此题最佳答案应选B,因为下文的答句说“只有Bob和Tim请假了”,这说明问句是在查人数,故用Is everybody here? (大家都到齐了吗?)
例2:I agree with most of what you said, but I don't agree with_____.
A. everything
B. anything
C. something
D. nothing
解析:
此句若从表面看,有可能误选B,因为填空句为否定句。但实际上最佳答案为A,因为上文说“我同意他说的大部分内容”,这与下文的but I don't agree with everything (但并不是同意他说的所有内容)完全相符。
例3:—Doyouhave_____athomenow,Mary?
—No, we still have to get some fruit and tea.
A. something
B. anything
C. everything
D. nothing
解析:答案:C,句意为“玛丽,现在家里东西都准备齐了吗?”“还没有,我们还要买些水果和茶。”
例4:—If you want a necklace, I'll buy one for you at once.
—Oh, no. A necklace is not_____that I need most.
A. anything
B. something
C. nothing
D. everything
解析:
此题容易误选A,机械地认为:something用于肯定句,anything用于否定句或疑问句。但是,此题的最佳答案是B,something在此的意思不是“某种东西”,而是指“那种东西”或“这种东西”,即心中最想要的那种东西(相当于the thing)。
形容词的概念:
形容词(adjective),简称adj.或a,形容词用来修饰名词或代词,表示人或事物的性质、状态,和特征的程度好坏与否,形容词在句中作定语、表语、宾语补足语。通常,可将形容词分成性质形容词和叙述形容词两类,其位置不一定都放在名词前面。
形容词的作用与位置:
形容词是用来修饰名词的,常被放在名词前作定语,或放在系动词后面作表语。以下属几种特殊情况,须牢记;
(1)形容词短语作定语,定语后置。
如:a language difficult to master,
a leaning tower about 180 feet high
(2)表语形容词(afraid、alike、alone、asleep、awake、alive等)作定语,定语后置。如a man alive。有些表身体健康状况的形容词如well、faint、ill只作表语。sick既可作表语又可作定语,ill如作定语意为“bad”。
(3)用作定语,修饰由不定代词one、no、any、some和every构成的复合词如anything、something等时,通常后置。
如:I have something important to tell you.
(4)else常用作疑问代词和不定代词的后置定语。
(5)enough、nearby修饰名词前置或后置,程度副词一般位于形容词、副词前面,enough修饰形容词、副词时,必须后置。
(6)几个并列的形容词作定语,其语序通常为:限定语(The、A)+描绘性形容词+size(大小)+shape(形状)+age(年龄、时间)+color(颜色)+origin(国籍、来源)+material(材料)+purpose(目的)+名词。
口诀:
限定描绘大长高,形状年龄和新老;颜色国籍跟材料,作用类别往后靠。
如:a heavy black Chinese steel umbrella,
the man's first tow interesting little red French oil paintings
形容词的用法:
1、形容词修饰名词,说明事物或人的性质或特征。通常,可将形容词分成性质形容词和叙述形容词两类,其位置不一定都放在名词前面:
1)直接说明事物的性质或特征的形容词是性质形容词,它有级的变化,可以用程度副词修饰,在句中可作定语、表语和补语。例如:hot热的。
2)叙述形容词只能作表语,所以又称为表语形容词。这类形容词没有级的变化,也不可用程度副词修饰。
大多数以a开头的形容词都属于这一类。例如:
afraid害怕的。(错)Heisanillman. (对)Themanisill. (错)Sheisanafraidgirl. (对)Thegirlisafraid.
这类词还有:well,unwell,ill,faint,afraid,alike,alive,alone,asleep,awake等。
3)形容词作定语修饰名词时,要放在名词的前边。但是如果形容词修饰以-thing为字尾的词语时,要放在这些词之后。例如:somethingnice
2、用形容词表示类别和整体:
1)某些形容词加上定冠词可以泛指一类人,与谓语动词的复数连接。如:the dead,the living,the rich,the poor,the blind,the hungry The poorarelosinghope.穷人失去了希望。
2)有关国家和民族的形容词加上定冠词指这个民族的整体,与动词的复数连用。如:the British,the English,the French,the Chinese. The English have wonderful senseofhumor.
以-ly结尾的形容词:
1)大部分形容词加-ly可构成副词。但friendly,deadly,lovely,lonely,likely,lively,ugly,brotherly,仍为形容词。改错:
如:(错)She sang lovely.
(错)He spoke to me very friendly.
(对)Her singing was lovely.
(对)He spoke to me in a very friendly way.
2)有些以-ly结尾既为形容词,也为副词。 daily,weekly,monthly,yearly,early .
如:The Times is a daily paper.
The Times is published daily.
形容词知识体系:
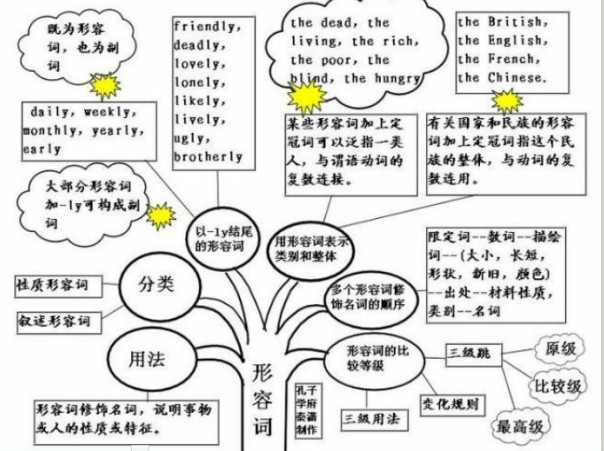
复合形容词的构成:
(1)形容词+名词+ed:
如:kind-hearted 好心的,white-haired 白发的
(2)形容词+形容词:
如:red-hot 炽热的,dark-blue 深蓝的
(3)形容词+现在分词:
如:good-looking 好看的,easy-going 随和的
(4)副词+现在分词:
如:hard-working 勤劳的,fast-moving 快速转动的
(5)副词+过去分词:
如:hard-won 得来不易的,newly-made 新建的
(6)名词+形容词:
如:life-long 终生的,world-famous 世界闻名的
(7)名词+现在分词:
如:peace-loving 爱好和平的,fun-loving 爱开玩笑的
(8)名词+过去分词:
如:snow-covered 白雪覆盖的,hand-made 手工的
(9)数词+名词+ed:
如:four-storeyed 4层楼的,three-legged 3条腿的
(10)数词+名词(名词用单数):
如:ten-year 10年的, two-man 两人的
副词的概念:
副词是指在句子中表示行为或状态特征的词,用来修饰动词、形容词、其他副词、介词短语、非谓语动词乃至整个句子,表示时间、地点、程度、方式等概念。
副词的位置:
1)在动词之前。
2)在be动词、助动词之后。
3)多个助动词时,副词一般放在第一个助动词后。
注意:
a. 大多数方式副词位于句尾,但宾语过长,副词可以提前,以使句子平衡。
如:We could see very clearly a strange light ahead of us.
