本试题 “Our county _____ vegetables.[ ]A. is rich inB. are rich inC. was rich onD. rich for” 主要考查您对介词和介词短语
主谓一致
等考点的理解。关于这些考点您可以点击下面的选项卡查看详细档案。
- 介词和介词短语
- 主谓一致
介词和介词短语的概念:
介词是一种用来表示词与词、词与句之间的关系的虚词,在句中不能单独作句子成分。介词后面一般有名词、代词或相当于名词的其他词类,短语或从句作它的宾语。介词和它的宾语构成介词词组,在句中作状语,表语,补语或介词宾语。介词可以分为时间介词、地点介词、方式介词和其他介词。
误用介词的三种情况:
1、多用介词:
多用介词可能是受汉语意思的影响将及物动词误用作不及物动词,也可能是受相关结构的影响而用错:
误:We discussed about the plan.
正:We discussed the plan. 我们讨论了计划。
误:Did he mention about the accident?
正:Did he mention the accident? 他提到那次事故了吗?
误:I saw her enter into the bank.
正:I saw her enter the bank. 我看见她进了银行。
误:He married with[to] a nurse.
正:He married a nurse. 他同一位护士结了婚。
误:How can contact with you?
正:How can contact you? 我怎么与你联系?
误:We should serve for the people heart and soul.
正:We should serve the people heart and soul. 我们应该全心全意地为人民服务。
误:Who controls over the factory? (但名词control可接over)
正:Who controls the factory? 谁管理这个工厂?
误:He has a great many of friends here. (比较a great number of)
正:He has a great many friends here. 他在这儿有很多朋友。
2、漏用介词:
漏用介词可能是受汉语意思的影响将不及物动词误用作及物动词,或是受相关结构的影响的影响而用错等:
误:This matter is difficult to deal. (deal with=处理)
正:This matter is difficult to deal with. 这事很难处理。
误:He is not a man to be depended.
正:He is not a man to be depended on. 他不是个可靠的人。
误:He took a cup of tea, and went on the story.
正:He took a cup of tea, and wentonwiththestory.他喝了一口茶,又接着讲故事。
误:My mother still regards me a child. (比较consider…as中的as可省略)
正:My mother still regards me as a child. 我母亲还把我当小孩看。
误:They insisted sending a car over to fetch us.
正:They insisted on sending a car over to fetch us.他们坚持要派车来接我们。
误:What he says is worth listening.
正:What he said is worth listening to.他的话值得一听。
3、错用介词:
错用介词的情况比较复杂,可能是因受汉语意思的而错,也可能是因弄不清搭配关系而错,可能是混淆用法而错,也可能是受相关结构的影响而错,可能是忽略语境而错,也可能是想当然的用错:
误:She called on his office yesterday. (call on+人,call at+地点)
正:She called at his office yesterday. 她昨天去了他办公室拜访。
误:He is engaged with a nurse.
正:He is engaged to a nurse.他与一位护士订了婚。
误:The sun rises from the east.
正:The sun rises in the east.太阳从东方升起。
误:Under his help, I finished it in time.
正:With his help, I finished it in time. 在他的帮助下,我及时做完了。
误:During he was in Japan, he visited many places.
正:During his stay in Japan, he visited many places.他在日本期间,参观过许多地方。
误:We are familiar to his character.
正:We are familiar with his character.我们了解他的性格。
误:Help yourself with the fruit.
正:Help yourself to the fruit.吃点水果吧。
介词的宾语:
1、名词或代词作介词宾语:
如:Are you interested in history? 你对历史感兴趣吗?
Don't worry about it. 别为它担心。
注:若是人称代词用作介词宾语,要注意用宾格。
如:No one can sing like her. 没有人能像她那样唱歌。(不能用like she)
2、动名词作介词宾语:
如:He is good at telling stories. 他善于讲故事。
In crossing the street he was run over. 他在穿过马路时被汽车撞倒。
3、过去分词作介词宾语:
如:We can't regard the matter as settled. 我们不能认为这事已经解决。
I take it for granted you have read the book. 我以为你读过这本书。
注:过去分词用作介词宾语通常只见于某些固定结构中,如上面第1句涉及regard…as(认为…是)结构,第2句涉及take sth for granted(认为某事属实)。在其他情况下,介词后通常不直接跟过去分词作宾语,若语义上需要接过去分词(表被动),可换用“being+过去分词”:
如:He went out without being seen by the others.他出去了,没有被其他人看见。
4、从句作介词宾语:
如:He was not satisfied with what she said. 他对她说的不满意。
I'm worried about where he is. 我担心他上哪儿去了。
注:介词后通常不接that从句,遇此情况需考虑用其他结构:
误:He paid no attention to that she was poor.
