本试题 “请根据句子意思,选用适当词或用所给词的适当形式填空。1. I wish to express my __________ (appreciate) for your kindness and thoughtfulness.2. If you’...” 主要考查您对名词
形容词
从属连词
现在分词的完成式
过去分词
一般过去时
过去完成时
it的用法
等考点的理解。关于这些考点您可以点击下面的选项卡查看详细档案。
- 名词
- 形容词
- 从属连词
- 现在分词的完成式
- 过去分词
- 一般过去时
- 过去完成时
- it的用法
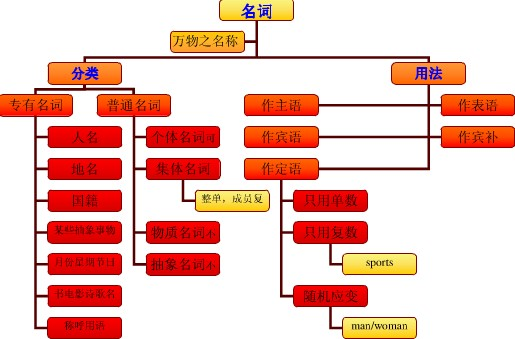
名词的概念:
名词(Nouns)是词性的一种,也是实词的一种,是指代人、物、事、时、地、情感、概念等实体或抽象事物的词。名词可以独立成句。在短语或句子中通常可以用代词来替代。名词可以分为专有名词(ProperNouns)和普通名词(CommonNouns),普通名词又可分为不可数名词和可数名词两大类。
名词的数:
1、名词复数的构成方法:
(1)在一般情况下,加词尾-s: book/books书 pen/pens钢笔 face/faces脸
(2)以s, x, z, sh, ch等结尾的名词,通常加词尾-es:bus/buses 公共汽车 box/boxes 盒子 dish/dishes 盘子
注:有些以ch结尾的名词,由于其发音不是[k]而是[tf],那么其复数形式应加词尾–s,如stomach/stomachs胃。
(3)以y结尾的名词,其复数构成要分两种情况:以“辅音字母+y”结尾的名词,将y改为ies;以“元音字母+y”结尾的名词,直接加词尾s:city/cities 城市 boy/boys 男孩 key/keys 钥匙
注:以y结尾的专有名词,若在某些特殊情况下需要复数,通常加s构成: Mary/Marys玛丽 Germany/Germanys德国
(4)以o结尾的名词,有些加词尾-s,有些加-es,有些加-s或-es均可: piano/pianos钢琴 tomato/tomatoes西红柿 zero/zero(e)s零
注:有人对英语中所有以o结尾的名词作了统计,一共近200个,其中绝大部分的复数形式通过加词尾-s构成,少数加词尾es。在中学英语范围内,加词尾es的主要有以下4个:
tomato西红柿,potato土豆,hero英雄,Negro黑人
(5)以f或fe结尾的名词,也有两种可能:即有些直接加词尾-s,有些则把f/fe改为ves: chief/chiefs首领 roof/roofs屋顶 knife/knives小刀
注:在中学英语范围内,要改f/fe为ves的只有以下10个词(它们都是日常生活中的常用词):
wife 妻子,life 生命,knife 小刀,leaf 树叶,thief 贼,half 一半,self 自己,shelf 架子,loaf 面包,wolf 狼。
另外,中学英语中的handkerchief(手帕)一词的复数有两种形式:handkerchiefs/handkerchieves,但在现代英语中,以用handkerchiefs为多见。
2、单数与复数同形式的名词:
中学英语中主要的有:sheep绵羊,fish鱼,deer鹿,Chinese中国人,Japanese日本人,Portuguese葡萄牙人,Swiss瑞士人,aircraft飞行器,means方法,series系列,head(牛等的)头数,works工厂,等。
注:fish有时也用fishes这样的复数形式,尤其表示种类时;
head若不是牲口的“头数”,而是表示“人的头”或“人数”,则要用heads这样的复数形式。
3、不规则的复数名词:
有的名词单数变复数时,没有一定的规则:
man/men男人 woman/women女人 child/children小孩 tooth/teeth牙齿 foot/feet脚 goose/geese鹅 mouse/mice老鼠 ox/oxen公牛
注:
(1)一些以man,woman结尾的合成词,在构成复数与man,woman的变化形式相同,如:
policeman/policemen警察,gentleman/gentlemen绅士,Englishman/Englishmen英国人,等等。但是human(人),German(德国人)不是合成词,其复数不能仿man的变化规律,而是按规则变化,即用humans,Germans。
(2)foot表示“英尺”时,其复数可以有两种形式feet/foot,如:
He is about six feet/foottall. 他大约6英尺高。
名词可数性的三个易错点:
(1)根据汉语习惯将英语的物质名词误认为是可数名词。如:
汉语中的“面包”,一般认为是可数的,可以说“一个面包”、“两个面包”等,但英语中的bread却通常是不可数的,不能相应地用a bread,two breads表示以上意思。不过有趣的是,loaf 表示“面包”却又是可数的,可说a loaf, two loaves。
(2)想当然地判断名词的可数性。如:
有的学生认为news (消息)和paper (纸)都不可数,于是便想当然地认为 newspaper (报纸)就一定不可数,但事实上,newspaper却是可数名词;又如:
有的同学认为 tear (眼泪)即“泪水”,并将其与water(水)相联系,认为tear 是不可数的,但事实上,tear却是可数的。
(3)受名词一词多义的影响。有的名词不止一个意思,且用于不同意思时,其可数性也有不同,不要形成思维思势。如:
aim表示“目的”时是可数名词,表示“瞄准”时是不可数名词;又如 experience表示“经验”时不可数,表示“经历”时则可数;再如:
fortune,当它表示“运气”时,不可数(=luck),当它表示“命运”时,可数,当它表示“财产”时,不可数,但可与a连用。
可数与不可数名词的常用修饰语:
(1)修饰可数名词的常用修饰语有:
these, those, few, a few, many, a good[great] many, agreat[good]number of 等。
注:a good[great]many后直接跟名词,没有介词of。
(2)修饰可数名词的常用修饰语有:
this, that, a few, a little, a bit of, much, no, a great deal of 等。
(3)有些修饰语既可修饰可数名词也可修饰不可数名词:
all, some, enough, a lot of, lots of, plenty of, a large amount of, a large quantity of等。
(4)有些名词形式上是复数,但却被用作不可数名词,使用much, little等修饰语:
He hasn't got much brains.他没什么头脑。
He took much pains to do the work. 他费了不少心做这工作。
I said I wouldn't want much wages. 我说过我不要很多工资。
It's high time you were taught a little manners.该是你学一点礼貌的时候了。
单位词与不可数名词数量表示法:
单位词是表示事物个体性的词语,不可数名词通常没有复数形式,也不可以用个数计算,要表示不可数名词的个体性需借助单位词:
a piece of paper一张纸
a piece of advice一条建议
a piece of news一条消息
an article of furniture一件家具
a cake of soap一块香皂
a slice of meat一块
a cup of tea一杯茶
a bottle of ink一瓶墨水
注:不要按汉语习惯在不该用单位词的地方错用单位词,如“一张邮票”只能说a stamp,而不能说a piece of stamp。
名词的可数性:
1、名词根据其可数性,可分为可数名词与不可数名词。一般说来,个体名词和大部分集合名词是可数的;而专有名词、物质名词、抽象名词以及少部分集合名词则通常是不可数的。但是这种区分只是大致的,原则性的,并不是绝对的。英语有些名词往往既是可数也可以是不可数的。
A:Would you like a cake? 要吃块蛋糕吗?
