本试题 “My father said he ______ me a present unless I _____ in passing all the exams.[ ]A. had not given; had not succeededB. would not give; succeededC. ...” 主要考查您对一般现在时
一般将来时
等考点的理解。关于这些考点您可以点击下面的选项卡查看详细档案。
- 一般现在时
- 一般将来时
一般现在时的概念:
表示通常性、规律性、习惯性的状态或者动作(有时间规律发生的事件)的一种时间状态。
一般现在时的用法:
1)经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频度的时间状语连用。常用的时间状语有every...,sometimes,at...,on Sunday等。
例如:I leave home for school at 7 every morning. 每天早上我七点离开家。
2)客观真理,客观存在,科学事实。
例如:The earth moves around the sun. 地球绕太阳转动。
Shang hai lies in the east of China. 上海位于中国东部。
3)表示格言或警句。
例如:Pride goes before a fall. 骄者必败。
注意:此用法如果出现在宾语从句中,即使主句是过去时,从句谓语也要用一般现在时。
例如:Columbus proved that the earth is round. 哥伦布证实了地球是圆的。
4)现在时刻的状态、能力、性格、个性。
例如:I don't want so much. 我不要那么多。
Ann writes good English but does not speak well. 安英语写得不错,讲的可不行。
比较:Now I put the sugar in the cup. 把糖放入杯子。
I am doing my homework now. 我正在做功课。
第一句用一般现在时,用于操作演示或指导说明的示范性动作,表示言行的瞬间动作。
第二句中的now是进行时的标志,表示正在进行的动作的客观状况,所以后句用一般现在时。
一般现在时知识体系:

一般现在时用法拓展:
1、一般现在时表将来:
1)下列动词come, go, arrive, leave, start, begin, return的一般现在时可以表示将来,主要用来表示在时间上已确定或安排好的事情。
例如:The train leaves at six tomorrow morning. 火车明天上午六点开。
—When does the bus star? 汽车什么时候开
—It stars in ten minutes. ?十分钟后。
2)以here, there 等开始的倒装句,表示动作正在进行。
例如:Here comes the bus.=The bus is coming. 车来了。
There goes the bell.=The bell is ringing. 铃响了。
3)在时间或条件句中。
例如:When Bill comes(不是will come), ask him to wait for me. 比尔来后,让他等我。
I'll write to you as soon as I arrive there. 我到了那里,就写信给你。
4)在动词hope, take care that, make sure that 等的宾语从句中。
例如:I hope they have a nice time next week. 我希望他们下星期玩得开心。
Make sure that the windows are closed before you leave the room. 离开房间前,务必把窗户关了。
2、一般现在时代替一般将来时:
When, while, before, fter, till, once, as soon as, so long as, by the time, if, in case(that), unless, even if, whether, the moment, the minute, the day, the year, immediately等引导的时间状语从句,条件句中,用一般现在时代替将来时。
例如:He is going to visit her aunt the day he arrives in Beijing. 他一到北京,就去看他姨妈。
3、一般现在时代替一般过去时:
1)"书上说","报纸上说"等。
例如:The news paper says that it's going to be cold tomorrow. 报纸上说明天会很冷的。
2)叙述往事,使其生动。
例如:Napoleon's army now advances and the great battle begins. 拿破仑的军队正在向前挺进,大战开始了
4、一般现在时代替现在完成时:
1)有些动词用一般现在时代替完成时,如hear, tell, learn, write, understand, forget, know, find, say, remember等。
例如:I hear(=haveheard)he will go to London. 我听说了他将去伦敦。
I forget(=have forgotten)how old he is. 我忘了他多大了。
2)用句型"It is…since…"代替"It has been…since…"。
例如:It is(=has been)five years since we last met. 从我们上次见面以来,五年过去了。
5、一般现在时代替现在进行时:
在Here comes…/There goes…等句型里,用一般现在时代替现在进行时。
例如:There goes the bell.铃响了。
时态一致:
1、如果从句所叙述的为真理或相对不变的事实,则用现在时。
例如:At that time, people did not know that the earth moves. 那时,人们不知道地球是动的。
He told me last week that he is eighteen.上星期他告诉我他十八岁了。
2、宾语从句中的,助动词ought, need, must, dare的时态是不变的。
例如:He thought that I need not tell you the truth. 他认为我不必告诉你真相。
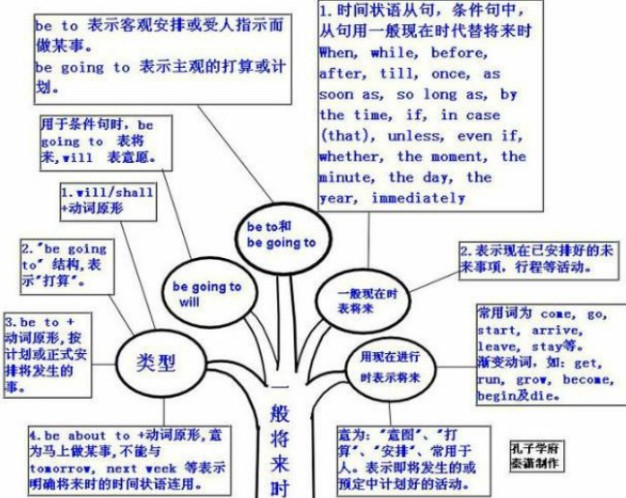
一般将来时的概念:
一般将来时表示将来某一时刻的发生动作或状态,或将来某一段时间内经常的动作或状态。常与表示将来的时间状语连用。
一般将来时用法:
1)shall用于第一人称,常被will所代替。will在陈述句中用于各人称,在征求意见时常用于第二人称。
例如:Which paragraph shall I read first?我先读哪一段呢?