正:He paid no attention to the fact that she was poor. 他根本不注意她很穷这一事实。
但有个别介词(如except)可接that从句。
比较:I know nothing about him except that he lives next door./I know nothing about him except for the fact that he lives next door. 我只知道他住在隔壁,其它的就不知道了。
5、不定式作介词宾语:
如:I had no choice but to wait. 除了等,我没有别的选择。
He wanted nothing but to stay there. 他只想留在那儿。
They did nothing but complain. 他们老是一个劲地抱怨。
He never did anything but watch TV. 除了看电视,他从不干任何事。
注:(1)介词后接不定式的情形通常只见于but, except等极个别个词。该不定式有时带to,有时不带to,其区别是:若其前出现了动词do,其后的不定式通常不带to;
若其前没有出现动词do,则其后的不定式通常带to。
(2)介词后虽然通常不直接跟不定式作宾语,但却可接“连接代词(副词)+不定式”结构:
如:He gave me some advice on how to do it. 对于如何做这事他给我提了些建议。
6、形容词作介词宾语:
如:Her pronunciation is far from perfect. 她的语音远不是完美的。
In short, we must be prepared. 总而言之,我们要有准备。
Things have gone from bad to worse. 事情越来越糟。
注:(1)有些形容词用作介词宾语可视为其前省略了动名词being:
如:He regarded the situationas(being) serious. 他认为形势严重。
His work is far from(being) satisfactory. 他的工作丝毫不令人满意。
(2)有些“介词+形容词”的结构已构成固定搭配:in full全部地,全面地,无省略地; in private私下地,秘密地; in particular特别地;in general一般地,通常地,概括地; in brief 简言之;in short总之,简言之; in vain徒然地,徒劳无益地;for fee免费地,无偿地; for certain肯定地,确切地;for sure肯定地,确切地; for short为了简短,简称;atl arge自由自在地,逍遥法外; by far…得多
7、副词作介词宾语:
如:I can't stay for long. 我不能久呆。
It's too hot in here. 这里面太热了。
I looked every where except there. 除了那儿,我到处都看过了。
8、数词作介词宾语:
如:The city has a population of four million. 这座城市有四百万人口。
He was among the first to arrive. 他是第一批到的。
9、介词短语作介词宾语:
如:Choose a book from among these. 从这些书中选一本吧。
I saw her from across the street. 我从街的对面望见了她。
注:通常可后接介词短语作宾语的介词是from, till, until, since, except, instead of等。
比较:I took it from the bed. 我从床那儿(或床上)拿的。
I took it from under the bed. 我从床下拿的。
10、复合结构用作介词宾语:
如:She had no objection to Mary marrying him. 她不反对玛丽与他结婚。
She came in with a book in her hand. 她手里拿着一本书走了进来。
All the afternoon he worked with the door locked. 整个下午他都锁着门在房里工作。
介词短语的句法功能:
1、表语:
如:He was with a friend. 他和一个朋友在一起。
Health is above wealth. 健康胜过财富。
This knife is for cutting bread. 这把小刀是用于切面包的。
注:有些介词(如because of)引出的短语通常只用作状语,不用作表语:
误:His absence is because of the rain.
正:His absence is due to the rain. 他因雨未来。
但是,若主语是代词(不是名词),becauseof引出的短语可用作表语:
如:It is because of hard work. 那是因为辛苦工作的原因。
2、状语:
如:Don't touch it with your hands. 别用手去摸它。
Did you do this by design or by accident? 你这样做是有意的还是无意的?
3、定语:
如:This is his reply to your letter. 这是他给你的回信。
This is the best way of doing it. 这是做此事最好的方法。
My love for you is deeper than the sea. 我对你的爱比海深。
4、宾语补足语:
如:I found everythingin good condition. 我发现一切正常。
Her illness kept her in bed for a week. 她因生病在床上躺了一星期。
注:用作宾语补足语的介词短语在相应的被动语态中则为主语补足语:
如:He was regarded as a hero. 他被看成是英雄。
5、宾语:
如:A man stepped out from behind the wall. 一个人从墙后走出来。
He cannot spare anytime except on Sunday. 除星期日外,他抽不出时间。
6、主语:
如:Between6 and 7 suits me. 六点到七点对我比较适合。
After the exams is the time to relax. 考试后是轻松一下的时间。
注:介词短语通常不用作主语,尽管有时也像上面这样用作主语,但通常可视为是在一定的上下文中有所省略:
如:—When are we going to have the next meeting? 我们下次什么时候见面?
