本试题 “单词拼写。根据下列各句句意和空白之后的汉语提示词,在横线上写出对应单词的正确形式,每空只写一词。1. Many college students think it ______ (值得) lea...” 主要考查您对单词、词组
可数名词及其单复数
形容词的最高级
过去分词
过去进行时
主谓一致
等考点的理解。关于这些考点您可以点击下面的选项卡查看详细档案。
- 单词、词组
- 可数名词及其单复数
- 形容词的最高级
- 过去分词
- 过去进行时
- 主谓一致
单词和短语:
由两个以上的词组成的,没有完整的句子结构,但又有一定的语法和逻辑关系的词的组合就是短语或词组。短语又包括固定短语,和自由短语。
比如说,put off (推迟),look up(查阅,查字典)have a heavy heart(心情沉重)…我们都习惯称为短语或词组(phrase)。put off是由一个动词和介词组成的,但他在句子中充当一个动词的作用,也就是说在这个词组中,put 是词头(head of the phrase) 所以它是动词词组,或动词短语。
题型特点:
对于英语学习来说,词汇是基础,掌握并灵活运用英语单词对学好英语至关重要,它会直接影响到我们的听、说、读、写能力。从高考单词拼写试题来看,单词拼写把单词放在句中考查,不仅是单词拼写,而且还要考查单词的形式,即将单词的写与用结合起来。这一点主要是要求学生对词汇的应用要有所掌握,体现了学以致用,从而根据语境选用适当的词。因此,答题时必须认真阅读全句,弄懂句意,在理解的基础上考虑选用适当的词汇。所考词汇多为多音节词,多数单词均有不同的变化形式,一般不少于4个字母。
题型种类:
1、句子中被考查的单词突出,画横线,横线标有该单词的首字母,要求学生写出该单词的正确形式。
2、句子中被考查的单词突出,画横线,横线后的括号内注有汉语,要求学生写出该单词的正确形式。
例题解析:
(一)读懂句意,确定单词。
例如:The f____day of the week is Sunday. 该句意为“一周的第一天是星期天”,需要填的词的首字母是“f”,根据常识和序数词有关知识应填“第一”,故填 first。此类题还可考月份。
例如::September is the n ____ month of the year (答案:ninth)
(二)瞻前顾后,确定形式写出单词后,还要注意分析该单词是否需要变化形式。现分类说明如下:
1、名词一般考虑单、复数和所有格。
例1:Do you like white?We have shirts of different c____. 根据句意,可确定单词为“color”,通过前面的shirts和different两词可确定此处应用colors。
例2:September10 this T____Day. 根据句意,确定单词“Teacher”,它与Day之间存在所有格关系,将Teacher变为复数,再变为所有格,应填Teachers'。
2、形容调和副词这两类词学生极易混淆,做题时应仔细分析,慎重选择究竟用哪类词,有时还要考虑到形容词和副词“级”的变化。
例1:He was very a____with the man upstairs and began to shout, "Stop singing!" 根据句意,此处应填形容词原级angry。
例2:On Sundays, Children play h____in the park. 此处应填副词happily,副词修饰动词。
3、动词动词变化形式较为复杂,一般有五种:动词原形、第三人称单数形式、现在分词,过去式和过去分词。可综合考查学生运用英语知识的能力。
例1:Thank you very much for l____me your bike. 介词后动词用-ing形式,故填lending。
例2:When he was ten, he became i____in maths. become interested in 为固定词组,意为“对……感兴趣”,故此处应填interested。
4、数词注意确定用基数词还是序数词。
例1:There are t____months in a year. 此处应用基数词twelve。
例2:December is the t____month of the year. 此处应填序数词twelfth。
5、代词主要从人称代词、物主代词、反身代词、不定代词和疑问代词几方面考虑,有时还要考虑用单数还是用复数。
例1:Help y____to some fish, Jim. 根据句意,此处应用yourself.
