本试题 “_________is reported in the newspaper,_________ no need to go shopping to the supermarket,for shopping online is so convenient.[ ]A. It ; it isB. I...” 主要考查您对关系代词
非限制性定语从句
there be句型
等考点的理解。关于这些考点您可以点击下面的选项卡查看详细档案。
- 关系代词
- 非限制性定语从句
- there be句型
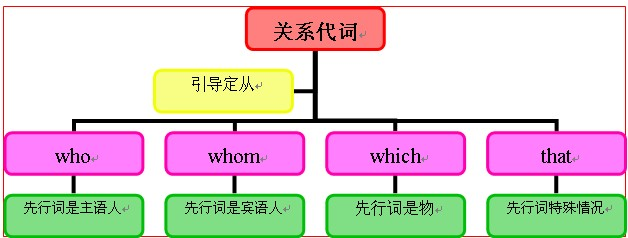
关系代词的概念:
英语中的关系代词有who, whom, whose, that, which, 它们是用来引导定语从句的。关系代词既代表定语从句所修饰的词,又在其所引导的从句中承担一个成分,如主语、宾语、表语、或定语。
如:This is the man who saved your son. (who在从句中作主语,先行词是man)
The man whom I met yesterday is Jim.
A child whose parents are dead is an orphan.
He wants a room whose window looks out over the sea.
关系代词用法:
1、that与which的用法区别:
两者都可指物,常可互换。其区别主要在于:
(1)引导非限制性定语从句时,通常要用which:
如:She received an invitation from her boss, which came as a surprise. 她收到了老板的邀请,这是她意想不到的。
(2)直接放在介词后作宾语时,通常要用which:
如:The tool with which he is working is called a hammer. 他干活用的那个工具叫做锤子。
(3)当先行词是下列不定代词或被它们修饰时much, little, none, all, few, every(thing), any(thing), no(thing)等时,通常用that:
如:There was little that the enemy could do but surrender. 敌人无法,只有投降了。
All[Everything] that can be done must be done. 凡能做的事都必须做。
(4)当先行词有the very, the only, the same等修饰时,通常用that:
如:This is the only example that I know. 我知道的例子只有这一个。
Those are the very words that he used. 那是他的原话。
(5)当先行词有形容词最高级或序数词(包括last, next等)等修饰时,通常用that:
如:This is the best dictionary that I've ever used. 这是我用过的最好的词典。
The first thing that you should do is to work out a plan. 你应该做的第一件事是订个计划。
(6)当关系代词在定语从句中用作表语时,通常用that:
如:China is not the country(that) it was. 中国已不是过去的中国了。
(7)当先行词是一个既指人又指物的并列词组时,通常用that:
如:They talked about the persons and things that most impressed them. 他们谈论了使他们印象最深的人和事。
(8)当要避免重复时:
如:Which is the course that we are to take? 我们选哪门课程?
2、that与who的用法区别:
(1)两者均可指人,有时可互换:
如:All that[who] heard him were delighted. 所有听了他讲话的人都很高兴。
Have you met anybody that[who] has been to Paris? 你遇见过到过巴黎的人吗?
He is the only one among us that[who] knows Russian. 他是我们中间唯一懂俄语的人。
(2)但是在下列情况,通常要用that:
①当先行词是一个既指人又指物的并列词组时:
如:I made a speech on the men and things that I had seen abroad. 我就我在国外所见到的人和事作了报告。
②当先行词是who时(为避免重复):
如:Who was it that won the World Cup in1982? 谁赢得了1982年的世界杯?