B:No, I don't like cake.不吃,我不喜欢吃蛋糕。
以上第一句用a cake,这是把cake视为一块一块的“蛋糕”,所以它是可数的;而第二句只用cake,这是把它当作物质名词看待,所以它成了不可数名词。
2、不同类别名词的可数性。
(1)专有名词的可数性。
在通常情况下,专有名词具有“独一无二”的含义,因此它通常没有复数形式,即不可数。但是,专有名词的独一无二性通常是相对的,随着范围的扩大,这种独一无二性便会受到破坏。
如在一个星期(week)内,只有一个星期六(Saturday),一个星期日(Sunday)等,但是在一个月中甚至一年中,便有多个星期六,多个星期日了。所以我们有时可以说:
We have spent many happy Sundays there. 我们在那儿度过了许多个愉快的星期日。
又如,在一个小范围内,可能只有一个Henry,但在一个较大的范围内则可能有多个Henry,因此我们有时会见到这样的句子:
There are five Henrys in our school. 我们学校有五个亨利。
另外,若专有名词转化成了普通名词,也可以是可数的:
Thousands of LeiFengs have emerged in China.中国涌现出了千千万万个雷锋。
(2)个体名词的可数性。
个体名词表示的是一个一个的人或物的个体,所以它通常是可数的。
(3)物质名词的可数性。
由于物质名词在通常情况下不能分为个体,所以它通常是不可数的。但是,在某些特殊情况下(如表示种类等),有些物质名词也可以连用不定冠词或用复数形式:
wine酒(不可数),a wine一种酒(可数), beer啤酒(不可数),two beers两杯啤酒(可数) ,glass玻璃(不可数),some glasses一些玻璃杯(可数)
(4)抽象名词的可数性。
抽象名词是表示事物性质、行为、状态、感情等抽象概念的,因此它通常是不可数的。但是,有时抽象名词也可转化为具体名词(可数),表示具有某种性质的人或事物:
success成功(不可数),asuccess成功的人或事(可数) ,pleasure愉快(不可数),apleasure令人愉快的人或事(可数)
(5)集合名词的可数性。集合名词表示若干个体组成的集合体,它本身通常是可数的,其复数形式表示多个集合体:
a family一个家庭,three families三个家庭 a team一个队,two teams两个队 a crowd一群人,crowds多群人
名词知识体系:
特殊名词的复数形式:
1、复合名词的复数形式。通常是将其主要名词变为复数:
passer-by/passers-by 过路人
shoe-maker/shoe-makers 鞋匠
looker-on/lookers-on 旁观者
on-looker/on-lookers 旁观者
father-in-law/fathers-in-law 岳父
若没有主要名词,则通常在最后一个词加s:
go-between/go-betweens中间人,
媒人 know-all/know-alls 万事通
注:由man/woman用于另一名词前构成的合成名词,两者均变为复数:
man doctor/men doctors男医生
woman writer/women writers 女作家
2、字母、文字、数字、符号等的复数形式。原则上加词尾-'s:
There are two i's in the word"skiing". skiing.这个词里有两个字母i。
如:Mind your p's and q's. 要谨言慎行。
All the–'s should be changed to+'s. 所有的正号应改为负号。
注:若不至于发生混淆,也可只加词尾s。
如:He was born in the 1930(')s. 他出生在20世纪30年代。
Your 3(')s look like 8(')s. 你写的3看起来像似8。
3、度量衡单位的缩写词的复数形式。
一般不加词尾-s:
m(meter, meters)米 km(kilometer, kilometers)千米 kg(kilogramme, kilogrammes)千克 cm(centimeter, centimeters)厘米;
有的缩写词也加s:
hr(hours)/hrs(hours)小时 No(number)/Nos(Numbers)号码;
有个别缩写词采用重复最后一个字母的方式构成复数形式:
p.10(page10)第10页 pp.10(pages10through15)第10至15页
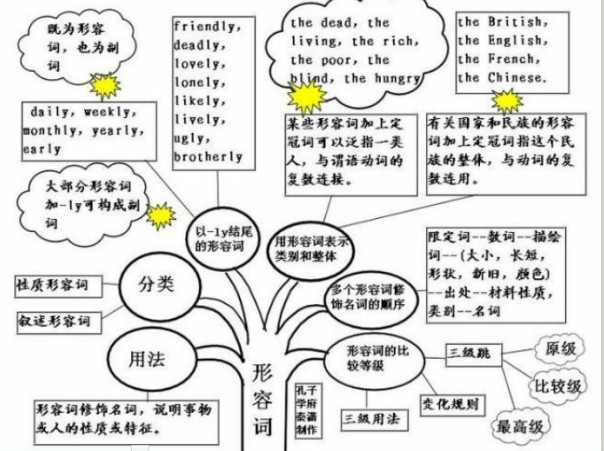
形容词的概念:
形容词(adjective),简称adj.或a,形容词用来修饰名词或代词,表示人或事物的性质、状态,和特征的程度好坏与否,形容词在句中作定语、表语、宾语补足语。通常,可将形容词分成性质形容词和叙述形容词两类,其位置不一定都放在名词前面。
形容词的作用与位置:
形容词是用来修饰名词的,常被放在名词前作定语,或放在系动词后面作表语。以下属几种特殊情况,须牢记;
(1)形容词短语作定语,定语后置。
如:a language difficult to master,
a leaning tower about 180 feet high
(2)表语形容词(afraid、alike、alone、asleep、awake、alive等)作定语,定语后置。如a man alive。有些表身体健康状况的形容词如well、faint、ill只作表语。sick既可作表语又可作定语,ill如作定语意为“bad”。
(3)用作定语,修饰由不定代词one、no、any、some和every构成的复合词如anything、something等时,通常后置。
如:I have something important to tell you.