例2:"Help y____to some fish, please." Mrs Green said to the twins. 根据句意,thetwins为复数,故填yourselves。
6、连词若前后两个词或句子存在转折、因果、并列、选择等关系,一般应填连词。
例1:She didn't go to school yesterday b____she was il1. 从句和主句互为因果关系,故填because。
例2:The football match still went on t____it was raining heavily. 该从句为让步状语从句,故应填though。
解题技巧:
以下是解单词拼写的基本程序:首先要仔细审题,明确大意。在句子缺词的情况下,尽量弄懂句子大意并根据已给出的语境,判断出所缺的单词,试将该单词放入句子当中,看是否能使句子完整,句意明确。注意词性,写出词形。在解题过程中,要特别注意根据句子中所缺成分,判断所缺单词的词类。
1、名词,就要注意单复数;
2、动词,就要注意主谓一致、时态和语态的一致性;
3、形容词和副词,就要注意形容词和副词之间的转化规则;
4、词组和短语,就要注意固定搭配。
重读句子,验证答案。完成拼写后,要把句子重读一遍,检查句子是否通顺,单词拼写是否准确无误,单词形式是否正确,如名词的数、格,动词的时态、语态、语气和非谓语形式,形容词、副词的级等。这一步很重要,因为差之毫厘,谬以千里。总而言之,高考单词拼写题既考查学生的词汇量,又考查学生在特定的语境中灵活运用词汇的综合应变能力。要想提高得分率,绝非一日之功。正如谚语所说:“Rome was not built in one day”。所以,考生应该以命题特点为指导,在平时的复习中运用构词法知识多读、多记、多练,并增强语感,辅以行之有效的解题方法,才能熟练掌握,灵活运用,避免出错。
题型拓展:
1、单纯的翻译题,考查考生对单词的记忆。例句:The little girl is wearing a____ (粉红色的)dress. (正确答案:pink)
2、根据语境要求,填入所写单词的适当形式。
例句:The story was first written in English and later____ (翻译) into Chinese.(正确答案:translated)
3、从词在拼写上有可能存在的“盲点”(相对难写、难记)考虑命题。
例句:The book gives a short ____(描述) of the city.(正确答案:description)
4、在有可能出现多个近似答案的情况下,对词的用法进行甄别。
例句:Very few people ____(成功) in losing weight these days.(正确答案:succeed)
5、从词在用法上有可能存在的“盲点”(相对少见的用法,在一般规律中考查特殊)考虑命题。
例句:All the boys were standing up ____(笔直). (正确答案:straight)
6、侧重选择多音节词汇(构成各单词的字母数一般都超过了7个)命题,考查考生对多音节词汇的把握程度。
例句:One of ____ (邻居) kept a very beautiful garden. (正确答案:neighbours或neighbors)
7、侧重选择词义较为生僻或使用率偏低的词汇命题,考查考生对单词拼写记忆的广泛程度。
例句:He turned on the television set hanging from the____ (天花板). (正确答案:ceiling)
8、侧重从词音与词形不相吻合的部分命题(包括不发音字母),考查考生对单词拼写记忆的准确程度。
例句:I usually just have a____ (三明治) for lunch. (正确答案:sandwich)
9、能根据语境的要求,将所给的中文提示(该提示给人以名词或动词的假象)转译成正确的英语表现形式。
例句:I changed into my sports shoes so that I could walk more____(舒服). (正确答案:comfortably)
10、对近义词不同搭配用法的一般常识,在有可能出现多个答案的情况下,对词的用法进行反复推敲,考生应对最常用词汇的易混易错现象给予注意。
例句:A fence at the back of garden (分开) us from the neighbours.(正确答案:separates或separated)
可数名词:
是指能以数目来计算,可以分成个体的人或东西;因此它有复数形式,当它的复数形式在句子中作主语时,句子的谓语也应用复数形式。
可数名词复数的规则变化:
| 情况 | 构成方法 | 读音 | 例词 |
| 一般情况 | 加 –s | 1.清辅音后读/s/; 2.浊辅音和元音后读/z/; |
map-maps bag-bags car-cars |
| 以s,sh,ch,x等结尾的词 | 加 -es | 读 /iz/ | bus-buses watch-watches |
| 以ce,se,ze,(d)ge等结尾 的词 |
加 -s | 读 /iz/ | license-licenses |
| 以辅音字母+y结尾的词 | 变y 为i再加es | 读 /z/ | baby-babies |
1)以y 结尾的专有名词,或元音字母+y结尾的名词变复数时,直接加s变复数:
如:two Marys the Henrys monkey---monkeys holiday---holidays
比较:层楼:storey---storeys story---stories
2)以o 结尾的名词,变复数时:
a. 加s,如: photo---photos piano---pianos
b. 加es,如:potato--potatoes tomato--tomatoes
c. 均可,如:zero---zeros / zeroes
3)以f或fe 结尾的名词变复数时:
a. 加s,如: belief---beliefs roof---roofs safe---safes gulf---gulfs;
b. 去f, fe 加ves,如:half---halves knife---knives leaf---leaves wolf---wolves wife---wives life---lives thief---thieves;
c. 均可,如:handkerchief: handkerchiefs / handkerchieves
可数名词复数的不规则变化:
1)child---children foot---feet tooth---teeth mouse---mice man---men woman---women
注意:与 man 和 woman构成的合成词,其复数形式也是 -men 和-women。
如:an Englishman,two Englishmen. 但German不是合成词,故复数形式为Germans;Bowman是姓,其复数是the Bowmans。
2)单复同形 如:
deer,sheep,fish,Chinese,Japanese
li,jin,yuan,two li,three mu,four jin
但除人民币元、角、分外,美元、英镑、法郎等都有复数形式。如:
a dollar, two dollars; a meter, two meters
3)集体名词,以单数形式出现,但实为复数。
如:staff people police cattle 等本身就是复数,不能说a staff a people,a police,a cattle,
但可以说a person,a policeman,a head of cattle, the English,the British,the French,the Chinese,the
Japanese, the Swiss 等名词,表示国民总称时,作复数用。
如:The Chinese are industries and brave. 中国人民是勤劳勇敢的。
4)以s 结尾,仍为单数的名词,如:
a. maths,politics,physics等学科名词,为不可数名词,是单数。
b. news 是不可数名词。
c. the United States,the United Nations 应视为单数。
The United Nations was organized in 1945. 联合国是1945年组建起来的。
d. 以复数形式出现的书名,剧名,报纸,杂志名,也可视为单数。
"The Arabian Nights" is a very interesting story-book.