③当关系代词在定语从句中作表语时(可省略):
如:Tom is not the boy(that) he was. 汤姆这孩子已不是以前那个样子了。
关系代词知识体系:
关系代词用法拓展:
1、as与which的用法区别:
(1)引导限制性定语从句时,在such,as,thesame后只能用as,其他情况用which:
如:I never heard such stories as he tells. 我从未听过他讲那样的故事。
It's the same story as I heard yesterday. 这故事跟我昨天听到的一样。
This is the photo which shows my house. 这张照片拍的是我的住宅。
(2)引导非限制性定语从句时,有时两者可互换:
如:I live a long way from work, as [which] you know. 我住得离工作单位很远,这你是知道的。
(3)但在,在以下情况引导非限制性定语从句时,两者不可换用:
①当从句位于主句前面时,只用as:
如:As is known to everybody, the moon travels round the earth once every month. 月球每月绕地球转一周,这是每个人都清楚的。
②as引导的非限制性定语从句应与主句在意义上和谐一致,which无此限制:
如:He went abroad, as[which] was expected. 他出国了,这是大家预料到的。
He went abroad, which was unexpected. 他出国了,这让大家感到很意外。(不用as)
③as引导非限制性定语从句时,先行词通常不能是主句中某个具体的词,而应是整个句子、整个短语或某个短语推断出来的概念,而which则无此限制:
如:The river, which flows through London, is called the Thames. 这条流经伦敦的河叫泰晤士河。(不用as)
④当as引导非限制性定语从句作主语时,其谓语通常应是连系动词,而不宜是其他动词,而which则无此限制:
如:She has married again, as[which] seemed natural. 她又结婚了,这似乎很自常。
She has married again, which delighted us.她又结婚了,这使我们很高兴。(不用as)
2、who与whom的用法区别:
两者均只用于人,从理论上说,who为主格,whom为宾格:
如:Where's the girl who sells the tickets? 卖票的女孩在哪里?
The author whom you criticized in your view has written a letter in reply. 你在评论中批评的那个作者已写了一封回信。
但实际上,除非在正式文体中,宾格关系代词whom往往省略不用,或用who或that代之:
如:The man(that, who, whom) you met just now is called Jim. 你刚遇见的那个人叫吉姆。
不过,在以下几种情况值得注意:
(1)直接跟在介词后面作宾语时,只能用whom,而且不能省略:
如:She brought with her three friends, none of whom I had ever met before. 她带了3个朋友来,我以前都没见过。
(2)引导非限制性定语从句且作宾语时,who和whom均可用,但以用whom为佳,此时也不能省略:
如:This is Jack, who[whom] you haven't met before. 这是杰克,你以前没见过。
非限制性定语从句的概念:
非限制性定语是对被修饰名词或代词的附加说明,它不是必需的,如果去掉,也不会影响句子的意思,它与被修饰名词之间通常用逗号分开。
如:The travellers, knowing about the floods, took another road. 游客们知道发了大水,都改道走了。
The boys, wanting to play football, were disappointed when it rained. 那些男孩子想踢足球,因为下雨感到失望。
非限制性定语从句用法:
1、引导非限定性定语从句时,只能用which(不用that)。
例如:Heat is another form of energy, which is as important as other kinds of energy.
热是另一种形式的能量,与其他形式的能量一样重要。 (从句表补充说明,而且关系代词which不能换成that。)
2、引导非限定性定语从句的which可以指代前面的先行词,也可以指前面整个句子的含义。
例如:That Peter will marry Alice, which has not been announced yet, has spread around.
彼特要娶爱丽斯这件事还没宣布,却已传得沸沸扬扬。(句子中的which指“彼特要娶爱丽斯”这整个句子的意思。)
3、除which外,还可用when,where,who等关系代、副词引导非限定性定语从句。
例如:After graduation, I decided to stay in Chongqing, where I spent my childhood and four years of college life.
毕业后,我决定留在重庆,在那里我曾度过了我的童年和四年大学生活。
Albert Einstein left Germany for the United States during World WarII, when Jews were badly treated in Germany.
第二次世界大战期间,爱因斯坦离开德国去了美国,那时犹太人在德国受到不好的对待。
4、在限定性定语从句中作宾语时,引导词可以省略,但引导非限定性定语从句的关联词不能省。
如:He was eager to go to the hospital to see his stepmother, whom he loved and respected as his own mother.
他急于想去医院看望他的继母,他把他的继母当作亲生母亲一样热爱和尊敬。
The American journalist(whom/who) the announcer mentioned in the news broadcast is said to have been killed by the gangsters.
播音员在新闻广播中提到的那位美国记者据说已经被匪徒杀害了。
两例中的关系代词都在从句中作宾语。由于第二例是限定性定语从句,可以省略关系代词;第一例中的引导词不能省略,因为它引导的是非限定性定语从句。
5、表示“正如”的含义时,通常用as引导非限定性定语从句,也可用which引导;但置于句首时,只能用as引导。
如:China has basically succeeded in defeating SARS, which/as we have expected.
正如我们所预料的那样,中国已基本上战胜了“非典”。
As is well known to everybody, Tai wan is an inseparable part of China.
