本试题 “短文改错。此题要求改正所给短文中的错误。对标有题号的每一行作出判断:如无错误,在该行右边横线上画一个(√);如有错误(每行只有一个错误),则按下列情...” 主要考查您对不可数名词
不定冠词
连接代词
形容词
介词和介词短语
系动词
动名词
一般将来时
等考点的理解。关于这些考点您可以点击下面的选项卡查看详细档案。
- 不可数名词
- 不定冠词
- 连接代词
- 形容词
- 介词和介词短语
- 系动词
- 动名词
- 一般将来时
不可数名词的概念:
不可数名词是指不能以数目来计算,不可以分成个体的概念、状态、品质、感情或表示物质材料的东西;它一般没有复数形式,只有单数形式,它的前面不能用不定冠词a / an ,若要表示它的个体意义 时,一般要与一个名词短语连用。
例如: a cup of tea 一杯茶
a piece of news 一则新闻
two pieces of paper 两张纸
不可数名词量的表示:
1)物质名词:
a. 当物质名词转化为个体名词时。
比较:Cake is a kind of food. 蛋糕是一种食物。(不可数)
These cakes are sweet. 这些蛋糕很好吃。(可数)
b. 当物质名词表示该物质的种类时,名词可数。
Thisfactoryproducessteel.(不可数)
如:We need various steels. (可数)
c. 当物质名词表示份数时,可数。
如:Our country is famous for tea. 我国因茶叶而闻名。
Two teas, please. 请来两杯茶。
2)抽象名词有时也可数。
如:four freedoms 四大自由
the four modernizations 四个现代化
注:物质名词和抽象名词可以借助单位词表一定的数量。
如:a glass of water 一杯水
a piece o fadvice 一条建议
不可数名词用法:
1、不可数名词前不能直接加数词或a(an)。切忌犯以下错误: meat, two tea, 应说a piece of meat, two cups oftea。
2、不可数名词无单复数变化,谓语动词一般用单数形式。
如:There is some milk in the glass. 杯里有一些牛奶。
Some food on the table goes bad. 桌子上的食物变质了。
3、能修饰不可数名词的词有:much, a little, little, a bit, some, any, a lot of, plenty of等,以此来表示不确定的数量。如:
much bread 许多面包
a little milk 一点牛奶
a lot of work 许多工作
4、表示具体的数量时应用单位词加of结构。
如:I bought two kilos of meat. 我买了两公斤肉。
He ate three pieces of bread. 他吃了三块面包。
Would you like a cup of coffee? 你想喝杯咖啡吗?
不定冠词的概念:
冠词是置于名词前,说明各词所表示的人或事物的一种虚词,它不能离开名词而单独存在。冠词有两种,一种是定冠词,一种是不定冠词。定冠词是the,不定冠词有两种形式,一是a,另一是an。不定冠词a用于辅音音素起首的单词前,an用于元音音素起首的单词前。如:a bike, a dog, an egg, an elephant
不定冠词的特殊用法:
(1)用于序数词之前,表示数量或序数的增加:
如:Soon I saw a second plane.不久我又看到了另一架飞机。
"This is the second time that I've read the book." “这是我第二次看这本书。”
"Do you want to read it a third time?"“你还想看第三次吗?”
(2)用于表示“非常”、“很”等意义的most前:
如:This is a most interesting story. 这是一个非常有趣的故事。
(3)用于物质名词前,使之转化为具体名词,表示“一种”、“一杯之量”等:
如:A coffee, please. 请给我来杯咖啡。
I'd like a tea, please. 我要来杯茶。
(4)用于抽象名词前,使之具体化,表示与该之相关的具体的人或事:
如:He was a success in business. 他事业成功。
It's a pleasure to talk with you. 同你谈话是件令人愉快的事。
(5)用于指人的专有名词前,指某人、某人的作品或艺术品、…似(式)的人等:
如:A Mr Smith wants to see you. 一位名叫史密斯先生的人想见你。
He bought a complete Lu Hsun. 他买了一套鲁迅全集。
He thought he was a Zhu Geliang. 他自以为是诸葛亮。
(6)用于某些由动词转化来或具有动作意味的名词前,表示一次、一番等义(通常与have,take,make,give等动词连用):
如:Let's go out for a walk. 我们出去走走吧。
如:Do you care for as moke? 抽烟吗?
Would you like a drink? 要喝一杯吗?