(4)else常用作疑问代词和不定代词的后置定语。
(5)enough、nearby修饰名词前置或后置,程度副词一般位于形容词、副词前面,enough修饰形容词、副词时,必须后置。
(6)几个并列的形容词作定语,其语序通常为:限定语(The、A)+描绘性形容词+size(大小)+shape(形状)+age(年龄、时间)+color(颜色)+origin(国籍、来源)+material(材料)+purpose(目的)+名词。
口诀:
限定描绘大长高,形状年龄和新老;颜色国籍跟材料,作用类别往后靠。
如:a heavy black Chinese steel umbrella,
the man's first tow interesting little red French oil paintings
形容词的用法:
1、形容词修饰名词,说明事物或人的性质或特征。通常,可将形容词分成性质形容词和叙述形容词两类,其位置不一定都放在名词前面:
1)直接说明事物的性质或特征的形容词是性质形容词,它有级的变化,可以用程度副词修饰,在句中可作定语、表语和补语。例如:hot热的。
2)叙述形容词只能作表语,所以又称为表语形容词。这类形容词没有级的变化,也不可用程度副词修饰。
大多数以a开头的形容词都属于这一类。例如:
afraid害怕的。(错)Heisanillman. (对)Themanisill. (错)Sheisanafraidgirl. (对)Thegirlisafraid.
这类词还有:well,unwell,ill,faint,afraid,alike,alive,alone,asleep,awake等。
3)形容词作定语修饰名词时,要放在名词的前边。但是如果形容词修饰以-thing为字尾的词语时,要放在这些词之后。例如:somethingnice
2、用形容词表示类别和整体:
1)某些形容词加上定冠词可以泛指一类人,与谓语动词的复数连接。如:the dead,the living,the rich,the poor,the blind,the hungry The poorarelosinghope.穷人失去了希望。
2)有关国家和民族的形容词加上定冠词指这个民族的整体,与动词的复数连用。如:the British,the English,the French,the Chinese. The English have wonderful senseofhumor.
以-ly结尾的形容词:
1)大部分形容词加-ly可构成副词。但friendly,deadly,lovely,lonely,likely,lively,ugly,brotherly,仍为形容词。改错:
如:(错)She sang lovely.
(错)He spoke to me very friendly.
(对)Her singing was lovely.
(对)He spoke to me in a very friendly way.
2)有些以-ly结尾既为形容词,也为副词。 daily,weekly,monthly,yearly,early .
如:The Times is a daily paper.
The Times is published daily.
形容词知识体系:
复合形容词的构成:
(1)形容词+名词+ed:
如:kind-hearted 好心的,white-haired 白发的
(2)形容词+形容词:
如:red-hot 炽热的,dark-blue 深蓝的
(3)形容词+现在分词:
如:good-looking 好看的,easy-going 随和的
(4)副词+现在分词:
如:hard-working 勤劳的,fast-moving 快速转动的
(5)副词+过去分词:
如:hard-won 得来不易的,newly-made 新建的
(6)名词+形容词:
如:life-long 终生的,world-famous 世界闻名的
(7)名词+现在分词:
如:peace-loving 爱好和平的,fun-loving 爱开玩笑的
(8)名词+过去分词:
如:snow-covered 白雪覆盖的,hand-made 手工的
(9)数词+名词+ed:
如:four-storeyed 4层楼的,three-legged 3条腿的
(10)数词+名词(名词用单数):
如:ten-year 10年的, two-man 两人的
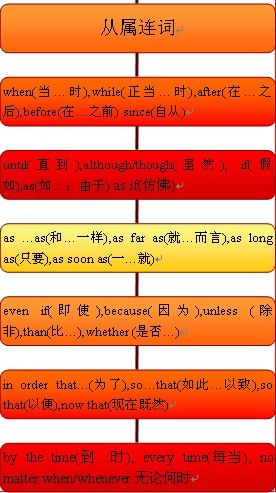
从属连词的概念:
连词用于引导从句以形成句子的一部分或修饰句子的构成要素的叫作从属连词。
英语从属连词用法分类详解:
1、引导时间状语从句的从属连词:
(1)表示“当…时候”或“每当”的时间连词。主要的when, while, as, whenever:
如:He jumped up when the phone rang. 电话铃响时他吓了一跳。
We listened while the teacher read. 老师朗读时我们听着。
The phone rang just as I was leaving. 我正要离开,电话铃就响了起来。
(2)表示“在…之前(或之后)”的时间连词。主要的有before, after:
如:Turn the lights off before you leave. 离开前请关灯。
He started the job soon after he left the university. 他大学毕业后就开始做这份工作。
(3)表示“自从”或“直到”的时间连词。主要的有since, until, till:
如:He has lived here since he got married. 他结婚后就一直住在这儿。
Most men worked until[till] they're 65. 大多数男人工作到65岁。
(4)表示“一…就”的时间连词。主要的有as soon as, the moment, the minute, the second, the instant, immediately, directly, instantly, once, no sooner…than, hardly…when等:
如:Tell him the news as soon as you see him. 你一见到他就把这消息告诉他。
I recognized her the moment(that) I saw her. 我一看到她就认出她来了。
I want to see him the minute(that) he arrives. 他一到来我就要见他。
I went home directly I had finished work. 我一干完活就回家了。
Once he arrives, we can start. 他一来我们就可以开始。
(5)表示“上次”、“下次”、“每次”等的时间连词。主要的有every time(每次),each time(每次),(the) next time(下次),any time(随时),(the) last time(上次),the first time(第一次):
如:Last time I saw him, he looked ill. 上次我见到他的时候,他好像有病。
Next time you're in London come and visit us. 你下次来伦敦过来探望我们。
Do look me up next time you're in London. 你下次到伦敦来,一定来找我。
Every time I call on him, he is out. 我每次去访问他,他都不在。
You can call me any time you want to. 你随时都可以给我打电话。
【注】every time,each time,any time前不用冠词,(the)next time, (the)last time中的冠词可以省略,而the first time中的冠词通常不能省略。
2、引导条件状语从句的从属连词:
这类连词主要有if, unless, as[so] long as, incase等:
如:If anyone calls tell them I'm not at home. 要是有人打电话来,就说我不在家。
You will fail unless you work hard. 你若不努力就会失败。
As[So] long as you need me, I'll stay. 只要你需要我,我就留下。
In case I forget, please remind me about it. 万一我忘记,请提醒我一下。
【注】在条件状语从句中,通常要用一般现在时表示将来意义,而不能直接使用将来时态。不过,有时表示条件的if之后可能用will,但那不是将来时态,而是表示意愿或委婉的请求(will为情态动词):
如:If you will wait a moment, I'll fetch the money. 请等一下,我就去拿钱。
3、引导目的状语从句的从属连词:
主要有in order that, so that, in case, for fear等:
如:We used the computer in order that we might save time. 我们使用计算机是为了节约时间。