<<一千零一夜>>是一本非常有趣的故事书。
5) 表示由两部分构成的东西,如:glasses (眼镜) trousers, clothes ;
若表达具体数目,要借助数量词 pair(对,双); suit(套); a pair of glasses; two pairs of trousers
6)另外还有一些名词,其复数形式有时可表示特别意思,如:goods货物,waters水域,fishes(各种)鱼
复合名词的复数形式:
名词作定语名词作定语一般用单数,但也有以下例外。
1)用复数作定语。
如:sports meeting 运动会
students reading-room 学生阅览室
talks table 谈判桌
the foreign languages department 外语系
2)man, woman, gentleman等作定语时,其单复数以所修饰的名词的单复数而定。
如:men workers
women teachers
gentlemen officials
3)有些原有s结尾的名词,作定语时,s保留。
如:goods train (货车)
arms produce 武器生产
customs papers 海关文件
clothes brush衣刷
4)数词+名词作定语时,这个名词一般保留单数形式。
如:two-dozen eggs 两打/(二十四个鸡蛋)
a ten-mile walk 十里路
two-hundred trees 两百棵树
a five-year plan 一个五年计划
可数名词单复数知识体系:

不同国籍人的单复数:
国籍
总称(谓语用复数)
单数
复数
中国人
the Chinese
a Chinese
two Chinese
瑞士人
the Swiss
a Swiss
two Swiss
澳大利亚人
the Australians
an Australian
two Australians
俄国人
the Russians
a Russian
two Russians
意大利人
the Italians
an Italian
two Italians
希腊人
the Greek
a Greek
two Greeks
法国人
the French
a Frenchman
two Frenchmen
日本人
the Japanese
a Japanese
two Japanese
美国人
the Americans
an American
two Americans
印度人
the Indians
an Indian
two Indians
加拿大人
the Canadians
a Canadian
two Canadians
德国人
the Germans
a German
two Germans
英国人
the English
an Englishman
two Englishmen
瑞典人
the Swedish
a Swede
two Swedes
形容词最高级概念:
表示“三者、三者以上之中之最”,用形容词的最高级句式,形容词最高级前必加冠词the。
形容词最高级用法:
1)the+最高级+比较范围:
如:The Sahara is the biggest desert in the world.
形容词最高级前通常必须用定冠词the,副词最高级前可不用。形容词most前面没有the,不表示最高级的含义,只表示“非常”。
如:It is a most important problem.=It is a very important problem.
注意:使用最高级要注意将主语包括在比较范围内。
如:(错)Tom is the tallest of his three brothers.
(对)Tom is the tallest of the three brothers.
2)下列词可修饰最高级,by far, far, much, mostly, almost :
如:This hat is nearly/almost the biggest.
注意:
1、very可修饰最高级,但位置与much不同。
如:This is the very best.
This is much the best.
2、序数词通常只修饰最高级。
如:Africa is the second largest continent.
3)句型转换:
如:Mike is the most in telligent in his class.
Mike is more intelligent than any other students in his class.
4)“否定词语+比较级”,“否定词语+so…as”结构表示最高级含义:
如:Nothing is so easy as this.=Nothing is easier than this.=This is the easiest thing.
形容词最高级用法特别提示:
1、表示“最…之一”的句式:one of the+.最高级+名词复数:
如:Jim is one of the best students in his class.
Su zhou is one of the most beautiful cities in China.
2、“the+序数词+最高级”表示“第几个最…”:
如:The Yellow River is the second longest river in China.
3、当最高级前有物主代词或名词所有格时,不加the;
如:Monday is my busiest day.
Jack is Jim's best friend.
4、比较级与最高级的转换:
如:He is taller than any other boys in his class.
He is the tallest boy in his class.