众所周知,台湾是中国不可分割的一部分。
但是当非限定性定语从句是否定含义时,就只能用which(而不用as)引导。
如:He didn't win the championship, which I hadn't expected.
他没获得冠军,这一点是我没预料到的。
非限制性定语丛句中as, which的区别:
1、which引导非限制性定语丛句代表前面的整个句子的时候,一般是对主句的结果的说明。
如: He grows too fast, which makes him taller than his classmates.
2、as引导非限制性丛句代表前面整个句子时一般来讲丛句的谓语动词有三种:
A. 含有be动词:
如:He failed the exam, as is natural.
B. 实意动词的被动形式:
如:As is reported, the fire caused a great loss.
C.感官动词和意识类动词如:
如:see, hear, notice, know, learn, realize 等。
As you know, I am a teacher.
3、as可翻译为正如,它引导的丛句可位于主句之前,也可位于主句之后;which引导的该丛句只能位于主句之后。
例1:__A___he realized, I was very useful to him.
例2:This elephant is like a snake, ___A__anybody can see.
例3:The sun gives us light and heat, __B___makes the plan tgrow well.
A. As(as)
B. which
C. that
D. who
限定性定语从句与非限定性定语从句的区别:
|
定 |
限制性定语从句 | 非限制性定语从句 |
| 1、不能省略,如果省略整个句子意思不完整。 | 可以省略,如果省略整个句子意思仍然完整。 | |
| 2、可以用that引导。 | 不可以用that引导。 | |
| 3、关联词有时可以省略。 | 关联词不可以省略。 | |
| 4、不用逗号把它和句子的其他部分隔开。 | 用逗号把它和句子的其他部分隔开。 | |
| 5、只能修饰先行词。 | 可以修饰先行词,也可以修饰整个句子或句子的一部分。 |
非限制性定语从句的关系词:
| 关系代词 | 指代对象 | 指代人 | 指代物 |
| 主格 | who | which, as | |
| 宾格 | whom | which, as | |
| 所有格 | of, whom, whose | which, of which, whose | |
| 关系副词:when, where | |||
非限定性定语从句的使用规则及注意事项:
1、which引导的非限定性定语从句是用来说明前面整个句子的情况或主句的某一部分。
2、在引导限定性定语从句时,that有时相当于in which, at which, for which或at which。其中,介词的选用,依据从句中的动词所需搭配的介词来选用。例句:
① Attitudes towards day dreaming are changing in much the same way that(inwhich)attitudes towards night dreaming have changed.
人们对白日做梦的态度正在改变,这与人们对夜间做梦的看法的变化有非常相似之处。
② I like the music for the very reason that(for which) he dislike it.
我出于某种原因喜欢这种音乐,而他恰恰与我相反。
③ We arrived the day that(on which) they left.
刚好我们到的那天他们走了。
3、as有时也可用作关系代词。
4、在非限定性定语从句中,关系词不能用that。
there be句型的概念:
英语中的there be结构主要表示某处存在有某物,所以通常被称为存在句。其中的there为引导词,无词义,be为谓语动词,therebe后面的名词为句子主语。
therebe结构的否定式和疑问式:
1、否定式:
there be结构的否定式通常应将否定词置于动词be之后:
如:There is not any bread left. 没有一点面包了。
There isn't anything I can do for you. 我帮不了你什么忙。
若谓语中包括有助动词或情态动词,通常将否定词置于助动词与情态动词之后:
如:There can't be so many mistakes. 不可能有那么多错误。
There shouldn't be any doubt about it. 对此不应有什么怀疑。
There haven't been any parties in weeks. 好几个礼拜没开过晚会了。
另外注意以下类型的否定式:
如:There doesn't seem to have been any difficulty over the money question. 在钱的问题上似乎没发生什么困难。
2、疑问式:
there be结构的疑问式通常应将否定词置于动词be之后:
如:Is there any good film on? 映什么好电影吗?
Is there room for me in the car? 车子里还有我坐的地方吗?
Are there any letters for me? 有我的信吗?
若谓语中包括有助动词或情态动词,通常将助动词或情态动词移至句首构成疑问式:
如:Has there been an accident? 出事了吗?
Have there been any new developments? 有什么新的发展吗?
Can there have been so much rain there?那儿会下过那么多雨吗?