b. 方式副词well,badly糟、坏,hard等只放在句尾。
如:He speaks English well.
副词的排列顺序:
1)时间,地点副词,小单位的在前,大单位在后。
2)方式副词,短的在前,长的在后,并用and或but等连词连接。
如:Please write slowly and carefully.
3)多个不同副词排列:程度+地点+方式+时间副词。
注意:副词very可以修饰形容词,但不能修饰动词。
改错:(错)I very like English.
(对)I like English very much.
注意:副词enough要放在形容词的后面,形容词enough放在名词前后都可。
如:I don't know him well enough.
There is enough food for everyone to eat.
There is food enough for everyone to eat.
兼有两种形式的副词:
1)close与closely:
close意思是“近”;closely意思是“仔细地”。
如: He is sitting close to me.
Watch him closely.
2)late与lately:
late意思是"晚";lately意思是“最近” 。
如:You have come too late.
What have you been doing lately?
3)deep与deeply:
deep意思是“深”,表示空间深度;deeply时常表示感情上的深度,“深深地” 。
如:He pushed the stick deep into the mud.
Even father was deeply moved by the film.
4)high与highly:
high表示空间高度;highly表示程度,相当于much。
如:The plane was flying high.
I think highly of your opinion.
5)wide与widely:
wide表示空间宽度;widely意思是“广泛地”,“在许多地方”。
如:He opened the door wide.
English is widely used in the world.
6)free与freely:
free的意思是“免费”;freely的意思是“无限制地”。
如:You can eat free in my restaurant whenever you like.
You may speak freely, say what you like.
副词知识体系:
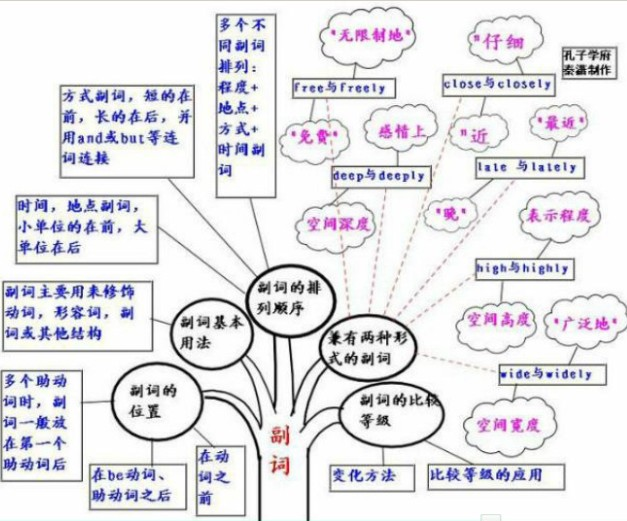
介词和介词短语的概念:
介词是一种用来表示词与词、词与句之间的关系的虚词,在句中不能单独作句子成分。介词后面一般有名词、代词或相当于名词的其他词类,短语或从句作它的宾语。介词和它的宾语构成介词词组,在句中作状语,表语,补语或介词宾语。介词可以分为时间介词、地点介词、方式介词和其他介词。
误用介词的三种情况:
1、多用介词:
多用介词可能是受汉语意思的影响将及物动词误用作不及物动词,也可能是受相关结构的影响而用错:
误:We discussed about the plan.
正:We discussed the plan. 我们讨论了计划。
误:Did he mention about the accident?
正:Did he mention the accident? 他提到那次事故了吗?
误:I saw her enter into the bank.
正:I saw her enter the bank. 我看见她进了银行。
误:He married with[to] a nurse.
正:He married a nurse. 他同一位护士结了婚。
误:How can contact with you?
正:How can contact you? 我怎么与你联系?
误:We should serve for the people heart and soul.
正:We should serve the people heart and soul. 我们应该全心全意地为人民服务。
误:Who controls over the factory? (但名词control可接over)
正:Who controls the factory? 谁管理这个工厂?
误:He has a great many of friends here. (比较a great number of)
正:He has a great many friends here. 他在这儿有很多朋友。
2、漏用介词:
漏用介词可能是受汉语意思的影响将不及物动词误用作及物动词,或是受相关结构的影响的影响而用错等:
误:This matter is difficult to deal. (deal with=处理)
正:This matter is difficult to deal with. 这事很难处理。
误:He is not a man to be depended.
正:He is not a man to be depended on. 他不是个可靠的人。
误:He took a cup of tea, and went on the story.
正:He took a cup of tea, and wentonwiththestory.他喝了一口茶,又接着讲故事。
误:My mother still regards me a child. (比较consider…as中的as可省略)
正:My mother still regards me as a child. 我母亲还把我当小孩看。
误:They insisted sending a car over to fetch us.
正:They insisted on sending a car over to fetch us.他们坚持要派车来接我们。
误:What he says is worth listening.