形容词最高级用法的注意点:
1)最高级后常有介词短语、从句或所有格来表比较范围。
2)最高级前有作定语的物主代词、指示代词或名词所有格等时,不再加定冠词the。
3)形容词最高级用在oneof结构中,这时最高级后面的名词要用复数。
4)形容词最高级有时单独使用,没有比较的范围。
如:Greece's best writers lived in ancient Athens. 希腊最好的作家居住在古雅典。
The most violent have winds of more than 400kilometres per hour. 最猛烈的风力达到每小时400千米以上。
5)形容词最高级前有时有定语或状语修饰。
如:Japan's second largest city is Osaka. 日本的第二大城市是大阪。
Here in Vancouver,you're in Canada's warmest part. 这里是温哥华,加拿大最暖和的地方。
Tai Lake is nearly the biggest in EastChina. 太湖在华东几乎是最大的。
6)形容词最高级有时有特殊用法。
①most同形容词连用而不用the时,表示“非常,十分”。
②当形容词最高级作表语,而又不与别的人或物作对比时,不用the。
如:The supermarket is busiest on weekend. 这个超市周末最忙。
③用作宾语补足语的形容词最高级前的the常省略。
如:We feel it most difficult to write a composition in English. 我们觉得用英语写作文最难。
I think it best not to ask him about it now. 我想现在还是不要向他询问此事为妙。
④形容词最高级还可用在某些短语中。
如:You can at least go and get your jacket. 你至少可以去拿你的夹克衫。
I guess it should only cost at most fifty dollars. 我猜想它最多值五十元。
We'll do our best to make the transportation unimpeded. 我们将尽最大努力使交通畅通。
形容词最高级变化有规则和不规则两种:
1、规则变化:
|
构成 |
原级 | 最高级 |
| 单音节以及少数双音节的词后面直接加-est | tall | tallest |
| short | shortest | |
| 以不发音的e结尾只加-st | large | largest |
| “以辅音字母+y”结尾的词改y为i,再加-est | happy | happiest |
| easy | easiest | |
| 以一个元音加一个辅音字母结尾的单音节词(即重读闭音节词),双写结尾的辅音字母, 再加-est | hot | hotter |
| big | bigger |
注:大部分双音节词和多音节的词(即音标中含有三个或三个以上元音音素的词),要在前面加more,most。
如:interesting→most interesting
expensive→most expensive
特别提醒:
1、以形容前缀un构成的三音节形容词不适合上述情况:
如:unhappy→unhappiest,
2、以形容词+ly构成的副词要在前面加 more,most:
如:slowly→most slowly
2、不规则变化:
|
原级 |
最高级 |
| good | best |
| bad/ill | worse |
| little | least |
| many/much | most |
| far | farthest/furthest |
| old | oldesteldest/ |
形容词最高级用法解密:
1、形容词最高级前必须加定冠词the,但如果最高级前有物主代词、指示代词、名词所有格等修饰时,则不用定冠词。
如:My oldest daughter is 16 years old. 我最大的女儿16岁。
2、形容词最高级常与由介词in或of引导的表示范围的短语连用。若介词后的名词或代词与句中的主语是同一事物时,则用of短语;
当只说明是在某一空间、时间范围内的比较时,则用in短语。
如:This apple is the biggest of all. 在所有的苹果中,这个苹果最大。
He is the youngest in his class. 他在他班里年龄最小。
3、形容词最高级前可用序数词限定,共同修饰后面的名词,其结构为:“the+序数词+形容词最高级+名词”。
如:Hai nan is the second largest island in China. 海南是中国的第二大岛。
4、形容词最高级的意义还可以用比较级形式表达。常见的有:
(1)形容词比较级+than any other+单数名词。
如:This is more difficult than any other book here. (=This is the most difficult book of all.) 这些书当中这本最难。
(2)形容词比较级+thantheother+复数名词。
如:Asia is bigger than the other continents on the earth. 亚洲是地球上最大的洲。
5、形容词最高级前若有不定冠词a,这时,它不表示比较,而表示“非常”的意思。
如:Spring is a best season. 春天是一个非常好的季节。形容词最高级前通常要加定冠词the,而以下几种情况一般不需要加定冠词the:
(1)形容词最高级前有序数词、物主代词、指示代词或名词所有格等限定词修饰时,最高级前不用the。
如:The Yellow River is the second longest river in China. 黄河是中国第二长河。
(2)形容词最高级在句中作表语而比较范围又不明确时,最高级前不用the。
如:They are happiest on Saturdays. 他们在星期六最快乐。
(3)如果两个形容词最高级并列修饰同一个名词时,第二个形容词最高级前不加the。
如:He is the youngest and tallest boy in his class. 他是班上年龄最小、个子最高的男孩。
(4)如果形容词最高级用来加强语气,作“十分;非常”之意时,前面不加the。但形容词最高级作单数名词的定语时,可用不定冠词a/an。
如:That book is most interesting. 那本书非常有趣。
(5)作宾语补足语的形容词最高级前不加the。
如:I found it most difficult to get to sleep. 我发现入睡最难。
(6)在一些固定用法中,最高级前通常省略the。
如:With best wishes for you. 向你致以最美好的祝愿。
过去分词的概念:
过去分词一般表示完成和被动的动作,只有一种形式。即:动词原形加-ed构成。
如:fallen leaves 落叶
boiled water 开水
I heard the door closed. 我听见门被关上了。
过去分词与现在分词被动式的区别:
两者均可表示被动,其区别主要在于它们所表示的时间概念不同,但有时它们也可表示相同的意思。
如:Written in haste, the book has many mistakes. 这书因写得仓促,所以错误不少。
Being written in haste, the book has many mistakes. 这书因写得仓促,所以错误不少。
Having been written in haste, the book has many mistakes. 这书因写得仓促,所以错误不少。
有时虽然所表示的时间概念相同,但有细微区别:
如:Having been show the lab, we left. 被领着看了实验室后,我们就离开了。
过去分词的句法功能:
1、作定语:
如:I don't like the book written by Martin.