另外注意以下类型的疑问式:
如:Uncle Jesse, why do there have to be poor people like those? 杰西叔,为什么一定要有他们那样的穷人?
there be结构的谓语形式:
1、主谓一致问题:
若只有一个主语,谓语的数则取决于该主语的数;若有几个主语并列,则通常是与靠近的主语保持一致:
如:There is a man at the door. 门口有个人。
There are some girls in the room. 房间里有几个女孩。
There is a pen and some books on the desk. 桌上有一支钢笔和一些书。
2、时态问题:
there be结构的时态由其中的谓语动词be来体现,它可以有一般现在时、一般将来时、一般过去时、现在完成时以及过去完成时等多种时态形式:
如:There is going to be[will be] an English film tonight. 今晚将有一场英语电影。
There was a lot to be done. 有很多事要做。
There were some children swimming in the river. 有些小孩在河里游泳。
There have been many such accidents. 已发生了好几起那样的事故。
There had been two seafights between them. 他们之间发生了两场海战。
3、与情态动词连用:
there be结构有时可以与情态动词连用:
如:There may be a storm tomorrow. 明天可能有风暴。
There used to be a hospital here. 原来这里有家医院。
He felt there must be something wrong. 他感到准有什么问题。
There might still be hope. 可能还有希望。
There ought to be a comma here. 这儿应有一个逗号。
4、动词be换成其他动词:
有时可将there be中的动词:be换为live, remain, seem, appear, exist, stand, lie, come等:
如:Once upon a time there lived a man known by the name of Joe Beef. 从前有个人名叫乔·比夫。
There seems[appears] something the matter with her. 她好像是出了什么事似的。
There existed different opinions on this problem. 对这个问题曾有不同看法。
There remained just twenty-eight pounds. 只剩28英镑了。
At the top of the hill there stands an old temple. 在小山顶上有一座古庙。
5、与其他动词搭配使用:
there be结构有时可与其他动词搭配使用,构成一种复合谓语:
如:There seemed to be nobody about, so I went in. 附近似乎没有人,因此我就走了进去。
There happened to be a man walking by. 恰好有一个人从旁经过。
therebe结构的非谓语形式:
基本结构:there be结构的非谓语形式有两种基本结构,即there being和there to be:
1、there being结构该结构的主要用法有:
(1)用作状语:
如:There being nothing else to do, we went home. 由于没什么其他的事要干,所以我们就回家了。
There having been no rain, the ground was dry. 由于没有下雨,所以地面很干。
【注】有时可与状语从句转换:
如:There being no further business(=As there was no further business), I declared the meeting closed. 由于没有别的事了,我宣布闭会。
(2)用作介词宾语:
如:There is now some hope of there being a settle ment of the dispute. 现在有点希望可以解决这次争端。
2、There to be结构该结构的主要用法有:
(1)用作动词宾语:该结构可用作某些动词(如like, prefer, hate, want, mean, intend, expect, consider等)的宾语:
如:I don't want there to be any misunderstanding. 我可不希望有任何误解。
Students hate there to be too much homework. 学生讨厌做太多的家庭作业。
We expect there to be more discussion about this. 我们期望能对此展开更多的讨论。
【注】在let there be结构中,动词be不带to:
如:Don't let there be any noise. 不允许有任何吵闹。
Let there be no mistake about it. 这事不要出错。
(2)用作介词for的宾语:
如:They asked for there to be another meeting. 他们要求再开一次会议。
【注】用作介词宾语一般用there being,但用作介词for的宾语时,只能用there to be。
比较:They planned on there being another meeting. 他们打算再开一次会议。
They planned for there to be another meeting. 他们打算再开一次会议。
几个重要句型和结构:
1、There is no doing结构:
其意为“不可能…”、“无法…”:
如:There's no denying the fact. 这一事实不容否认。
There is no getting over the difficulty. 这困难无法克服。
There is no knowing what he will do next. 无法知道他下一步要干什么。
There was no telling when she would be back. 没法知道她什么时候回来。
2、There is no difficulty in doing sth结构:
意为“做某事没有困难”:
如:There is no difficulty in finding his office. 找到了他的办公室没费一点劲。
There was no difficulty in carrying out the plan. 执行这项计划没什么困难。
3、There's no doubt…结构:
意为“毫无疑问…”:
如:There is no doubt of his success. 毫无疑问他一定会成功。
There could be no doubt that he was one of the best writer in this country. 毫无疑问他是这个国家最优秀的作家之一。
4、There is no hurry(to do sth)句式:
其意为“不用急(于做某事)”:
如:There's no hurry to return the book. 现在不急于还书。
There's no hurry, so do it slowly and carefully. 不用赶时间,要慢慢细心地做。
5、There's no need for…结构:
其意为“不需要或不必要…”:
如:There is no need for help. 不需要帮助。
There is no need for you to go. 你没有必要去。
6、There is no question about...结构:
其意为“…是毫无疑问的”:
如:There's no question about his success. 毫无疑问他会成功。
There's no question about his honesty. 毫无疑问他是诚实的。
7、There is no question of doing sth句式:
其意为“做某事是不可能的”:
如:There is no question of his coming. 他不可能会来。
There is no question of our arriving on time. 我们不可能准时赶到。
8、There is no sense in doing sth结构:
意为“做某事没有道理或好处”:
如:There's no sense in criticizing him. 批评他也没有用。
There's no sense in waiting three hours. 等三小时是不没有道理的。
9、There's no point in doing sth句式:
意为“做某事没有用”:
如:There's no point(in) telling her about it. 告诉她没有用。
如:There's no point in wasting time. 耗时间没用。
【注】以上有的结构中的no根据情况也可换成其他限定词:
如:There is some difficulty in doing sth 意为“做某事有些困难”。
There is much difficulty in doing sth 意为“做某事许多困难”。
There's a need for… 意为“需要或有必要…”。
10、“there be+名词+动词”结构:
(1)there be+宾语+现在分词现在分词表示主动关系,同时表示动作正在进行:
如:There is some one waiting for him. 有人在等他。
There was a man standing in front of me. 我前面站着一个男人。
There were some children swimming in the river. 有些小孩在河里游泳。
There were a group of young people working in the fields. 有一群青年在地里劳动。
有时现在分词可表示一种状态:
如:There's a piano standing against the wall. 靠墙有一架钢琴。
There're a lot of difficulties facing us. 我们面前有很多困难。
There is a door leading to the garden. 有一座门通往花园。
有个别现在分词用于该结构时可以表示将来(正如它们可用进行时表示将来一样):
如:There are ten people coming to dinner. 有10个人来吃晚饭。
(2)there be+宾语+过去分词过去分词表示一种被动关系,同时表示动作已经发生:
如:There is nothing written on it. 上面没写东西。
There were ten people killed in the accident. 事故中有10人丧生。有时过去分词也可表示一种状态(可转换成被动结构):
There were some old men seated(=who were seated)in the back. 有些老人坐在后面。
There is a red car parked(=which is parked)outside the house. 房子外边停着一辆红色汽车。
(3)therebe+宾语+不定式不定式通常表示动作尚未发生:
如:There was nobody to look after the child. 没有人照顾这孩子。
There was a large crowd to send him off. 有一大群人要来给他送行。
There was so much to lose that we couldn't take any risks. 可能会有很大的损失,因此我们不能冒险。
【注】当其中的宾语与其后的不定式为被动关系时,可用主动表被动,也可用被动式:
如:There is much work to do[to be done]. 有许多工作要做。有时其中的不定式为系表结构:
There is nothing to be afraid of. 没什么可怕的。
What was there to be afraid of. 有什么可怕的?
There's nothing to be ashamed of. 没有什么值得羞愧的。
与“_________is reported in the newspaper,_________ no need t...”考查相似的试题有:
- He advised the fanners to choose the best seed-heads,____ that had the best colour.A.the oneB.the onesC.oneD.ones
- — Have you got used to the Chinese food, Robert?— Yes. But I don't like _____ when a Chinese host keeps serving me th...
- The Chinese government has decided to develop the west of China,____,I dare say,will benefit thepeople there,especial...
- Whatever is left over may be put into the refrigerator, _____ it will keep for two or three weeks.A. whenB. whichC. w...
- Most electronic devices of this kind, _______ manufactured for such purpose, are tightly packed.[ ]A. that areB. as a...
- This is my dear teacher without_________help I couldn’t have passed that difficult exam.A.whoB.whomC.whoseD.that
- I passed by the sports field the other day,______ there was a football match going on then.[ ]A. thatB. whereC. which...
- Finding her car stolen, _____.A.a policeman was asked to helpB.the area was searched thoroughlyC.it was looked for...
- The doctor thought ________ would be good for you to have a holiday.A.thisB.thatC.oneD.it
- ____ is it to ask her about that? She doesn’t know it either.A.What goodB.How goodC.What a goodD.How much good