正:What he said is worth listening to.他的话值得一听。
3、错用介词:
错用介词的情况比较复杂,可能是因受汉语意思的而错,也可能是因弄不清搭配关系而错,可能是混淆用法而错,也可能是受相关结构的影响而错,可能是忽略语境而错,也可能是想当然的用错:
误:She called on his office yesterday. (call on+人,call at+地点)
正:She called at his office yesterday. 她昨天去了他办公室拜访。
误:He is engaged with a nurse.
正:He is engaged to a nurse.他与一位护士订了婚。
误:The sun rises from the east.
正:The sun rises in the east.太阳从东方升起。
误:Under his help, I finished it in time.
正:With his help, I finished it in time. 在他的帮助下,我及时做完了。
误:During he was in Japan, he visited many places.
正:During his stay in Japan, he visited many places.他在日本期间,参观过许多地方。
误:We are familiar to his character.
正:We are familiar with his character.我们了解他的性格。
误:Help yourself with the fruit.
正:Help yourself to the fruit.吃点水果吧。
介词的宾语:
1、名词或代词作介词宾语:
如:Are you interested in history? 你对历史感兴趣吗?
Don't worry about it. 别为它担心。
注:若是人称代词用作介词宾语,要注意用宾格。
如:No one can sing like her. 没有人能像她那样唱歌。(不能用like she)
2、动名词作介词宾语:
如:He is good at telling stories. 他善于讲故事。
In crossing the street he was run over. 他在穿过马路时被汽车撞倒。
3、过去分词作介词宾语:
如:We can't regard the matter as settled. 我们不能认为这事已经解决。
I take it for granted you have read the book. 我以为你读过这本书。
注:过去分词用作介词宾语通常只见于某些固定结构中,如上面第1句涉及regard…as(认为…是)结构,第2句涉及take sth for granted(认为某事属实)。在其他情况下,介词后通常不直接跟过去分词作宾语,若语义上需要接过去分词(表被动),可换用“being+过去分词”:
如:He went out without being seen by the others.他出去了,没有被其他人看见。
4、从句作介词宾语:
如:He was not satisfied with what she said. 他对她说的不满意。
I'm worried about where he is. 我担心他上哪儿去了。
注:介词后通常不接that从句,遇此情况需考虑用其他结构:
误:He paid no attention to that she was poor.
正:He paid no attention to the fact that she was poor. 他根本不注意她很穷这一事实。
但有个别介词(如except)可接that从句。
比较:I know nothing about him except that he lives next door./I know nothing about him except for the fact that he lives next door. 我只知道他住在隔壁,其它的就不知道了。
5、不定式作介词宾语:
如:I had no choice but to wait. 除了等,我没有别的选择。
He wanted nothing but to stay there. 他只想留在那儿。
They did nothing but complain. 他们老是一个劲地抱怨。
He never did anything but watch TV. 除了看电视,他从不干任何事。
注:(1)介词后接不定式的情形通常只见于but, except等极个别个词。该不定式有时带to,有时不带to,其区别是:若其前出现了动词do,其后的不定式通常不带to;
若其前没有出现动词do,则其后的不定式通常带to。
(2)介词后虽然通常不直接跟不定式作宾语,但却可接“连接代词(副词)+不定式”结构:
如:He gave me some advice on how to do it. 对于如何做这事他给我提了些建议。
6、形容词作介词宾语:
如:Her pronunciation is far from perfect. 她的语音远不是完美的。
In short, we must be prepared. 总而言之,我们要有准备。
Things have gone from bad to worse. 事情越来越糟。
注:(1)有些形容词用作介词宾语可视为其前省略了动名词being:
如:He regarded the situationas(being) serious. 他认为形势严重。
His work is far from(being) satisfactory. 他的工作丝毫不令人满意。
(2)有些“介词+形容词”的结构已构成固定搭配:in full全部地,全面地,无省略地; in private私下地,秘密地; in particular特别地;in general一般地,通常地,概括地; in brief 简言之;in short总之,简言之; in vain徒然地,徒劳无益地;for fee免费地,无偿地; for certain肯定地,确切地;for sure肯定地,确切地; for short为了简短,简称;atl arge自由自在地,逍遥法外; by far…得多
7、副词作介词宾语:
如:I can't stay for long. 我不能久呆。
It's too hot in here. 这里面太热了。
I looked every where except there. 除了那儿,我到处都看过了。
8、数词作介词宾语:
如:The city has a population of four million. 这座城市有四百万人口。
He was among the first to arrive. 他是第一批到的。
9、介词短语作介词宾语:
如:Choose a book from among these. 从这些书中选一本吧。
I saw her from across the street. 我从街的对面望见了她。
注:通常可后接介词短语作宾语的介词是from, till, until, since, except, instead of等。
比较:I took it from the bed. 我从床那儿(或床上)拿的。
I took it from under the bed. 我从床下拿的。
10、复合结构用作介词宾语:
如:She had no objection to Mary marrying him. 她不反对玛丽与他结婚。
She came in with a book in her hand. 她手里拿着一本书走了进来。
All the afternoon he worked with the door locked. 整个下午他都锁着门在房里工作。
介词短语的句法功能:
1、表语:
如:He was with a friend. 他和一个朋友在一起。
Health is above wealth. 健康胜过财富。
This knife is for cutting bread. 这把小刀是用于切面包的。
注:有些介词(如because of)引出的短语通常只用作状语,不用作表语:
误:His absence is because of the rain.
正:His absence is due to the rain. 他因雨未来。
但是,若主语是代词(不是名词),becauseof引出的短语可用作表语:
如:It is because of hard work. 那是因为辛苦工作的原因。
2、状语:
如:Don't touch it with your hands. 别用手去摸它。
Did you do this by design or by accident? 你这样做是有意的还是无意的?