Our class went on an organized trip last Monday. 上周一我们班开展了一次有组织的旅行。
注意:当过去分词是单词时,一般用于名词前,如果是过去分词短语,就放在名词的后面。过去分词做定语相当于一个被动语态的定语从句。
2、过去分词作表语:
如:They were very excited at the news. 听到这个消息,他们非常激动。
The window is broken. 窗户破了。
They were frightened at the sad sight. 他们对眼前悲惨的景象感到很害怕。
注意:be+过去分词,如果表示状态是系表结构,如果表示被动的动作是被动语态。
区别:The window is broken.(系表)
The window was broken by the boy.(被动)
有些过去分词是不及物动词构成的,不表示被动,只表示完成。
如:boiled water(开水) fallen leaves(落叶) newly arrived goods(新到的货) the risen sun(升起的太阳) the changed world(变了的世界)
这类过去分词有:gone, come, fallen, risen, changed, arrived, returned, passed等。
3、过去分词作宾语补足语:
如:I heard the song sung several times last week. 上周我听见这首歌被唱了好几次。
有时过去分词做with短语中的宾语补足语:
如:With the work done, they went out to play. 工作做完了,他们出去玩去了。
4、过去分词作状语:
如:Praised by the neighbours, he became the pride of his parents. 受到邻居们的表扬,他成为父母的骄傲。(表示原因)
Onceseen, it can never be forgotten. 一旦它被看见,人们就忘不了。(表示时间)
Given more time, I'll be able to do it better. 如果给予更多的时间,我能做得更好。(表示条件)
Though told of the danger, he still risked his life to save the boy. 虽然被告之危险,他仍然冒生命危险去救那个孩子。(表示让步)
Filled with hopes and fears, he entered the cave. 心中充满了希望与恐惧,他走进山洞。
5、过去分词与逻辑主语构成独立主格:
如:All books returned at the end of the term, the library assistant was satisfied. 所有的书期末时都还了,图书管理员很高兴。
The field ploughed, he began to spread seed. 地耕好了,他开始撒种子。
现在分词与过去分词的区别:
1、分词作表语:
分词做表语有两种情况,一种是现在分词做表语,一种是过去分词做表语,这两者区别是考试中经常考到的地方。一般来说,表示心理状态的动词如excite,interest等都是及物动词,汉语意思不是“激动”,“高兴”,而是“使激动”、“使高兴”,因而现在分词应该是“令人激动的”、“令人高兴的”,过去分词则是“感到激动的”和“感到高兴的”。所以,凡表示“令人……的”都是-ing形式,凡是表示“感到……”都用-ed形式。换句话说,若人对……感兴趣,就是somebody is in terestedi n...,若人/物本身有兴趣时,就是说sb./sth. is interesting。这类词常见的有:
interesting 使人感到高兴—interested感到高兴的
exciting令人激动的—excited感到激动的
delighting令人高兴的—delighted感到高兴的
disappointing令人失望的—disappointed感到失望的
encouraging令人鼓舞的—encouraged感到鼓舞的
pleasing令人愉快的—pleased感到愉快的
puzzling令人费解的—puzzled感到费解的
satisfying令人满意的—satisfied感到满意的
surprising令人惊异的—surprised感到惊异的
worrying令人担心的—worried感到担心的
如:Travelling is interesting but tiring. 旅行是有趣的,但是使人疲劳。
The pupils will get confused if they are made to learn too much. 如果要学生学得太多,他们会感到糊涂的。
The game is exciting. (现在分词作表语)
We were excited at the news. (过去分词作表语)
2、分词作定语:
分词作定语时有下面几个特点:
1)现在分词表示主动意义,过去分词一般表示被动含意。
2)现在分词表示正在进行,过去分词表示状态或做完(完成)的事。
如:He rushed into the burning house. 他冲进了正在燃烧着的房子。
The child standing over there is my brother. 站在那儿的男孩子是我弟弟。
The room facing south is our classroom. 朝南的房间是我们的教室。
He is an advanced teacher. 他是个先进教师。
3)下列不及物动词也以过去分词形式做定语或表语,但不具有被动意义,这点要注意:
departed, elapsed, faded, fallen, gone, frown-up, retired, returned, risen, set, vanished, much-traveled, newly-arrived, recently-come
3、分词作状语:
现在分词做状语与过去分词做状语的最主要区别在于两者与所修饰的主语的主动与被动关系的区别。
1)现在分词作状语时,现在分词的动作就是句子主语的动作,它们之间的关系是主动关系。
如:He went out shutting the door behind him. 他出去后将门随手关上。
Not knowing what to do, he went to his parents for help. 由于不知如何办是好,他去找父母帮忙。
Smiling, they came in.