—On Tuesday may be convenient. 星期二可能比较方便。
此句中onTuesday虽用作主语,但可视为是其前省略了meeting一词:
即:Meeting during the vacation may be convenient.
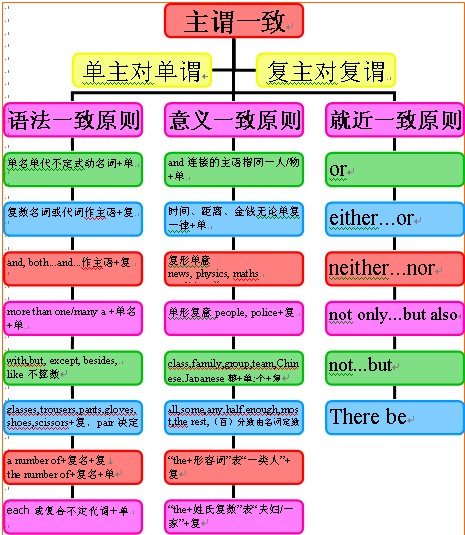
主谓一致的概念:
谓语的数必须和主语的人称和数保持一致,这就叫主谓一致。
主谓一致的基本原则:
1)语法一致原则,即在语法形式上取得一致。例如,主语是单数形式,谓语动词也采取单数形式;主语是复数形式,谓语动词也采取复数形式。
例如:The students are very young.
This picture looks beautiful.
2)意义一致原则,即从意义着眼处理一致关系。例如,主语形式虽是单数但意义是复数,谓语动词也采取复数形式;
而有些主语形式虽是复数但意义上看作单数,谓语动词也采取单数形式。
例如:The people in that country are fighting for independence.
The crowd deeply respect their leader.
Three years in a strange land seems a long time.
3)就近原则,即谓语动词的单数或复数形式取决于最靠近它的词语。
例如:Neither hen or I am going to see the film tonight because we are busy.
几对容易混淆词组的一致用法:
1、由“this/thatkind/typeof+名词”作主语,谓语动词用单数形式;而由"these/thosekind/typeof+复数名词”作主语,谓语动词用复数形式。
例如:This kind of apples is highly priced.
Those kind(s) of tests are good.
2、由“a number of,a totalo f,an average of+复数名词”作主语,谓语动词用复数形式;由“the number of,the total of,the average of+复数名词”作主语,谓语动词用单数形式。
例如:A number of students are waiting for the bus.
The number of the students in this university is increasing yearly.
3、one of,the(only) one of的一致用法
例如:This is one of the books that have been recommended.
This is the(only) one of the books that has been recommended.
主谓一致用法点拨:
1、并列结构作主语谓语用复数:
如:Reading and writing are very important.
注意:当主语由and连结时,如果它表示一个单一的概念,即指同一人或同一物时,谓语动词用单数,and此时连接的两个词前只有一个冠词。
如:The iron and steel industry is very important to our life.
典型例题:
The League secretary and monitor___asked to make a speech at the meeting.
A. is
B. was
C. are
D. were
答案:B.
注:先从时态上考虑。这是过去发生的事情应用过去时,先排除A、C本题易误选D,因为The League secretary and monitor 好象是两个人,但仔细辨别,monitor前没有the,在英语中,当一人兼数职时只在第一个职务前加定冠词。后面的职务用and相连。这样本题主语为一个人,所以应选B。
2、主谓一致中的靠近原则:
1)当there be句型的主语是一系列事物时,谓语应与最邻近的主语保持一致。
例如:There is a pen, a knife and several books on the desk.
There are twenty boy-students and twenty-three girl-students in the class.
2)当either…or…与neither…nor,连接两个主语时,谓语动词与最邻近的主语保持一致。
如果句子是由here, there引导,而主语又不止一个时,谓语通常也和最邻近的主语一致。
例如:Either you or she is to go.
Here is a pen, a few envelops and some paper for you.
3、谓语动词与前面的主语一致:
当主语后面跟有with, together with, like, except, but, no less than, as well as等词引起的短语时,谓语动词与前面的主语一致。
例如:The teacher together with some students is visiting the factory.
He as well as I wants to go boating.
4、谓语需用单数:
1)代词each和由every, some, no, any等构成的复合代词作主语,或主语中含有each,every,谓语需用单数。
例如:Each of us has a tape-recorder.
2)当主语是一本书或一条格言时,谓语动词常用单数。
例如:The Arabian Night is a book known to lovers of English.