Speak clearly so that they may understand you. 说清楚,以便让他们能明白你的意思。
Be quiet in case you should wake the baby. 安静些,免得把婴儿吵醒。
He is working hard for fear he should fail. 他努力工作以免会失败。
4、引导结果状语从句的从属连词:
主要的有so that, so…that, such…that等:
如:We're all here now, so that the meeting can begin at last. 我们现在都到齐了,终于能开会了。
It's so difficult a question that none of us can answer it. 那是一个很难的问题,我们没有一个人能回答。
He shut the window with such force that the glass broke. 他关窗户用力很大,结果玻璃震破了。
【注】so that中的that在口语中通常可以省略。
5、引导原因状语从句的从属连词:
主要的有because, as, since, seeing(that), now(that), considering(that)等:
如:He couldn't got to school because he had a cold. 他因患感冒而未能去上学。
Since everybody is here, let's begin our discussion. 大家都到了,我们就开始吧。
Seeing that it is 8o'clock, we'll wait no longer. 由于时间已到8点,我们将不再等了。
Now that you are here, you'd better stay. 你既然来了,最好还是留下吧。
6、引导让步状语从句的从属连词:
主要有although, though, eventhough, even if, while, however, whatever, whoever, whenever, wherever等:
如:Although[Though] he is poor, he is well contented. 他虽穷却能知足常乐。
Though[Even though] it's hard work, I enjoy it. 尽管是苦活,但我乐意干。
Even if you don't like wine, try a glass of this. 即使你不喜欢喝酒,也尝尝这杯吧。
7、引导方式状语从句的从属连词:
主要有as, like, as if, as though, the way等:
如:Do it as[like] he does. 像他那样做。
He behaved as if nothing had happened. 他装作若无其事的样子。
They treat me as though I were a stranger. 他们待我如陌生人。
Nobody else loves you the way(=as) I do.没有人像我这样爱你。
8、引导地点状语从句的从属连词:
主要有where, wherever, everywhere等:
如:There were lots of parks where I lived. 我住的地方有许多公园。
Sit wherever you like. 你想坐在那儿就坐在那儿。
Everywhere they went, they were warmly welcomed. 他们每到一个地方都受到热烈欢迎。
9、引导比较状语从句的从属连词:
主要有than和as…as:
如:It's easier than I thought. 这比我想像的要容易。
They are as often wrong as they are right. 他们错对各半。
10、引导名词性从句的从属连词:
主要有that, if, whether:
如:It is clear enough what he meant. 他是什么意思很清楚。
Your greatest fault is that you are careless. 你最大的缺点是粗心大意。
Whether it will do us harm remains to be seen.是否对我们有害还要看一看。
She didn't say if he was still alive. 她没说他是否还活着。
从属连词知识体系:
用作从属连词的六类名词结构:
英语中有些名词结构可用作从属连词,用以引导状语从句,且主要是时间状语从句。这类结构归纳起来有以下六类:
一、the+瞬间名词:
其中的瞬间名词主要包括moment, minute, instant, second等,其意为“一……就……”,相当于as soon as。
如:The minute he saw her he fell in love. 他对她一见倾心。
Telephone me the moment(that) you get the results. 你一有结果,马上给我打电话。
I was so tired that I fell asleep the instant I closed my eyes. 我很累,一合上眼就睡着了。
Sheputdownthereceiverthesecondsherecognizedmyvoice.她一听出是我的声音,马上就放下电话听筒。
注:其中的瞬间名词后可接that,也可省略。另外,有的个别副词(如directly/immediately等)也可表示类似意思。
如: Immediately the meal was over,he switchedon the radio.饭一吃完他就把收音机打开。
二、the+季节名词:
其中的季节名词包括spring,summer,autumn,winter,其意为“在……的那年春天、夏天、秋天、冬天。
如:His wife left him thes pring he went abroad.在他出国的那年春天,他的妻子离开了他。
He sold his house and went to the souththe summer he lost hisjob.在他失业的那年夏天,他卖掉房子去了南方。
He was sentto prison the winter his third daughter was born.在他第三个女儿出生的那年冬天,他被关进了监狱。
She got married the autumn she graduated from college.她大学毕业的那年秋天就结婚了。
三、the+时间名词:
其中的时间名词主要包括hour,day,night,week,month,season,year等,其意为“在……的时候、那天、那个晚上、那周、那个月、那个季节、那年”。
如: The hour he wa sin her office,he felt very sad.当他在她办公室的时候,他感到很伤心。
The day here turned home,his father was already dead.他回家的那一天,他的父亲已经死了。
The night I wenttoseeher,shehadleftforBeijingtoattendanimportantmeeting.就我去看她的那个晚上,她到北京去开一个重要的会议了。
Mr Smith didn't go to work the week his wife was ill.史密斯先生在他妻子生病的那个星期没去上班。
They ear helivedinthecountry,he learned alot.他在乡下呆的那一年,他学到了不少东西。
四、the+序数词+time
其中的序数词包括first,second,third,fourth等,其意为“当第几次……的时候”。
如: My girlfriend beat me at pokert he first time weplayed.我头一次和女朋友打扑克,她就把我赢了。
These cond time I saw her,she looked like an old woman.我第二次见到她时,她看上去像一个老太婆。
The third time I went there,I found all of them had left and the offices were all empty.我第三次去那儿时,我发现他们都离开了,所有的办公室都是空的。
注:
1.next,last也具有类似序数词的性质,因此也具有以上用法。
如: Nexttimeyoucomein,pleaseclosethedoor.下次你进来,请关门。
Thelasttimewetalkedhesaidheneededanothertwodays.上次我们谈话时他说他还需要两天。
2.thefirsttime,thesecondtime,thethirdtime等用作连词引导时间状语从句时,其前通常要有定冠词,而(the)nexttime,(the)lasttime引导状语从句时,其中的冠词可以省略,如下面这道上海高考题,其答案是C,不是A:
I though ther nice and honest______Imether.