2)过去分词作状语时,过去分词表示的动作是句子主语承受的动作,它们之间的关系是被动关系。
如:Cleaned, the room looks nice.
Given more attention, the trees could have grown better. 如果对这些树多关心一些,它们本来会长得更好。
Faced with difficulties, we must try to overcome them. 在遇到困难的时候,我们必须设法克服。
过去进行时的概念:
过去进行时表示在过去某一时刻或某一段时间内进行或发生的动作。其形式为was /were + V-ing。
常与表示过去的时间状语连用,如:last night, last Saturday等;或者与when, while, as引导的过去时间状语连用。
过去进行时的基本用法:
1、主要表示过去某一时间正在进行的动作:
如:He fell asleep when he was reading. 他看书时睡着了。
We were expecting you yesterday. 我们昨天一直在等你。
He was playing while I was studying. 我在做功课时他在玩。
2、过去进行时表示现在:
用过去进行时表示现在主要是为了使语气委婉、客气。
如:I was wondering if you could give me a lift. 我不知你能否让我搭一下车。
We were hoping you would stay with us. 我们很希望你能跟我们住在一起。
How much did you want to spend, sir? 先生,您打算花多少钱?
【注】一般过去时也有类似用法,但比较而言,用过去进行时显得更客气,更不肯定。
3、过去进行时表示感情色彩:
与现在进行时相似,过去进行时也可表示满意、称赞、惊讶、厌恶等感情色彩,也通常与always, forever, continually等副词连用。
如:They were always quarrelling. 他们老是吵架。
The boy was continually asking questions. 这个男孩子老是问东问西的。
4、动词be的过去进行时:
动词be的进行时也可表示过去一时的表现或暂时的状态。
如:He was friendly. 他很友好。(指过去长期如此)
He was being friendly. 他当时显得很友好。(指当时一时的表现)
过去进行时与一般过去时的区别:
(1)过去进行时强调动作在过去某时刻正在进行或持续,而一般过去时表示动作的完成。
如:He was writing his composition last night. 他昨晚在写作文。(不一定写完)
He wrote his composition last night. 他昨晚写了一篇作文。(已经写完)
(2)表示过去的状态、感觉及心理活动的静态动词(如be, like, love, hate, fear, own, hear, see, know, want, notice)可用于一般过去时,但通常不用于进行时。
如:I hated it when a man spoke with his mouth full of food. 我讨厌人们说话时口里含着食物。
(3)一般过去时与always, constantly, forever, continually等连用,表示“过去经常性、习惯性的动作”;
而过去进行时与always, constantly, forever, continually等连用,表示动作的重复,常带有感情的色彩。
如: He always got up at six. 他过去总是六点起床。
He was always thinking of his work. 他总是一心想到工作。
(4)有时过去进行时可以用来替换一般过去时,但一般过去时表示主语的行为是经过认真考虑的;
而过去进行时表示一种较随便或没有进行仔细考虑的行为。
如:I thought that he would agree with us. 我原以为它会同意我们的。
I was thinking of persuading him to follow my advice. 我想到了要说服他接受我们的建议。
注:下面几种情况不用一般过去时而要用过去进行时:
1、表示过去某一阶段暂时性的习惯动作时。
如:Tom was getting up at six o'clock every day that week. 汤姆那一周里每天都是六点钟起床。
2、与always连用表示赞美,厌烦等感情色彩时。
如:John was always coming to school late. 约翰上学总是迟到。
LeiFeng was always doing good deeds for the people. 雷锋总是为人民做好事。
3、用来描写故事发生的情景时。
如:It was a dark night. The wind was blowing hard and the rain was falling heavily. A PLA man suddenly appeared on the river bank. He wanted to cross the river.