3、定语:
如:This is his reply to your letter. 这是他给你的回信。
This is the best way of doing it. 这是做此事最好的方法。
My love for you is deeper than the sea. 我对你的爱比海深。
4、宾语补足语:
如:I found everythingin good condition. 我发现一切正常。
Her illness kept her in bed for a week. 她因生病在床上躺了一星期。
注:用作宾语补足语的介词短语在相应的被动语态中则为主语补足语:
如:He was regarded as a hero. 他被看成是英雄。
5、宾语:
如:A man stepped out from behind the wall. 一个人从墙后走出来。
He cannot spare anytime except on Sunday. 除星期日外,他抽不出时间。
6、主语:
如:Between6 and 7 suits me. 六点到七点对我比较适合。
After the exams is the time to relax. 考试后是轻松一下的时间。
注:介词短语通常不用作主语,尽管有时也像上面这样用作主语,但通常可视为是在一定的上下文中有所省略:
如:—When are we going to have the next meeting? 我们下次什么时候见面?
—On Tuesday may be convenient. 星期二可能比较方便。
此句中onTuesday虽用作主语,但可视为是其前省略了meeting一词:
即:Meeting during the vacation may be convenient.
并列连词的概念:
连词是一种虚词,它不能独立担任句子成分而只起连接词与词,短语与短语以及句与句的作用。连词主要可分为两类:并列连词和从属连词。并列连词用来连接平行的词、词组和分句。如:and, but, or, nor, so, therefore, yet, however, for, hence, as well as, both...and, notonly...butalso, either...or, neither...nor, (and)then 等等。
并列连词与并列结构:
并列连词引导两个并列的句子。
1)and与or:
判断改错:
(错) They sat down and talk about something.
(错) They started to dance and sang.
(错) I saw two men sitting behind and whisper there.
(对) They sat down and talked about something.
(对) They started to dance and sing.
(对) I saw two men sitting behind and whispering there.
解析:第一句:and连接两个并列的谓语,所以talk应改为talked。
第二句:and连接两个并列的动词不定式,第二个不定式往往省略to,因此sang应改为sing。
第三句:and连接感观动词saw后面的用作的宾补的两个并列分词结构,因此whisper应改为whispering。
注意:and还可以和祈使句或名词词组连用表示条件。(or也有此用法)
如:Make up your mind, and you'll get the chance.=If you make up your mind, you'll get the chance.
One more effort, and you'll succeed.=If you make one more effort, you'll succeed.
2)both...and 两者都
如:She plays(both) the piano and the guitar.
3)not only...but(also), as well as 不但…而且
如:She plays not only the piano, but(also) the guitar.
注意:not only…but also关联两个分句时,一个分句因有否定词not而必须倒装。
如:Not only does he like reading stories, but also he can even write some.
4)neither...nor 意思为“既不……也不……”谓语动词采用就近原则,与nor后的词保持一致。
如:Neither you nor he is to blame.
比较so和such :
so与such的用法由不同词性决定。such是形容词,修饰名词或名词词组,so是副词,只能修饰形容词或副词。so还可与表示数量的形容词many,few,much,little连用,形成固定搭配。
构成:so+adj.
such+a(n)+n.
so+adj.+a(n)+n.
such+n.(pl.)
so+adj.+n.(pl.)
such+n.(pl.)
so+adj.+n.[不可数]
such+n.[不可数]
如:so foolish
such a fool
so nice a flower
such a nice flower
so many/few flowers
such nice flowers
so much/ little money.
such rapid progress
so many people
such a lot of people
注:so many 已成固定搭配,a lot of 虽相当于many,但a lot of为名词性的,只能用such搭配。 so...that与such...that之间的转换既为so与such之间的转换。
并列连词用法点拨:
1、表示并列关系:
1)or意思为“否则”。
如:I must work hard, or I'll fail in the exam.
2)either...or意思为“或者……或者……”。注意谓语动词采用就近原则。
如:Either you or I am right.
2、表示转折或对比关系:
1)but表示转折,while表示对比。
如:Some people love cats, while others hate them.
典型例题:
—Would you like to come to dinner tonight?
—I'd like to, ___ I'm too busy.
A. and
B. so
C. as
D. but
答案:D。but与前面形成转折,符合语意。而表并列的and,结果的so,原因的as都不符合句意。
2)not...but...意思为“不是……而是……” not和but后面的用词要遵循一致原则。
如:They were not the bones of an animal, but(the bones) of a human being.
3、表示原因关系:
1)for 判断改错:
(错)For he is ill, he is absent today.
(对)He is absent today, for he is ill. for是并列连词,不能置于含两个并列分句的句子的句首,只能将其放在两个分句中间。
并列连词知识体系:
| 种类 | 用法 | 举例 |
| 并列连词 | 表示转折关系 | yet, but等 |
| 表示并列关系 | and, or, either...or..., as welll as等 | |
| 表示因果关系 | for, so等 |
比较and和or的用法:
1)并列结构中,or通常用于否定句,and用于肯定句。
2)但有时and也可用于否定句。请注意其不同特点:
如:There is no air or water in the moon.
There is no air and no water on the moon.
在否定中并列结构用or连接,但含有两个否定词的句子实际被看作是肯定结构,因此要用and。
典型例题:
—I don't like chicken___fish.
—I don't like chicken, ___I like fish very much.
A. and;and
B. and;but
C. or;but
D. or;and
答案:C。否定句中表并列用or,but表转折。
判断改错:
(错)We will die without air and water.
(错)We can't live without air or water.
(对)We will die without air or water.
(对)We can't live without air and water.
系动词的概念:
连系动词(link verb)是一个表示谓语关系的动词。它必须后接表语(通常为名词或形容词)。连系动词的功能主要是把表语(名词、形容词、某些副词、非谓词、介词短语、从句)和它的主语联系在一起,说明主语的属性、特征或状态。它有自己的但不完全的词义,不能在句中独立作谓语,必须和后面的表语一起构成句子的谓语。它是虚词。
系动词的分类:
1、状态系动词:
用来表示主语状态,只有be一词。
例如:He is a teacher. 他是一名教师。(is与补足语一起说明主语的身份。)
2、持续系动词用来表示主语继续或保持一种状况或态度,主要有keep, rest, remain, stay, lie, stand:
例如:The weather will continue cold and wet.
He remained poor after 20years.
The shop will stay open at 11:00p.m.
He stood/sat silent there.
3、表像系动词:
用来表示"看起来像"这一概念,主要有seem, appear, look。
例如:She appears to have know this thing.