(7)有的不可数名词或本来带有定冠词the的名词,由于受定语的修饰,其前可用不定冠词,表示某种状态。此时的不定冠词含有类似akindof的意思:
如:have breakfast 吃早餐─have a quick breakfast 吃快餐
the world 世界─a world like ours 像我们这样的世界
(8)构成短语表示数量:
如:a few apples 几个苹果
a little money 一点点钱
a lot of time 许多时间
a great many friends 许多朋友
不定冠词与one的用法解析:
1、两者均可表示“一”的意思,有时可互换。
如:About a[one] thousand students attended the meeting. 大约有1000学生参加了会议。
注:在数字开头时,两者均可用;但若不是数字开头,则应用one,如不可说three thousand a hundred,而说three thousand one hundred
如:A [One]Mr Smith wants to see you. 一个名叫史密斯先生的人想见你。(a Mr...与one Mr...同义,也可说a certain Mr...,但如果没有Mr这样的词,两者则不宜随便互换,否则含意会发生变化。
2、尽管两者均可表示“一”,有时也可换用,但毕竟由于两者的词性不同,用法不同,在多数情况下是不能互换的:
(1)从词性上看:a(an)是不定冠词,主要表示类别,即着重表示其后的名词是某物,而不是其他物;而one表示“一(个)”时是数词,主要表示数量,即强调在数量上是一个,而不是两个或多个。
比较:Give me a dictionary. 给我一本字典。
Give me one dictionary. 给我一本字典。
前者强调的是,我要的是一本字典,而不是一本教材,也不是一本小说等;而后者强调的是,我要的是一本字典,而不是两本字典或多本字典)。
再比较以下一组表达在意义上的区别:
more than a year一年多 (如一年零三个月等)
more than one year 不止一年 (如两年或三年等)
(2)由于one是数词,着重数量意义,所以当要强调数量、进行数量对比或回答how many的提问时,均应用one,而不能用a(an)。
如:He has only one pen, but I have two. 他只有一枝钢笔,但我有两枝。
I want one box, not five. 我想要一个盒子,不是要五个。
—How many friends do you have here? 你在这儿有多少个朋友?
—Only one. 只有一个。
(3)在某些表达中,两者均可用,但含义不同:at a time 每次,同时 at one time 一度,曾经 as a man 就一个人的性格而论 as one man一起,同时,全体一致地
在某些表达中,两者均可用,虽含义相同,但表达不同:
on a hot summe rafternoon 一个炎热的夏日的下午(注意用介词on)
one hot summer afternoon 一个炎热的夏日的下午(注意不用介词on)
an hour and a half一个半小时(通常不说one hour and a half)
one and a half hours 一个半小时
a minute or two一两分钟(通常不说one minute or two)
one or two minutes 一两分种
在绝大多数习语中,两者是不能换用的。如:
in a hurry 匆忙 once up on a time 从前 as a result 结果 all of a sudden突然 oneday 一天
one by one一个一个地 one and all 全部,每个人 one and the same 完全相同的
英语不定冠词(a/an)的用法:
1、用a还是an:一般说来,辅音或半元音[j, w]开头的词要前用a。
如:He has a computer (watch). 他有一台电脑(一块手表)。
He's a university student (European). 他是大学生(欧洲人)。
元音开头的词前要用an。
如:This is an egg (hones tboy). 这是一只鸡蛋(诚实的男孩)。
注意:有的字母(如a,e,f,h,i等) 或缩略词,若第一个音是元音也应用an。
如:He missed an "n" in the word. 他写的这个单词漏了一个n。
2、不要从汉语习惯出发,漏掉必用的a/an。
如:他父亲是著名诗人。
误:His father is famous poet.
正:His father is a famous poet.
3、用于转化为普通名词的专有名词前,表示某某人或某某人的一部作品、艺术品等。
如:A Mr Smith wants to see you. 一位叫史密斯先生的人想见你。
He bought a complete Lu Hsun. 他买了一套鲁迅全集。
4、用于转化为普通名词的物质名词前,表示相应的产品或种类,有时表示数量关系。
如:It’sagoodwine.这是(一种)好酒。 Twocoffeesandatea,please.请来两杯咖啡和一杯茶。
5、用于具体化的抽象名词前,表示与该抽象名词意义相关的人或事等。
如:The party was a great success. 晚会开得非常成功。
It's a pleasure to talk with you. 同你谈话是件愉快的事。
6、用于某些由动词转化来或具有动作意味的名词前,表示一次、一番等意义。
如:Let me have a look. 让我看看吧。
I'll give the car a good wash. 我要把车好好洗一洗。
7、用于序数词前表示数量或序数的增加。
如:He bought a second computer. 他又买了一台(即第二台)电脑。
Later she borne a third son. 后来她又生了第三个儿子。
8、有的不可数名词或本来应该带定冠词(the)的名词,由于受定语(尤其是形容词)的修饰,其前一般要用不定冠词或改用不定冠词,表示某种状态,此时的不定冠词通常含有a kind of的意思。
如:have breakfast 吃早餐→have a quick breakfast 吃快餐
the world 世界→a world like ours 像我们这样的世界
注:有些不可数名词即使受形容词的修饰也不能用不定冠词,容易弄错的有:news(消息),advice(忠告),luck(运气),fortune(运气),work(工作),fun(娱乐,有趣的事),weather(天气),homework(家庭作业),housework(家务活),information(情报),behavior(行为),harm(伤害),damage(损害),progress(进步),furniture(家具),baggage(行李),luggage(行李),poetry(诗),scenery(风景)等。
9、两个单数可数名词连用表示一个整体时,只用一个不定冠词。
如:He is a teacher and poet. 他既是老师又是诗人。
There's a horse and cart on the road. 路上有一辆马车。
10、不定冠词可用来表示“类属”,这是其基本用法,它表明的是某一类属中的每一个人和东西都能说明该类属的整体情况(有类似汉语的“举一反三”或“以此类推”的含义)。此时也可用定冠词或名词复数形式来表示。
如:马是有用的动物。
正:A horse is a useful animal.