那是一个漆黑的夜晚,风刮得很厉害,雨下得很大,一个解放军战士突然出现在河岸上,他想过河去。
4、when作并列连词,表示“(这时)突然”之意时,第一个并列分句用过去进行时,when引导的并列分句用一般过去时。
如:I was taking a walk when I met him. 我正在散步,突然遇见了他。
We were playing outside when it began to rain. 我们正在外边玩,这时下起雨来了。
5、go, come, leave, start, arrive等动词可用过去进行时表示过去将来的含义。
如:I was leaving for Wuhan that day. 那天我正要去武汉。
She was coming later. 她随后就来。
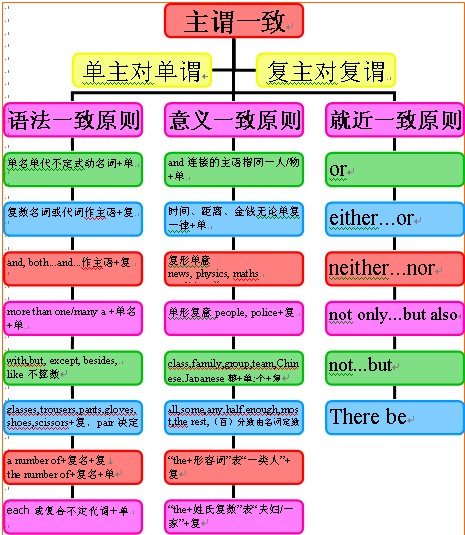
主谓一致的概念:
谓语的数必须和主语的人称和数保持一致,这就叫主谓一致。
主谓一致的基本原则:
1)语法一致原则,即在语法形式上取得一致。例如,主语是单数形式,谓语动词也采取单数形式;主语是复数形式,谓语动词也采取复数形式。
例如:The students are very young.
This picture looks beautiful.
2)意义一致原则,即从意义着眼处理一致关系。例如,主语形式虽是单数但意义是复数,谓语动词也采取复数形式;
而有些主语形式虽是复数但意义上看作单数,谓语动词也采取单数形式。
例如:The people in that country are fighting for independence.
The crowd deeply respect their leader.
Three years in a strange land seems a long time.
3)就近原则,即谓语动词的单数或复数形式取决于最靠近它的词语。
例如:Neither hen or I am going to see the film tonight because we are busy.
几对容易混淆词组的一致用法:
1、由“this/thatkind/typeof+名词”作主语,谓语动词用单数形式;而由"these/thosekind/typeof+复数名词”作主语,谓语动词用复数形式。
例如:This kind of apples is highly priced.
Those kind(s) of tests are good.
2、由“a number of,a totalo f,an average of+复数名词”作主语,谓语动词用复数形式;由“the number of,the total of,the average of+复数名词”作主语,谓语动词用单数形式。
例如:A number of students are waiting for the bus.
The number of the students in this university is increasing yearly.
3、one of,the(only) one of的一致用法
例如:This is one of the books that have been recommended.
This is the(only) one of the books that has been recommended.
主谓一致用法点拨:
1、并列结构作主语谓语用复数:
如:Reading and writing are very important.
注意:当主语由and连结时,如果它表示一个单一的概念,即指同一人或同一物时,谓语动词用单数,and此时连接的两个词前只有一个冠词。
如:The iron and steel industry is very important to our life.
典型例题:
The League secretary and monitor___asked to make a speech at the meeting.
A. is
B. was
C. are
D. were
答案:B.
注:先从时态上考虑。这是过去发生的事情应用过去时,先排除A、C本题易误选D,因为The League secretary and monitor 好象是两个人,但仔细辨别,monitor前没有the,在英语中,当一人兼数职时只在第一个职务前加定冠词。后面的职务用and相连。这样本题主语为一个人,所以应选B。
2、主谓一致中的靠近原则:
1)当there be句型的主语是一系列事物时,谓语应与最邻近的主语保持一致。
例如:There is a pen, a knife and several books on the desk.
There are twenty boy-students and twenty-three girl-students in the class.
2)当either…or…与neither…nor,连接两个主语时,谓语动词与最邻近的主语保持一致。
如果句子是由here, there引导,而主语又不止一个时,谓语通常也和最邻近的主语一致。
例如:Either you or she is to go.
Here is a pen, a few envelops and some paper for you.
3、谓语动词与前面的主语一致:
当主语后面跟有with, together with, like, except, but, no less than, as well as等词引起的短语时,谓语动词与前面的主语一致。
例如:The teacher together with some students is visiting the factory.
He as well as I wants to go boating.
4、谓语需用单数:
1)代词each和由every, some, no, any等构成的复合代词作主语,或主语中含有each,every,谓语需用单数。
例如:Each of us has a tape-recorder.
2)当主语是一本书或一条格言时,谓语动词常用单数。
例如:The Arabian Night is a book known to lovers of English.