She seems a student.
4、感官系动词:
感官系动词主要有feel, smell, sound, taste。
例如:The silk feels soft.
Your idea sounds a good one.
He looked like his mother.
The mixture tasted terrible.
The flower smells sweet.
5、变化系动词:
这些系动词表示主语变成什么样,变化系动词主要有become, grow, turn, fall, get, go, come, run。
例如:My dream o fcoming to China has come true.
In summer food often goes bad.
He turned doctor./ He became a doctor.
He fell asleep as soon as he went to bed.
6、终止系动词表示主语已终止动作,主要有prove, turn out,表达"证实","变成"之意。
例如:The truth he stuck to proved true.
系动词基本用法:
连系动词是表示不完全谓语关系的动词,它与其后的表语一起构成谓语。
常见的连系动词有be(是),become(成为),get(变成),remain(还是),seem(似乎是),look(看上去),feel(感觉)等。
连系动词后的表语通常是名词和形容词,有时也可以是代词、数词、副词、介词短语、不定式、动名词、从句等:
如:His English is excellent. 他的英语很棒。(跟形容词)
He is a famous poet. 他是著名诗人。(跟名词)
Money isn't everything. 金钱不是一切。(跟代词)
She was the first to arrive. 她是第一个到达的人。(跟数词)
Who is up stairs? 谁在楼上?(跟副词)
He is with his friends. 他和朋友在一起。(跟介词短语)
He seems to be ill.他似乎病了。(跟不定式)
Seeing is believing. 眼见为实。(跟动名词)
This is what you need. 这就是你需要的。(跟从句)
注:有些系动词又是实义动词,该动词表达实义时,有词义,可单独作谓语。
例如:1、She tasted①the soup to see if it tasted②too salty. 她尝了一口汤,看是否太咸。
2、The doctor is feeling①his pulse because he feels②sick. 因为身体不舒服,医生正在给他切脉。
3、The mother looked①at the sick child sadly and she looked②sad. 母亲难过地看着生病的孩子。
4、She smelled①the meat to make sure it still smelled②good. 她闻了闻肉,看看是否还新鲜。
5、The teacher asked the students to keep②quite when they were keeping①everything in order. 当学生整理东西时,老师让他们保持安静。
从以例子不难出,标①的动词为实义动词,他们后跟有宾语;标②的动词为系动词,其后往往跟形容词、名词、不定式等作表语。
系动词知识体系:
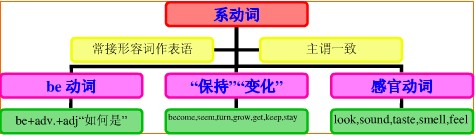
连系动词使用应注意的两点:
1、关于连系动词后接副词作表语:
连系动词后通常可接形容词作表语,一般不接副词:
误:His English is very well. 他的英语很好。(应将well改为good)
误:Be carefully. 小心点。(应将carefully改为careful)
误:The soup tastes nicely. 这汤味道不错。(应将nicely改为nice)
但是,有时连系动词后也可接副词作表语,不过这主要限于in, on, off, out, away, behind, up, down, over, through, around, round, below, inside, outside等少数副词小品词以及here, there, upstairs, downstairs等少数表示地点或方位的副词:
如:Mother wasn't in last night. 母亲昨晚不在家。
The meeting was over at five. 会议五点结束。
Come along. The taxi is outside. 来吧,出租车在外面。
Mother is downstairs waiting for you. 母亲在楼下等你。
2、关于连系动词后接不定式:
(1)连系动词be后根据情况可自由地接不定式作表语:
如:My dream is to be a scientist. 我的梦想是当一名科学家。
All I could do was to wait. 我只能等。
My plan was to go from London to Paris. 我计划从伦敦去巴黎。
I was to have seen Mr Kay. 我本要去见凯先生的。
(2)seem, appear, prove, continue, turn out, get, grow, come等连系动词后也可接不定式(尤其是to be)作表语:
如:She always seems to be sad. 她常常显得很忧伤。
My advice proved to be wrong. 我的意见证明是错的。
She appears to have many friends. 他好像有很多朋友。
The weather turned out to be fine. 天气结果很好。
Circumstances continue to be favorable. 情况仍然是有利的。
He has grown to like studying English. 他渐渐喜欢学英语了。
【注】
若所接不定式为to be,通常可以省略。不过,若其后接的是表语形容词,则to be通常不宜省略。
另外,连系动词look后能否接tobe似乎尚有争论,不过,在现代英语中接to be的现象已较普遍。
(3)sound, smell, feel, taste, become等连系动词后通常不能接不定式:
误:These oranges taste to be good. (应去掉to be)
误:The roses smell to be nice.(应去掉to be)
(4)有的连系动词后接的从句可用不定式来改写:
如:It seems that she's right./ She seems to be right. 她似乎是对的。
It appears that you have made a mistake./You appear to have made a mistake. 似乎你弄错了。
情态动词的概念:
情态动词表示说话人对某一动作或状态的态度。
几组词的辨析:
1、need和dare的用法:
need和dare既可用作情态动词,也可用作实义动词。用作情态动词时,主要用于否定句和疑问句。用作实义动词时,可用于各种句式。
(1)用作情态动词:
如:—Need I come? 我需要来吗?
—Yes, you must. 需要。
You needn′t telephone him now. 你现在不必打电话给他。
I don′t think you need worry. 我想你不必发愁。
She dare not go out alone at night. 她晚上不敢一个人出去。
How dare you say I′m unfair? 你竟敢说我不公平?
Not one of them dared mention this.他们谁也不敢提这件事。
(2)用作实义动词:
如:You don′t need to do it yourself. 你不必亲自做这件事。
We need to tell them the news. 我们需要把这消息告诉他们。
The table needs painting(to be painted.). 桌子需要油漆一下。
We should dare to give our own opinion.我们要敢于提出自己的观点。
He did not dare(to) look up. 他不敢抬头看。
I dare day he′ll come again. 我想他会再来的。
2、can和be able to:
(1)情态动词can只有两种时态形式,现在式can和过去式could,而be able to有多种时态形式。
如:Mary can play the piano. She has been able to play it since she was 5. 玛丽会弹钢琴。她五岁起就会弹了。
(2)用在过去时中,could经常表示能够做某事,事实上不一定去做,而was∕were able to则表示“过去做成了某事”。在否定句中两者可通用。
如:He could swim across the English Channel. But he didn′t feel like it that day.