3)表示金钱,时间,价格或度量衡的复合名词作主语时,通常把这些名词看作一个整体,谓语一般用单数。(用复数也可,意思不变。)
例如:Three weeks was allowed for making the necessary preparations.
Ten yuan is enough.
5、指代意义决定谓语的单复数:
1)在代词what, which, who, none, some, any, more, most, all等词的单复数由其指代的词的单复数决定。
例如:All is right. (一切顺利。)
All are present. (所有人都到齐了。)
2)集体名词作主语时,谓语的数要根据主语的意思来决定。
例如:family, audience, crew, crowd, class, company, committee等词后用复数形式时,意为这个集体中的各个成员,用单数时表示该个集体。
例如:His family isn't very large. 他家不是一个大家庭。
His family are music lovers. 他的家人都是音乐爱好者。
但集合名词people, police, cattle, poultry等在任何情况下都用复数形式。
例如:Are there any police around?
3)有些名词,如variety, number, population, proportion, majority等有时看作单数,有时看作复数。
A number of+名词复数+复数动词。 The number of+名词复数+单数动词。
例如:A number of books have lent out.
The majority of the students like English.
6、与后接名词或代词保持一致:
1)用half of, part of, most of, a portion of等词引起主语时,动词通常与of后面的名词,代词保持一致。
例如:Most of his money is spent on books.
Most of the students are taking an active part in sports.
2)在一些短语,如many a或more than one所修饰的词作主语时,谓语动词多用单数形式。
但由more than…of作主语时,动词应与其后的名词或代词保持一致。
例如:Many a person has read the novel. 许多人都读过这本书。
More than 60percent of the students are from the city. 百分之六十多的学生都来自这个城市
主谓一致知识体系:
主谓一致用法拓展:
1)当everyone,everybody,noone,nobody,anyone,anybody,someone,somebody,everything,anything,something,nothing等用作主语时,其相应的代词一般用单数形式。
例如:If anybody calls, tell him that I'm out.
Something strange happened, didn't it?
2)人称代词与名词的呼应:人称代词I(me),he(him),she(her),it(it) 都是代替前面的单数名词,而they(them),we(us)则是代替复数名词的,you既可以代表单数,也可以代表复数。但表示泛指的时候,用he或one来表示。
例如:If a young person enters a classical music field only for money, he is in the wrong profession.
3)物主代词与名词的呼应:my,our,his,her,its,their要与代替的名词在数上一致。
例如:The welfare department,as well as the other social services,will have its budget cut.
4)反身代词与其所代成分间的呼应。
例如:Many primitive people believed that by eating ananimal they could get some of the good qualities of that animal for themselves.
5)指示代词与所代名词间的呼应:this和that指代单数名词或不可数名词,these和those指代复数名词(those还可以用作先行词,引导定语从句,表示“那些人”)。
例如:She invited all those who had been her former colleagues.
6)much和muchof后接不可数名词,而many和manyof后接可数名词的复数。
例如:There is not much coal left.
A great many of the houses were knocked down by the earthquake.
7)表示量的词后面有的接可数名词,有的接不可数名词。
接可数名词的有:a number of,a rangeof,a series of十复数名词;
接不可数名词的有:a great deal of,an amount of十不可数名词;
既可接可数又可接不可数名词的有:a lot of,a variety of。
例如:1.The government attached a great deal of importance to education.
2.Quiteanumberofwomenappliedforthisjob.
3.The college library has avariety of books.
4.An apple is avariety off ruit.
与“Our county _____ vegetables.[ ]A. is rich inB. are rich i...”考查相似的试题有:
- The computer system broke _____ suddenly while he was searching for information on the Internet.A.downB.outC.upD.in
- Mary came late not ___ the heavy rain, but ___ she was ill.A.because, becauseB.because, because ofC.because of, be...
- He is a man of ______ ideas and he often makes a careful plan ______.[ ]A. advanced; before advanceB. advancing ; in ...
- A friend of mine will go to France________Hong Kong,and we agree to contact each other________email.A.via;byB.acr...
- 32. I suggested that they set off early to avoid (避开) the traffic jam, ____________ no one responded.A.on whichB....
- He suddenly saw Sue _____ the room. He pushed his way ______ the crowd ofpeople to get to her?[ ]A. across; acrossB. ...
- _We must read not only between the lines,but sometimes_______the lines so that we can fully understand the writer.A....
- ___________ the little boy John they would all have died from the gas leakage.A.Except forB.ExceptC.But forD.For all
- About 6% of the population in New Zealand _________ Asians.A.areB.isC.make upD.are from
- The boy sitting by the window is the only one of the students who from the countryside in our school. A.areB.isC.w...