Will you be at home at seven this evening? 今晚七点回家好吗?
2)be going to+不定式,表示将来。
a. 主语的意图,即将做某事。
例如:What are you going to do tomorrow? 明天打算作什么呢?
b. 计划,安排要发生的事。
例如:The play is going to be produced next month。这出戏下月开播。
c. 有迹象要发生的事。
例如:Look at the dark clouds, there is going to be a storm. 看那乌云,快要下雨了。
3)be+不定式表将来,按计划或正式安排将发生的事。
例如:We are to discuss the report next Saturday. 我们下星期六讨论这份报告。
4)be about to+不定式,意为马上做某事。
例如:He is about to leave for Beijing. 他马上要去北京。
注意:be about to do不能与tomorrow, next week 等表示明确将来时的时间状语连用。
一般将来时知识体系:
一般现在时表将来:
1)下列动词come, go, arrive, leave, start, begin, return的一般现在时可以表示将来,主要用来表示在时间上已确定或安排好的事情。
例如:The train leaves a tsix tomorrow morning. 火车明天上午六点开。
—When does the bus star? 汽车什么时候开?
—It stars in ten minutes. ?十分钟后。
2)以here, there等开始的倒装句,表示动作正在进行。
例如:Here comes the bus.=The bus is coming. 车来了。
There goes the bell.=The bell is ringing. 铃响了。
3)在时间或条件句中。
例如:When Bill comes(不是will come), ask him to wait for me. 比尔来后,让他等我。
I'll write to you as soon as I arrive there. 我到了那里,就写信给你。
4)在动词hope, take carethat,makesurethat等的宾语从句中。
例如:I hope they have a nice time next week. 我希望他们下星期玩得开心。
Make sure that the windows are closed before you leave the room. 离开房间前,务必把窗户关了。
现在进行时表示将来:
下列动词come, go, arrive, leave, start, begin, return等现在进行时可以表示将来。
例如:I'm leaving tomorrow. 明天我要走了。
Are you staying here till next week? 你会在这儿呆到下周吗?
与“My father said he ______ me a present unless I _____ in p...”考查相似的试题有:
- ---Mr. White didn’t come last night, did he?---No. We for him. A whole night was wasted.A. had waited B. have been wa...
- My daughter________ hard for more than one year to realize her dream joining the Party and now her dream comes true.A...
- Opposite my school _______ a book store, _______ was built ten years ago.A.is standing, whichB.stood, itC.stands, ...
- If you be in time for the early bus , be sure to get up before five o’clock in the morning.A.are toB.are about toC...
- We________ up by an alarm clock every morning.A.wakeB.are wakenC.were wakenD.woke
- ----What’s the noise?----Oh, my neighbour’s house ________. They want to move into it next month.A.was decoratedB.w...
- 24.You'd better wash the shirt in cold water, or the color ______. A.runsB.is runningC.will runD.has run
- .——I hear you___in a pub. What’s it like?——Well, it’s very hard work and I’m always tired, but I don’t mind.A.are wo...
- I'm tired out.I ________ all afternoon and I don't seem to have finished anything.A.shoppedB.have shoppedC.had sho...
- If city noises _____ from increasing, people _____ shout to be heard even at the dinner table20 years from now.[ ]A. ...