他能游过英吉利海峡,但那天他不想游。
Yesterday I was able to get home before the heavy rain. 昨天我在下大雨前赶到了家里。
3、must和have to:
must表示主观意志,而have to表示由于客观因素不得不做某事。must没有过去式,除在间接引语中可用于表示过去时间,在直接引语中表示过去时间应该用had to代替。
如:I told her that she must give up smoking. 我叫她必须戒烟。
We had to get everything ready that night. 我们那晚得把一切准备就绪。
4、would和used to:
(1)usedto表示过去与现在或过去某时与后来的情况有不同,而would只表过去的情况。
如:People used to think that the earth was flat. 过去人们认为地球是平的。(现在人们不这么认为。)
She would go out for a walk in the morning when she was in the country.
在乡下时,她总是在早晨去散会儿步。(可能现在仍有散步的习惯。)
(2)used to可表示过去的习惯动作和经常的情况,而would只表示过去的习惯动作。
如:He used to∕would smoke while writing. 过去他写东西时常抽烟。
She used to be fat. 她过去很胖。
情态动词的基本用法:
1、can(could):
1)表示能力,could主要指过去时间。
如:Two eyes can see more than one. 两只眼比一只眼看得清。
Could the girl read before she went to school? 这女孩上学前能识字吗?
2)表示可能(理论上或是逻辑判断上)。
如:The temperature can fall to–60℃, that is 60℃ below freezing. 气温可降至-60℃,也就是零下60℃。
He can′t(couldn′t) have enough money for a new car. 他不可能有足够的钱买新车。
You mustn′t smoke while you′re walking around in the wood. You could start a fire.
在林子里走时勿吸烟,那样可能会引起火灾。
3)表示允许。
如:Can I have a look at your new pen? 我可以看一看你的新钢笔吗?
He asked whether he could take the book out of the reading-room. 他问他可不可以把书带出阅览室。
4)表惊异、怀疑、不相信等态度。主要用于否定句、疑问句或感叹句中。
如:Where can(could) they have gone to? 他们会去哪儿了呢?
He can′t(couldn′t) be over sixty. 他不可能超过六十岁。
How can you be so careless? 你怎么这么粗心?
5)比较委婉客气地提出问题或陈述看法。
如:Can(Could) you lend me a hand? 帮我一把好吗?
I′m afraid we couldn′t give you an answer today. 恐怕我们今天不能给你答复。
2、may(might):
1)表允许,might可以指过去时间,也可指现在时间,语气更委婉。
如:You may take what ever you like. 你喜欢什么就拿什么。
He told me that I might smoke in the room. 他告诉我可以在房间里抽烟。
May(Might) I ask for a photo of your baby? 我可以要一张你宝宝的照片吗?
在回答以may引起的问句时,多避免用这个词,而用其它方式:
如:Yes, please./Certainly. /Please don′t./You′d better not./No, you mustn′t.等,以免显得太严峻或不客气。
2)表可能(事实上)。可以指过去时间,也可以指现在时间,但语气更加不肯定。
如:He may be at home. 他可能在家。
She may not know about it. 她可能不知道这件事。
He was afraid they might not agree with him. 他担心他们可能不同意他的意见。
如:They might be having a meeting, but I′m not sure. 他们有可能在开会,不过我不肯定。
3、must:
1)表示义务。意为“必须”(主观意志)。
如:We must do everything step by step. 我们一切都必须循序渐进地做。
You mustn′t talk to her like that. 你不可能那样对她说话。
—Must we hand in our exercise-books now? 我们现在就要交练习本吗?
—No, you needn′t./No, you don′t have to.不必。(这种情况下,一般不用mustn′t)
2)表示揣测。意为“想必、准是、一定”等,只用于肯定句。
如:He must be ill. He looks so pale. 他准是病了。他的脸色苍白。
如:She′s wearing a diamond necklace. She must have a lot o fmoney. 她戴着钻石项链,一定很有钱。
4、shall:
1)表征询意见,用于第一、第三人称疑问句。
如:Shall I get you some tea? 我给你点茶好吗?
Shall the boy wait outside? 让那男孩在外面等吗?
What shall we do this evening? 我们今晚做什么?
2)表说话人的意愿,有“命令、允诺、警告、决心”等意思,用于第二、第三人称陈述句。
如:You shall do as I say. 按我说的做。(命令)
You shall have my answer tomorrow. 你明天可以得到我的答复。(允诺)
He shall be sorry for it one day, I tell you.有一天他会后悔的,我告诉你。(警告)
如:Nothing shall stop us from carrying out the plan.什么也不能阻止我们执行这项计划。(决心)
5、will:
1)表意愿,用于各种人称陈述句。
如:I will do anything for you. 我愿为你做任何事。
None is so blind as those who won′t see. 不愿看的人眼最瞎。
If you will read the book, I′ll lend it to you. 如果你愿意读这本书,我会把它借给你。
2)表请求,用于疑问句。
如:Will you close the window? It′s a bit cold. 请你把窗户关上好吗?有点冷。
Won′t you drink some more coffee? 再来一点咖啡好吗?
3)表示某种倾向或习惯性动作。
如:Fish will die out of water. 鱼离开水就不能活。
The door won′t open. 这门打不开。
The boy will sit there hour after hour looking at the traffic go by.