正:The horse is a useful animal.
正:Horses are useful animals.
若不是说明每一个人和东西的情况,而是说整个类属,则不能用不定冠词,而要用定冠词。
如:The tiger is indanger of becoming extinct.老虎面临绝种的危险。
Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone in 1876.亚历山大·格雷汉母·贝尔于1876年发明了电话。
不定冠词知识体系:
| 不定冠词 | a | 1、辅音音素开头的单词前用a,否则用an。 2、泛指,表“一个”但概念比one弱。 3、表类别 a+可数名词单数,不译为“一”。 4、表示单位,相当于“每”的意思。 5、用于序数词前,表“又一,再一”。 6、用于某些固定词组中,a lot of等。 |
| an |
使用不定冠词和不用不定冠词的差异:
1、英语中的某些名词即可用作不可数名词,又可用作可数名词,但是含义不同,用法也不一样。
如:iron 铁;an iron 一个熨斗
kindness 和善; a kindness 一件善事
2、“with+抽象名词”使用时相当于副词,抽象名词前不用不定冠词。
如:with pleasure 乐意地
with kindness 亲切地
with joy 高兴地
with diffculty 吃力地
with angry 生气地
但在“with+a+名词”结构中虽有不定冠词,却没有实际意义。
如:with a smile 微笑地
with an effort 努力地
with a light heart 愉快地
因汉语习惯用错不定冠词的几种情形:
(1)单数可数名词若泛指,其前需加a/an,不要按汉语习惯漏掉此不定冠词:
如:他是著名影星。
正:Heisafamousfilmstar.
误:Heisfamousfilmstar.
(2)不定冠词不能与指示代词、物主代词、所有格等连用:
如:我在公园遇到了我的一位朋友。
正:Imetafriendofmineinthepark.
误:Imetmyafriendinthepark.
(3)不要受汉语影响而用错不定冠词位置:
如:我从未读过如此有趣的书。
正:Ihaveneverreadsuchaninterestingbook.
误:Ihaveneverreadasuchinterestingbook.
误:Ihaveneverreadasointerestingbook.
不定冠词的省略与重复:
(1)在不引起误会的情况下,两个并列名词中的后一个名词前的不定冠词可以省略:
如:The noun is the name of a person or thing. 名词是人和物的名称。
(2)当两个并列名词指的是同一个人时,后一名词前的不定冠词通常省略:
如:His father is a teacher and poet. 他父亲是位教师兼诗人。
但如果要强调这两种身份,也可后一个不定冠词:
His father is a teacher and a poet. 他父亲既是教师,又是诗人。
有时,由于两个并列的名词关系比较紧密、被视为一个整体,也可只用一个冠词:
A man and woman are walking arm-in-arm.一对男女手挽着手走着。
(3)两个形容词并列同时修饰一个名词时,若该名词指的是两个事物,则通常应分别使用两个冠词:
如:We have a black and a white cat. 我们养了一只黑猫和一只白猫。
(比较:We have a black and white cat. 我们养了一只黑白花猫。)
但是,有时两个并列的名词只一个事物,为了加强语气,也有了两个冠词:
如:It was a cold and a dark night. 那是一个又冷又黑的夜晚。
(4)有些由两样东西构成的“自然成对”使用的事物,通常只在其前使用一个冠词:
如:a knife and fork一副刀叉
a cup and saucer 一副茶杯与茶托
a horse and cart 一辆马车
a needle and thread 一根带线的针
hire a car and driver 租一辆配有司机的汽车
有时连第一个冠词也省略(尤其是与介词连用时):
如:with knife and fork 用刀叉
(5)当要对两个并列的名词进行选择和比较方面的强调时,通常应重复两个冠词:
如:Give me a pen, not a pencil. 给我一支钢笔,不是铅笔。
Do you want a novel or a dictionary? 你是想要本小说,还是想要本字典?