A.first time B.fo rthe first time C.the first timeD.by the first time
五、不定代词+time
其中的不定代词主要包括each,every,any等。
如:Every time I ringher,the phone is engaged.我每次给她打电话,电话都占线。
Every time I see him he either wants to tell me his trouble or borrow some money.每次我见到他,他不是向我诉苦,就是要向我借钱。
He felt nervous each times he spoke to him.每次她和他讲话,他都感到紧张。
AnytimeyoucometoLondondolookmeup.你无论什么时候到伦敦来,一定要来看我。
注意:everytime,eachtime,anytime用作连词引导状语从句时其前习惯上不用冠词,它与the first time,these cond time,the third time等引导时间状语从句时其前必须要用定冠词不同。
六、其他名词结构
以上归纳的名词结构均用于引导时间状语从句,有些其他结构还可引导其他性质的状语从句,如the way可用于引导方式状语从句,表示“像……一样”。如:
The didn’t do it the way we do now.那时他们不像我们现在这样行事。
Joyce looked at me the way alotof girls did.乔伊丝像许多姑娘那样瞧着我。
注:这样用的theway与as用法相似。
如:Hold itin both hands,the way(=as)Mummy does.用两只手捧住,像妈妈那样。
现在分词完成式的概念:
从动作关系上看,现在分词的完成式主要表示发生在谓语动作之前的动作;从用法上看,现在分词完成式主要用作状语,表示时间或原因等。
现在分词完成式的基本用法:
1、表示时间:
如:Having noted down our names and addresses, the policeman dismissed us. 那警察把我们的姓名和地址记下之后就让我们走了。
Having found a hotel, we looked for somewhere to have dinner. 在找好旅馆之后,我们就去找吃饭的地方。
Having bought our tickets, we went into the theatre. 我们买好票后就走进剧场。
Having packed up her things, she went to book her ticket. 她收拾好行李之后就去买车票。
注:这样用的现在分词通常可以转换成时间状语从句。
如:Having finished her work, she went home. =After she had finished her work, she went home. 她干完工作就回家了。
2、表示原因:
如:Having been there once, she knew the place quite well. 由于去过那儿一次,她对那地方很熟悉。
Having invited him here to speak, we'd better go to his lecture. 我们邀请他来这儿讲演,所以我们最好去听讲。
注:这样用的现在分词通常可以转换成原因状语从句。
如:Having been there many times, he offered to be our guide. =As he had been there many times, he offered to be our guide. 他曾多次到过那里,主动提出当我们的向导。
现在分词的完成式用作状语时,通常位于主句之前,但有时也可置于主句之后,不过此时多见于表原因的场合。
如:I didn't feel terribly shocked, having expected all this. 这情况我早已料到,因此我并不感到过于震惊。
I was unable to accept your invitation. having promised to accompany my mother to the concert. 我因已答应陪我母亲赴音乐会而不能接受你的邀请。
现在分词完成式的否定式:
原则上应将not置于整个分词完成式之前。
如:Not having done it right, I tried again. 我由于没有做对,所以又试了试。
Not having finished his work, he could not leave the office. 由于工作没干完他不能离开办公室。
Not having received an answer, she decided to write him another letter. 由于没得到他的回信,她决定再给他写一封信。
现在分词完成式用于独立结构:
有时现在分词完成式可以用于独立结构。
如:The dark clouds having dispersed, the sun shone again. 乌云已散去,太阳又普照大地了。
The river having risen in the night, the crossing was impossible. 夜里河水上涨,渡河不可能了。
My turn having comeround, I was ushered into the examining room. 轮到我之后,我就被引入考场。
The last bus havingg one, we had to walk home. 最后一班公车已经走了,我们必须走路回家。
使用现在分词完成式的错点:
现在分词的完成式一般不用作定语,遇此情况可改用定语从句。
如:你知道有谁丢了一只猫吗?
误:Do you know anyone having lost a cat?
正:Do you know anyone who has lost a cat?
我想同打破窗户的人淡淡。
误:I want to talk to the person having broken the window
正:I want to talk to the person who has broken the window
注意:若将以上现在分词的完成式改为一般式也不可以,因为现在分词作后置定语时通常只表示与谓语动作同时或几乎同时发生的动作,而不能先于谓语动作而发生。
现在分词一般式与完成式的区别:
现在分词的一般式和完成式均可表示已完成或先于谓语的动作,但有区别:现在分词一般式所表示的动作虽然可以先于谓语动作,但两者之间没有时间间隔,而现在分同的完成式所表示的先于谓语的动作则与谓语动作有一定的时间间隔。
如:Locking the door, she went out. 她锁上门走了出去。
Having lost his job, he'd begun to interest himself in local voluntary work.他失业后便开始关注地方的志愿工作了。
注:有时两者意思差不多,可以换用。
如:Tying one end of the rope to his bed, he threw the other end out of the window.
Having tied one end of the rope to his bed, he threw the other end out of the window. 他把绳子的一头系在床上,另一头扔出窗外。
但是注意,用现在分词一般式代替完成式的用法通常只限于现在分词所表示的动作与谓语动词所表示的动作之间没有时间间隔的场合,比如以下情况就不可随便替换。
1、当换用会引起语义含混时。
如:看完了说明书之后,他迅速拿起了灭火器。
不妥:Reading the instructions, he snatched up the fireextinguisher.
正句:Having read the instructions, he snatched up the fireextinguisher.
前面一句用了现在分词的一般式,给人的印象好像是两个动作同时发生的,容易引起误解,故宜改用完成式。
2、当两个动作之间有一段间隔时,必须用分词的完成式。
如:Having failed twice, he didn't want to try again. 已经失败了两次,他不想再试了。
3、当第一个动作持续一段时间时,必须用分词的完成式。
如:Having been his own boss for such a long time, he found it hard to accept orders from another. 自己当老板已经这么久了,他觉得难以听从别人的差遣。
现在分词完成被动式与过去分词的区别:
现在分词的完成被动式有两个特点:一是表示完成,二是表示被动。
如:Having been bitten twice, the postman refused to deliver our letters unless we chained our dog up. 邮递员被狗咬了两次之后要我们把狗拴起来,不然就不给我们送信了。
过去分词的用法也有两个特点:一是表示完成,二是表示被动。所以有时现在分词的完成被动式与过去分词可以表示相同的意思。
如:(Having been)written in haste, the book has many mistakes. 这书因写得仓促,所以错误不少。
(Having been)born in America, he is proficient in English. 由于他是在美国出生的,所以英语很好。
有时虽然所表示的时间概念相同,但有细微区别:
如:Having been shown the lab, we left. 被领着看了实验室后,我们就离开了。
Shown the lab, we left. 被领着一看完实验室,我们就离开了。(有一种急促感)
注:以下情况通常用过去分词,而不用现在分词的完成式。
1、过去分词表示先于谓语动同发生的动作外,还可以表示与谓语动词同时(几乎同时)发生的动作,此时不可用现在分词的完成式代替。
如:He came in, followed by his secretary. 他走了进来,后面跟着他的秘书。
Convinced that they were going to poison him, he refused to eat anything. 他相信他们要毒死他,所以他拒绝进食。
2、当过去分词以表示现在或过去(当时)的状态时,也不可用现在分词的完成式代替。
如:The murderer was brought in, his hands tied behind. 凶手被带了进来,双手被绑在后面。
3、当连用具体明确的过去时间状语时,通常也只用过去分词。
如:Built in1501, the bridge is over 500 years old. 这座桥建于1501年,已有五百多年的历史。
过去分词的概念:
过去分词一般表示完成和被动的动作,只有一种形式。即:动词原形加-ed构成。
如:fallen leaves 落叶
boiled water 开水
I heard the door closed. 我听见门被关上了。
过去分词与现在分词被动式的区别:
两者均可表示被动,其区别主要在于它们所表示的时间概念不同,但有时它们也可表示相同的意思。
如:Written in haste, the book has many mistakes. 这书因写得仓促,所以错误不少。
Being written in haste, the book has many mistakes. 这书因写得仓促,所以错误不少。
Having been written in haste, the book has many mistakes. 这书因写得仓促,所以错误不少。
有时虽然所表示的时间概念相同,但有细微区别:
如:Having been show the lab, we left. 被领着看了实验室后,我们就离开了。
过去分词的句法功能:
1、作定语:
如:I don't like the book written by Martin.