3)表示金钱,时间,价格或度量衡的复合名词作主语时,通常把这些名词看作一个整体,谓语一般用单数。(用复数也可,意思不变。)
例如:Three weeks was allowed for making the necessary preparations.
Ten yuan is enough.
5、指代意义决定谓语的单复数:
1)在代词what, which, who, none, some, any, more, most, all等词的单复数由其指代的词的单复数决定。
例如:All is right. (一切顺利。)
All are present. (所有人都到齐了。)
2)集体名词作主语时,谓语的数要根据主语的意思来决定。
例如:family, audience, crew, crowd, class, company, committee等词后用复数形式时,意为这个集体中的各个成员,用单数时表示该个集体。
例如:His family isn't very large. 他家不是一个大家庭。
His family are music lovers. 他的家人都是音乐爱好者。
但集合名词people, police, cattle, poultry等在任何情况下都用复数形式。
例如:Are there any police around?
3)有些名词,如variety, number, population, proportion, majority等有时看作单数,有时看作复数。
A number of+名词复数+复数动词。 The number of+名词复数+单数动词。
例如:A number of books have lent out.
The majority of the students like English.
6、与后接名词或代词保持一致:
1)用half of, part of, most of, a portion of等词引起主语时,动词通常与of后面的名词,代词保持一致。
例如:Most of his money is spent on books.
Most of the students are taking an active part in sports.
2)在一些短语,如many a或more than one所修饰的词作主语时,谓语动词多用单数形式。
但由more than…of作主语时,动词应与其后的名词或代词保持一致。
例如:Many a person has read the novel. 许多人都读过这本书。
More than 60percent of the students are from the city. 百分之六十多的学生都来自这个城市
主谓一致知识体系:
主谓一致用法拓展:
1)当everyone,everybody,noone,nobody,anyone,anybody,someone,somebody,everything,anything,something,nothing等用作主语时,其相应的代词一般用单数形式。
例如:If anybody calls, tell him that I'm out.
Something strange happened, didn't it?
2)人称代词与名词的呼应:人称代词I(me),he(him),she(her),it(it) 都是代替前面的单数名词,而they(them),we(us)则是代替复数名词的,you既可以代表单数,也可以代表复数。但表示泛指的时候,用he或one来表示。
例如:If a young person enters a classical music field only for money, he is in the wrong profession.
3)物主代词与名词的呼应:my,our,his,her,its,their要与代替的名词在数上一致。
例如:The welfare department,as well as the other social services,will have its budget cut.
4)反身代词与其所代成分间的呼应。
例如:Many primitive people believed that by eating ananimal they could get some of the good qualities of that animal for themselves.
5)指示代词与所代名词间的呼应:this和that指代单数名词或不可数名词,these和those指代复数名词(those还可以用作先行词,引导定语从句,表示“那些人”)。
例如:She invited all those who had been her former colleagues.
6)much和muchof后接不可数名词,而many和manyof后接可数名词的复数。
例如:There is not much coal left.
A great many of the houses were knocked down by the earthquake.
7)表示量的词后面有的接可数名词,有的接不可数名词。
接可数名词的有:a number of,a rangeof,a series of十复数名词;
接不可数名词的有:a great deal of,an amount of十不可数名词;
既可接可数又可接不可数名词的有:a lot of,a variety of。
例如:1.The government attached a great deal of importance to education.
2.Quiteanumberofwomenappliedforthisjob.
3.The college library has avariety of books.
4.An apple is avariety off ruit.
与“单词拼写。根据下列各句句意和空白之后的汉语提示词,在横线...”考查相似的试题有:
- People from all over the world ________ China on the successful launch of Chang’E-1.A.celebratedB.greetedC.congrat...
- 根据下列各句句意和空白之后的汉语提示词,在答题卡指定区域的横线上写出对应单词的正确形式,每空只写一词。小题1: Their pl...
- —Hi, Mike! We’re going biking along the beach this weekend.—_______. I love being bathed in the sunshine.A.Count me ...
- We have strong __________ for believing that the mine accident in Heilongjiang was due to the poor management.A.grou...
- How dirty the windows are! They really require _______.A.to cleanB.being cleanedC.to have cleanedD.cleaning
- Having come to study in England, Wang Li had difficulty ______ the new environment.A.referring toB.devoting toC.ad...
- that he has to qualifications in his new job, Patrick plans to gain the necessary skills by taking a part-time course...
- The children went home from the grammar schoo1,their lessons ________ for the day.A.finishingB.finishedC.had fini...
- _____ by a greater demand of vegetables, farmers have built more green houses.A. DrivenB. Being drivenC. To driveD. H...
- 短文改措。此题要求改正所给短文中的错误。对标有题号的每一行作出判断;如有错误(每行只有一个错误),则按下列情况改正:...