那男孩常常坐在那里好几个钟点,看着车辆行人通过。
6、should:
1)表义务。意为“应该”(某件事宜于做),用于各种人称。
如:You should be polite to your teachers. 你对老师应该有礼貌。
You shouldn′t waste anytime. 你不应该浪费时间。
2)表推测,意为“想必一定、照说应该、估计”等。
如:The film should be very good as it is starring first-class actors. 这部新电影是一流演员主演的,估计拍得很好。
They should be home by now. 照说他们现在应当已经到家了。
7、would:
1)表意愿。
如:They would not let him in because he was poorly dressed. 他们不让他进去因为他衣着破旧。
I said I would do anything for you. 我说过我愿意为你做任何事。
2)表委婉地提出请求、建议或看法。
如:Would you like another glass of beer? 再来杯啤酒好吗?
Would you mind cleaning the window? 请把窗户擦一下好吗?
They wouldn′t have anything against it. 他们不会有什么反对意见。
3)表过去反复发生的动作或过去的一种倾向。
如:Every time she was in trouble, she would go to him for help. 她每遇到麻烦都会向她求助。
8、ought to:
1)表义务,意为“应该”(因责任、义务等该做),口气比should稍重。
如:You are his father. You ought to take care of him. 你是他父亲,应当管他。
You oughtn′t to smoke so much. 你不应该抽这么多烟。
2)表推测,暗含很大的可能,语气较弱。
如:Han Mei ought to know his telephone number. 韩梅该知道他的电话号码。
There′s a fine sun set; it ought to be a fine day tomorrow. 今天有晚霞,明天应该是个好天。
9、used to:
表示过去的习惯动作或状态,现在不复发生或存在。疑问式和否定式有两种。
如:He used to live in the countryside, but now he lives in the city. 他过去住在乡下,现在住在城里。
There used to be a building at the street corner, but it has been pulled down. 街道拐角处过去有座楼房,现在拆了。
I usedn′t (didn′t use) to smoke. 我过去不抽烟。
Used you(Did you use) to go to school on foot? 你过去常步行去学校吗?
情态动词的其他用法:
首先它是动词,而且不同于行为动词,行为动词表示的是可以通过行为来表达的动作(如写,读,跑),而情态动词只是表达的一种想法(如能,也许,敢)。
用法是:情态动词+行为动词原形:
句:I can read this sentence in English. 我能用英语读这句话。
情态动词是一种本身有一定的词义,表示说话人的情绪,态度或语气的动词,但不能单独作谓语,只能和其他动词原形构成谓语。
如:We can be there on time tomorrow. 我们明天能按时去那儿。
May I have your name? 我能知道你的名字吗?
Shall we begin now? 我们现在就开始吗?
You must obey the school rules. 你必须遵守校规。
情态动词知识体系:

情态动词表推测的三种句式:
1、在肯定句中一般用must(一定),may(可能),might/could(也许,或许)。
如:He must/may/might know the answer to this question? 他一定/可能/也许知道这个问题的答案。
It is cold in the room. They must have turned off the heating. 屋里很冷,他们肯定把暖气关了。
2、否定句中用can't/couldn't (不可能), may not/might not(可能不)。
如:It can't/couldn't be the headmaster. He has gone to America. 这不可能是校长,他去美国了
He may not/might not know the scientist. 他也许不认识那位科学家。
3、疑问句中用can/could(能……?)。
如:Could he have finished the task? 他可能把任务完成了吗?
Can he be at home now? 他现在能在家吗?
注:以上三种句式中情态动词的语气按程度都是依次递减的。Might, could并非may, can的过去式,而表示语气较为委婉或可能性较小。
情态动词表推测的三种时态:
1、对将来情况的推测,用“情态动词+动词原形”。
如:She must/may/might/could arrive before 5. 5:00前她一定/可能/也许到。
She must/may/might/could walk miles and miles among the hills without meeting anyone.
她一定/可能/也许会在山里一连走好几英里而遇不到一个人。
2、对现在或一般情况的推测,用“情态动词+be”,“情态动词+bedoing”或“情态动词+动词原形”。
如:He must/may/might/could be listening to the radio now. 他一定/可能/也许正在听收音机。
He can't(couldn't)/may(might) not be at home at this time. 这个时候他不可能/可能不在家。
Mr. Bush is on time for everything. How can(could) he be late for the opening ceremony?
布什先生一向准时,这次开幕式他怎么可能迟到呢?
3、对过去情况的推测,用“情态动词+have+过去分词”。
如:It must/may/might/ could have rained last night. The ground is wet. 地湿了,昨晚肯定/可能/也许下雨了。
The door was locked. He can(could) not/may(might) not have been at home. 门锁着,他不可能/可能不在家。
Can/Could he have gotten the book?难道他找到书了吗?
注:情态动词should/ought to表推测时,意为“想必会,理应……”但与“have+过去分词”连用时,则又可构成虚拟语气意为“本应该做某事却没做”。
如:It's seven o'clock. Jack should/ought to be here at any moment.