Our class went on an organized trip last Monday. 上周一我们班开展了一次有组织的旅行。
注意:当过去分词是单词时,一般用于名词前,如果是过去分词短语,就放在名词的后面。过去分词做定语相当于一个被动语态的定语从句。
2、过去分词作表语:
如:They were very excited at the news. 听到这个消息,他们非常激动。
The window is broken. 窗户破了。
They were frightened at the sad sight. 他们对眼前悲惨的景象感到很害怕。
注意:be+过去分词,如果表示状态是系表结构,如果表示被动的动作是被动语态。
区别:The window is broken.(系表)
The window was broken by the boy.(被动)
有些过去分词是不及物动词构成的,不表示被动,只表示完成。
如:boiled water(开水) fallen leaves(落叶) newly arrived goods(新到的货) the risen sun(升起的太阳) the changed world(变了的世界)
这类过去分词有:gone, come, fallen, risen, changed, arrived, returned, passed等。
3、过去分词作宾语补足语:
如:I heard the song sung several times last week. 上周我听见这首歌被唱了好几次。
有时过去分词做with短语中的宾语补足语:
如:With the work done, they went out to play. 工作做完了,他们出去玩去了。
4、过去分词作状语:
如:Praised by the neighbours, he became the pride of his parents. 受到邻居们的表扬,他成为父母的骄傲。(表示原因)
Onceseen, it can never be forgotten. 一旦它被看见,人们就忘不了。(表示时间)
Given more time, I'll be able to do it better. 如果给予更多的时间,我能做得更好。(表示条件)
Though told of the danger, he still risked his life to save the boy. 虽然被告之危险,他仍然冒生命危险去救那个孩子。(表示让步)
Filled with hopes and fears, he entered the cave. 心中充满了希望与恐惧,他走进山洞。
5、过去分词与逻辑主语构成独立主格:
如:All books returned at the end of the term, the library assistant was satisfied. 所有的书期末时都还了,图书管理员很高兴。
The field ploughed, he began to spread seed. 地耕好了,他开始撒种子。
现在分词与过去分词的区别:
1、分词作表语:
分词做表语有两种情况,一种是现在分词做表语,一种是过去分词做表语,这两者区别是考试中经常考到的地方。一般来说,表示心理状态的动词如excite,interest等都是及物动词,汉语意思不是“激动”,“高兴”,而是“使激动”、“使高兴”,因而现在分词应该是“令人激动的”、“令人高兴的”,过去分词则是“感到激动的”和“感到高兴的”。所以,凡表示“令人……的”都是-ing形式,凡是表示“感到……”都用-ed形式。换句话说,若人对……感兴趣,就是somebody is in terestedi n...,若人/物本身有兴趣时,就是说sb./sth. is interesting。这类词常见的有:
interesting 使人感到高兴—interested感到高兴的
exciting令人激动的—excited感到激动的
delighting令人高兴的—delighted感到高兴的
disappointing令人失望的—disappointed感到失望的
encouraging令人鼓舞的—encouraged感到鼓舞的
pleasing令人愉快的—pleased感到愉快的
puzzling令人费解的—puzzled感到费解的
satisfying令人满意的—satisfied感到满意的
surprising令人惊异的—surprised感到惊异的
worrying令人担心的—worried感到担心的
如:Travelling is interesting but tiring. 旅行是有趣的,但是使人疲劳。
The pupils will get confused if they are made to learn too much. 如果要学生学得太多,他们会感到糊涂的。
The game is exciting. (现在分词作表语)
We were excited at the news. (过去分词作表语)
2、分词作定语:
分词作定语时有下面几个特点:
1)现在分词表示主动意义,过去分词一般表示被动含意。
2)现在分词表示正在进行,过去分词表示状态或做完(完成)的事。
如:He rushed into the burning house. 他冲进了正在燃烧着的房子。
The child standing over there is my brother. 站在那儿的男孩子是我弟弟。
The room facing south is our classroom. 朝南的房间是我们的教室。
He is an advanced teacher. 他是个先进教师。
3)下列不及物动词也以过去分词形式做定语或表语,但不具有被动意义,这点要注意:
departed, elapsed, faded, fallen, gone, frown-up, retired, returned, risen, set, vanished, much-traveled, newly-arrived, recently-come
3、分词作状语:
现在分词做状语与过去分词做状语的最主要区别在于两者与所修饰的主语的主动与被动关系的区别。
1)现在分词作状语时,现在分词的动作就是句子主语的动作,它们之间的关系是主动关系。
如:He went out shutting the door behind him. 他出去后将门随手关上。
Not knowing what to do, he went to his parents for help. 由于不知如何办是好,他去找父母帮忙。
Smiling, they came in.
2)过去分词作状语时,过去分词表示的动作是句子主语承受的动作,它们之间的关系是被动关系。
如:Cleaned, the room looks nice.
Given more attention, the trees could have grown better. 如果对这些树多关心一些,它们本来会长得更好。
Faced with difficulties, we must try to overcome them. 在遇到困难的时候,我们必须设法克服。
一般过去时的概念:
一般过去时表示过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为;过去主语所具备的能力和性格。
一般过去时的用法:
1、表示过去发生的动作或存在的状态,常与表示过去时间的副词如:yesterday,last week,two hours ago等连用。
如:My family moved here five years ago. 我家五年前搬到了这里。
I was born in 1973. 我生于1973年。
2、表示过去一段时间经常或反复发生的动作。这时可与频度副词如:often,usually,always等连用。
如:He always worked in tonight those days. 那些日子他总是工作到深夜。
I often left on business in 1987. 1987年我经常出差。
注:表示“过去经常,而今不再”时,要用usedto.
如:I used to read newspaper after breakfast. 我过去经常早饭后看报纸。(意指现在已不是这样)
The children often swam in this river. 孩子们过去经常在这条河里游泳。
3、表示过去发生的一连串动作。
如:He put down the heavy box, took out the keys, and opened the door. 他放下这沉重的箱子,掏出钥匙开了房门。
注:过去发生的一连串动作,若用and,or,but等并列连词连接,则一律用过去式。
如:They moved the chairs to the table, sat down and began to have supper. 他们把椅子搬到桌边,坐下开始吃饭。
4、在时间和条件状语从句中,用一般过去时表示过去将来的动作。
如:He said that he would let me know as soon as he got the information. 他说他一得到消息就立即让我知道。
Mary told me that she would stay at home if it rained. 玛丽告诉我如果下雨她就呆在家里。
一般过去时的特别用法:
1、句型:It is time for sb. to do sth "到……时间了" "该……了"。
例如:It is time for you to go to bed.你该睡觉了。
It is time that sb.did sth. "时间已迟了" "早该……了"。
例如:It is time you went to bed. 你早该睡觉了。
2、would(had)rather sb.did sth. 表示'宁愿某人做某事'。
例如:I'd rather you came tomorrow. 还是明天来吧。
3、wish, wonder, think, hope等用过去时,作试探性的询问、请求、建议等,而一般过去时表示的动作或状态都已成为过去,现已不复存在。
例如:I thought you might have some. 我以为你想要一些。
比较:Christine was an invalid all her life.(含义:她已不在人间。)
Christine has been an invalid all her life.(含义:她现在还活着)
Mrs. Darby lived in Kentucky for seven years.(含义:达比太太已不再住在肯塔基州。)
Mrs. Darby has lived in Kentucky for seven years.(含义:现在还住在肯塔基州,有可能指刚离去)
注意:用过去时表示现在,表示委婉语气。
1)动词want, hope, wonder, think, intend等。
例如:Did you want any thing else? 您还要些什么吗?
I wondered if you could help me. 能不能帮我一下。
2)情态动词could, would。
例如:Could you lend me your bike? 你的自行车,能借用一些吗?
过去完成时的概念:
过去完成时既可表示过去某个时间或动作之前所发生的事情,也可表示过去某个时间或动作之 前所发生的动作一直持续到过去某个时间。过去完成时由“had+过去分词”构成。
如:She had leant 2000 English words by the end of last month.
过去完成时的应用:
(1)与过去完成时连用的时间状语可以多种多样,使用它的主要依据是看其是否发生在“过去的过去”。
如:He had learnt some English before I went here. 在来这儿之前我学过一些英语。
He had written three stories by last year.到去年他已经写了三篇故事。
We had cleaned the room when he got there. 当他到那儿时,我们已经把房子弄干净了。
He went there after he had finished his work. 他把事做完之后,就去哪儿了。
注意:当主句跟由before, after, as soon as所引导的时间从句的动作连接很紧密时,从句也可用一般过去时。
如:He went there after he read the letter. 他看了那封信后就去那儿了。
(2)过去完成时还经常用于主句为过去时的宾语从句中。
如:He said he had been a soldier. 他说他当过兵。
They said they had seen the film. 他们说这幕电影他们看过。
(3)在hardly/scarcely…when…,nosooner…than…两个结构中的主句通常要用过去完成时。
如:Hardly had I told her the news when she began to cry out. 她一听到这一消息就大哭了起来。
Scarcely had he finished his supper when he went out. 他已吃完晚饭就出去了。
No sooner had he fallen asleep than he lay down on the bed. 他一躺倒床上就睡着了。
(4)动词expect, hope, suppose, think, want等的过去完成时可用来表示未实现的计划、打算或希望。
如:I had hoped to see you. 我本希望来看你。
He had wanted to buy a house in Beijing. 他本想在北京买栋房子。
过去完成时与一般过去时:
(1)过去完成时表示以过去某时间为起点以前所发生的动作或存在的状态,即:过去完成时强调“过去的过去”,而一般过去时只表示以现在时间为起点以前所发生的事情或存在的状态。
如:He studied there two years ago. 他在那儿学习了两年。(离现在两年)
He said he had studied there two years ago. 他说他在那儿学习了两年。(离他说话时两年)
(2)表示过去某个时间以前所连续发生的两个或两个以上的动作时,一般用and, then, but按照动作的先后顺序连接,此时通常用一般过去时而不用过去完成时。
如:He said he went the shop and bought some food. 他说他去商店买了一些食品。
(3)两个动作相继发生,可用一般过去时;如第一个动作需要若干时间完成,用过去完成时。
如:When I heard the news, I was very excited.
(4)叙述历史事实,可不用过去完成时,而只用一般过去时。
如:Our teacher told us that Columbus discovered America in1492.
it的概念:
it可用作人称代词、指示代词、先行词及引导词等。
it 的用法:
1、it可指天气、温度、时间、距离等 。
如:It is cold today, isn't it?
2、用作人称代词,代替前文提到过的事物。
如:The dog is not acold-blooded animals. It doesn't need to hibernate.
3、为避免重复,it可用来代替前面说过的短语或句子。
如:I tried to persuade my father to give up smoking, but found it impossible. (it=to persuade my father to give up smoking)
4、代替指示代词this,that。
如:—What's this?
—It's an album.
—Whose new bike is that?
—It's Mary's.
注:it与one,that的区别:
it=the(this, that)+名词,特指并且代替前面所提到的某特定事物。
如:He's bought a new car, so he drives it everywhere to show ito ff.
one=a+名词,one指前面提到的同类事物中的不同的另一个。
如:He needs a computer, but he can't afford one.
that=the+名词,that指代的名词与前面的名词属于同一类,但不属同一个。
如:The population of China is larger than that of Japan. that指代population,但其后有一个of短语作定语,以区别于the population of China。
注:it与that的异同:
it指同一事物,that指同类但并不是同一事物。
如:I like the climate of Kunming more than that of Beijing.
The climate of Kunming is mild, and I like it.
5、It/This/That+be+the first(second, third...) time+that-clause 这个句型表示截止到说话时为止的某人的一种经历,关键是注意time前有序数词,主句是一般现在时is时,从句要用现在完成时;如果主句用一般过去时was时,则从句须相应地用过去完成时。
如:This is the first time(that) these Europeans have visited the Great Wall.
It was the fifth time(that) I had paid a friendly visit to America.
6、在一些相对固定的词组中,没有特殊含义,经常不翻译。
如:He's never really made it as an actor. 作为演员,他从未获得过真正的成功。
It is my turn. 轮到我了。
强调句中的it:
可以用来改变句子结构,使句子的某一成分得到强调:
1)强调句的基本句型it's/was+被强调成分+that/who+其他成分
原句:I told Jim the news in our office yesterday.
强调主语:It was I that/who told Jim the news in our office yesterday.
强调宾语:It was Jim that I told the news in our office yesterday.
或:It was the news that I told Jim in our office yesterday.
强调地点状语:It was in our office that I told Jim the news yesterday.
强调时间状语:It was yesterday that I told Jim the news in our office.
2)强调句的一般疑问句型Is/Was+it+所强调部分+that/who...?
如:Was it you that told Jim the news in your office yesterday?
3)强调句的特殊疑问句型疑问词+is/was+it+that/who...?
如:Who was it that told Jim the news in your office yesterday?
【注】强调句与主语从句虽然在形式上很相似,即都含有it is(was)...that。但,区别在于:强调句去掉it is(was)…that之后,句子结构仍然完整,而主语从句却不能这样。
如:(It is)our hope(that) the two sides will work towards peace.