现在七点钟了,杰克理应随时到达。(推测)
She should/ought to have attended your birthday party, but she had to look after her mother in hospital.(虚拟)
她本该出席你的生日晚会的,可是她得在医院照顾她妈妈。
Tom should not/ought not to have told me your secret, but he meant no harm.(虚拟)
汤姆本不该告诉我你的秘密,可是他并无恶意。
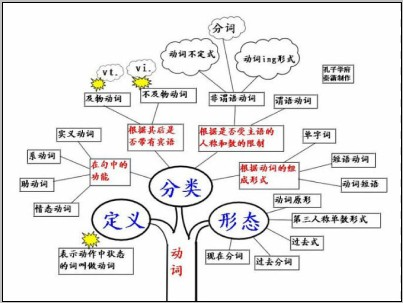
动词的定义:
表示动作中状态的词叫做动词。根据其在句中的功能,动词可分为行为动词、系动词、助动词和情态动词四类,有些动词是兼类词。
例如:We have lunch at 12. (have是行为动词)
We have been to NewYork. (have是助动词)
I am hungry. (am是系动词)
You need not have waited for me. (need是情态动词)
The door needs painting. (need是兼类词)
动词的分类:
1)表示动作中状态的词叫做动词。
2)根据其在句中的功能,动词可分为四类,分别是:
实义动词(Notional Verb)、系动词(Link Verb)、助动词(Auxiliary Verb)、情态动词(Modal Verb)。
说明:有些情况下,有些动词是兼类词。
例如:We are having a meeting. 我们正在开会。(having是实义动词。)
He has gone to NewYork.他已去纽约。(has是助动词。)
3)动词根据其后是否带有宾语,可分为两类,分别是:
及物动词(Transitive Verb)、不及物动词(Intransitive Verb),缩写形式分别为vt.和vi.。
说明:同一动词有时可用作及物动词,有时可用作不及物动词。
例如:She can dance and sing. 她能唱歌又能跳舞。(sing在此用作不及物动词。)
She can sing many English songs. 她能唱好多首英文歌曲。(sing用作及物动词。)
4)根据是否受主语的人称和数的限制,可分两类,分别是:
限定动词(Finite Verb)、非限定动词(Non-finite Verb)。
例如:She sings very well. 她唱得很好。(sing受主语she的限制,故用第三人称单数形式sings。)
She wants to learn English well. 她想学好英语。(to learn不受主语she的限制,没有词形变化,是非限定动词。
说明:英语中共有三种非限定动词,分别是:动词不定式(Infinitive)、动名词(Gerund)、分词(Participle)。
5)根据动词的组成形式,可分为三类,分别是:
单字词(One-Word Verb)、短语动词(Phrasal Verb)、动词短语(Verbal Phrase)
例如:The English language contains many phrasal verbs and verbal phrases. 英语里有许多短语动词和动词短语。(contains是单字动词。)
Students should learn to look up new words in dictionaries. 学生们学会查字典。(look up是短语动词。)
The young ought to take care of the old. 年轻人应照料老人。(takecareof是动词短语。)
6)动词有五种形态,分别是:
原形(OriginalForm)、第三人称单数形式(Singular From in Third Personal)、过去式(Past Form)、过去分词(Past Participle)、现在分词(Present Participle)。
动词知识体系:
一般过去时的概念:
一般过去时表示过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为;过去主语所具备的能力和性格。
一般过去时的用法:
1、表示过去发生的动作或存在的状态,常与表示过去时间的副词如:yesterday,last week,two hours ago等连用。
如:My family moved here five years ago. 我家五年前搬到了这里。
I was born in 1973. 我生于1973年。
2、表示过去一段时间经常或反复发生的动作。这时可与频度副词如:often,usually,always等连用。
如:He always worked in tonight those days. 那些日子他总是工作到深夜。
I often left on business in 1987. 1987年我经常出差。
注:表示“过去经常,而今不再”时,要用usedto.
如:I used to read newspaper after breakfast. 我过去经常早饭后看报纸。(意指现在已不是这样)
The children often swam in this river. 孩子们过去经常在这条河里游泳。
3、表示过去发生的一连串动作。
如:He put down the heavy box, took out the keys, and opened the door. 他放下这沉重的箱子,掏出钥匙开了房门。
注:过去发生的一连串动作,若用and,or,but等并列连词连接,则一律用过去式。
如:They moved the chairs to the table, sat down and began to have supper. 他们把椅子搬到桌边,坐下开始吃饭。
4、在时间和条件状语从句中,用一般过去时表示过去将来的动作。
如:He said that he would let me know as soon as he got the information. 他说他一得到消息就立即让我知道。
Mary told me that she would stay at home if it rained. 玛丽告诉我如果下雨她就呆在家里。
一般过去时的特别用法:
1、句型:It is time for sb. to do sth "到……时间了" "该……了"。
例如:It is time for you to go to bed.你该睡觉了。
It is time that sb.did sth. "时间已迟了" "早该……了"。
例如:It is time you went to bed. 你早该睡觉了。
2、would(had)rather sb.did sth. 表示'宁愿某人做某事'。
例如:I'd rather you came tomorrow. 还是明天来吧。
3、wish, wonder, think, hope等用过去时,作试探性的询问、请求、建议等,而一般过去时表示的动作或状态都已成为过去,现已不复存在。
例如:I thought you might have some. 我以为你想要一些。
比较:Christine was an invalid all her life.(含义:她已不在人间。)
Christine has been an invalid all her life.(含义:她现在还活着)
Mrs. Darby lived in Kentucky for seven years.(含义:达比太太已不再住在肯塔基州。)
Mrs. Darby has lived in Kentucky for seven years.(含义:现在还住在肯塔基州,有可能指刚离去)
注意:用过去时表示现在,表示委婉语气。
1)动词want, hope, wonder, think, intend等。
例如:Did you want any thing else? 您还要些什么吗?
I wondered if you could help me. 能不能帮我一下。
2)情态动词could, would。
例如:Could you lend me your bike? 你的自行车,能借用一些吗?
与“短文改错。英语课上,老师要求同桌同学相互修改作文。假设以下...”考查相似的试题有:
- (2014·河南郑州第一次质量预测)—How do you find the guy who took ________office last week?—He’s always finding________ ...
- 短文改错下面短文中共有10 处错误,每句中最多有两处。错误涉及一个单词的增加、删除或修改。增加:在缺词处加一个漏词符号(∧...
- Police can easily recognize your fingerprints by machine, because every person's fingerprints are__________.[ ]A. out...
- — I hear that Mary is ______ to stay with us for a few days. —That’s great.A.MaybeB.possibleC.likelyD.probable
- I like novels very much, ______ , novels written in English.A.in commonB.in returnC.in briefD.in particular
- The bargain they reached with their employers was to reduce their wage demand and accept a shorterworking week______....
- Anyone can borrow books from this library _______ he keeps them clean and returns them in time.A.even ifB.unlessC....
- ________ Barbara Jones offers to her fans is honesty and happiness.(2011·北京)A.WhichB.WhatC.ThatD.Whom
- 短文改错。假定英语课上老师要求同桌之间交换修改作文,请你修改你同学写的以下作文。文中共有10处语言错误,每句中最多有两...
- Words failed to ___________ my feelings the moment I saw my long-lost sister.A.controlB.affectC.exchangeD.convey