解析:去掉It is…that之后,句子是不成立的。由此得出该句不是强调句,而是一个简单的主语从句,it是形式主语,从句是真正的主语。
“it”的用法:
1、it 作形式主语:
it 在句中可作形式主语,而真正作主语的主语从句需要放在句子的末尾。主语从句后置常用以下几种结构:
1)It is/was+adj.+subject-clause可用于此句型的形容词有:
clear, certain, funny, good, impossible, likely, natural, obvious, possible, probable, strange, surprising, true, unusual, wonderful等。
如:It is obvious that going for sports will do a lot of good to your health.
2)It+be+adj./n.(forsb./ofsb.)+todosth. 该句型中的形容词通常表示事物的特点或特征的,如:
difficult, hard, easy, impossible, necessary, important等,此时用for;或表示人的性格特征或特点的,如:
nice, good, bad, kind, silly, foolish, wise, clever, careless, rude, brave, cruel, careful, grateful等,这时要用of 。
3)It is/was+名词词组+subject-clause可用于该结构的名词词组有:
a pity/duty, a good thing, no surprise, good news, an honor, a fact, a mystery, a shame, manners等。
如:It's a pity that I didn't attend the party.
4)It is/was+V-ed+subject-clause可用于该结构的动词的过去分词有:
said, reported, thought, supposed, believed, hoped, expected, known, decided, announced, arranged等。
如:It is said that something had been done to end the pollution.
注:本句还可改写为:Something is said to have been done to end the pollution.
5)It+vi.+subject-clause可用于该结构的动词有:appear, seem, happen, occur等。
如:It appeared to scientists that the stars had moved.
6)It doesn't matter(makes no difference,etc.) +连接代词或连接副词引起的从句作宾语。
如:It doesn't matter whether he'll join the army or not.
It makes no difference where we have the conference.
7)一些固定句型:
It takes sb. some time to do sth.
如:It will take you two days to get there on foot.
It costs sb. some money to do sth.
如:It costs 1,000 dollars to fly to America.
It is/was no use(useless) doing(做什么是没有用处的)
如:It's no use arguing with him.
It is/was no good doing(做什么是没有好处的)
8)以下句型结构中需要用虚拟语气
① It is/was important(necessary, strange) that...;
It is/was ordered(required, suggested, proposed) that...;
It is/was a pity(a shame) that...表示遗憾等感情的句子中,主语从句要用“should+动词原形”,should可以省略。
如:It's necessary that he(should) be operated on at once.
② It is (high)time that...结构中用should+动词原形(should不能省略)或动词过去式。
如:It is high time that you should make(made) full use of your time to go over your lessons.
2、it作形式宾语:
1)动词consider(feel, find, think等)+it+形容词(名词)+不定式(动词-ing形式,从句)。
如:She thinks it no use telling me.
2)主语+appreciate(enjoy,like,love,hate)+it+if(when)...结构
如:We would appreciate it if you could come to help us.
3)dependon, relyon, see to(负责/设法做到), takeforgranted(习以为常)等短语后跟that从句时,要以it作形式宾语。
如:We're depending on it that he will finish the job by Friday.
“it ”引起的几个易混淆的时间句型:
1)It be+时间+since-clause 这个句型表示从since从句谓语动作发生以后到现在或过去所经过的一段时间,意为“自从…以来已多久了”,主句多用一般现在时,从句用一般过去时,如果表示过去的情况,主句一般用过去时,从句用过去完成时,或主句用过去完成时,从句用一般过去时。
注:since引导时间状语从句时,从句若使用终止性动词,则表示该时间是主句时间段的终点(时间从现在算起);若从句使用延续性动词,则表示该动作状态的结束(时间从过去算起)。
如:It's five years since they got married. 他们结婚已经5年了。
It's five years since they were married. 他们离婚已经5年了。
It's ten years since his father was a worker. 他父亲不当工人已经10年了。
I haven't seen him since we were boys together. 我们长大以后再没有见过面。
2)It be+时间+before-clause 这个句型中的时间一般为表示一段时间的词语(如:long years, months, weeks, days, hours, minutes),主句中的谓语动词用肯定式,意为“过多长时间才…”。主句的谓语动词是否定式时,意为“没过多长时间就…”。主句的时态可用过去时was或将来时willbe;用was时,before从句的动词用一般过去时;用willbe时,before从句常用一般现在时。 如:It was not long before she learned those poems by heart. 她没过多久就背会了那些诗。
It was long before the police arrived. 过了很久警察才来。
It will be hours before he makes a decision. 要过好几个小时他才会作出决定。
It will not be hours before we meet again. 要不了几个小时我们还会再见面的
3)It be+时间+when-clause 这个句型中,it指时间,而且表示时间的词语前没有介词(时间一般是具体时间)。主句和从句中的谓语动词在时态上是一致的,主句是willbe,when从句用一般现在时代替将来时。
如:It was already 8 o'clock when we got home.
It will be late afternoon when they get there.
4)It be+时间+that-clause 这个句型是个强调句型。
如:It was at 5o'clock that he practiced playing the violin in the morning. (原句是:He practiced playing the violin at 5o'clock in the morning.)
比较:It was 5o'clock when he started in the morning.(5o'clock前没有介词,这个是定语从句)
5)It be+time+that-clause 这个句型属虚拟语气结构,不管主句中用的是is或was,that从句都须用动词的过去式或should+动词原形(但不及物动词通常用过去式),在time之前有时可以加上high 或about 以加强语气。
如:It is high time(that) he wrote a letter to his girl friend.
It is time(that) we made people's life a little easier.= It is time that we should make people's life a little easier.
与“请根据句子意思,选用适当词或用所给词的适当形式填空。1. I ...”考查相似的试题有:
- 填空题He is two years (比……大)me.
- .These are all ________houses for the homeless.A.newly – buildingB.newly-builderC.new - building D.newly - built
- Cycling is highly __________ to people’s health and the environment.A.fashionableB.beneficialC.changeableD.suitable
- ---How old is your sister? --She is __ than I.A.older six yearsB.six years olderC.six years elderD.older by six year
- 单句改错。增加:“在 …后加…”, 如, 在and 后 加 what删除: 写上多余的词,并用斜线划掉, 如, of 修改: …改为… , 如,an...
- While _____ football on tin playground, I found ’my keys ______.A.playing, lost ,B.play, losingC.played, being los...
- It’s a consensus in modern society that whoever breaks the law deserves _______, whether he is from the top class or ...
- 31._____for a strong and fair climate agreement at the key UN summit in Copenhagen, 50,000 people in London wore blue...
- The serious situation made it possible for laws preventing pollutions_________in many countries.A.from passingB.to ...
- _______ from the top of the towel, I find the city beautiful.A.SeeingB.SeenC.To seeD.Being seen