连接代词的概念:
连接代词常用来引导一个主语从句、宾语从句和表语从句,在句中可用作主语、宾语、表语、定语等,连接代词主要包括who, whom, what, which, whose, whoever, whatever, whichever, whosever等。
whatever, whoever, whichever 用法说明:
主要用于引导主语从句和宾语从句。
如:He does whatever she asks him to do. 她要他做什么,他就做什么。
Whoever breaks the rules will be punished.谁违反这些规则都将受到处罚。
I'll give the ticket to whoever want sit. 请想要这票,我就把它给谁。
Whichever team gains the most points wins. 哪个队得分最多,哪个队就赢。
注:其中的ever主要用于加强语气,含有“一切”、“任何”、“无论”之义。使用这类词时,注意不要按汉语习惯用错句子结构:
如:任何人(谁)先来都可以得到一张票。
误:Anyone comes first can get a ticket./ Who comes first can get a ticket.
正:Anyone who comes first can get a ticket./ Whoever comes first can get a ticket.
连接代词的用法:
1、连接代词主要包括who, whom, what, which, whose, whoever, whatever, whichever, whosever等,它们在句中可用作主语、宾语、表语、定语等,可以引导主语从句、宾语从句和表语从句:
如:I don't know who he is. 我不知道他是谁。
What he says sounds reasonable. 他说的话听起来很有道理。
The question is who(m) we should trust. 问题是我们该信任谁。
I'll take whoever wants to go. 谁想去我就带谁去。
Take whichever seat you like? 你喜欢坐哪个座位就坐哪个?
I will just say whatever comes into my mind. 我想到什么就说什么。
注:who, whom, whoever等不用于名词前作定语。
2、what的两种用法。请看以下两个句子:
(1)I didn't know what he wanted. 我不知道他想要什么。
(2)I gave her what she wanted. 我给了她想要的一切。
上面第一句中的what表示“什么”,带有疑问的意味;第二句中的what表示“所…的一切事或东西”,其意义上大致相当于that(those) which, the thing(things) that, anything that, all that, as much as等,又如:
What[=That which] you say is quite true. 你说的完全是事实。
He saves what[=all that] he earns. 他赚多少,积蓄多少。
Call it what[=anything that] you please. 你喜欢叫它什么就叫它什么。
这样用的what有时还可后接一个名词:
如:He gave me what money[=all the money that] he had about him. 他把身边带有的钱全给了我。
What friends[=All the friends that] he has are out of the country. 他所有的朋友都在国外。
连接代词知识体系:

whatever, whoever, whichever 用法说明:
主要用于引导主语从句和宾语从句。
如:He does whatever she asks him to do. 她要他做什么,他就做什么。
Whoever breaks the rules will be punished.谁违反这些规则都将受到处罚。
I'll give the ticket to whoever want sit. 请想要这票,我就把它给谁。
Whichever team gains the most points wins. 哪个队得分最多,哪个队就赢。
注:其中的ever主要用于加强语气,含有“一切”、“任何”、“无论”之义。使用这类词时,注意不要按汉语习惯用错句子结构:
如:任何人(谁)先来都可以得到一张票。
误:Anyone comes first can get a ticket./ Who comes first can get a ticket.
正:Anyone who comes first can get a ticket./ Whoever comes first can get a ticket.
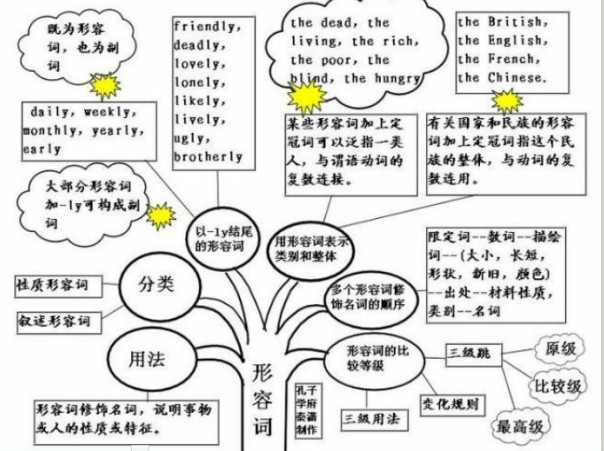
形容词的概念:
形容词(adjective),简称adj.或a,形容词用来修饰名词或代词,表示人或事物的性质、状态,和特征的程度好坏与否,形容词在句中作定语、表语、宾语补足语。通常,可将形容词分成性质形容词和叙述形容词两类,其位置不一定都放在名词前面。
形容词的作用与位置:
形容词是用来修饰名词的,常被放在名词前作定语,或放在系动词后面作表语。以下属几种特殊情况,须牢记;
(1)形容词短语作定语,定语后置。
如:a language difficult to master,
a leaning tower about 180 feet high
(2)表语形容词(afraid、alike、alone、asleep、awake、alive等)作定语,定语后置。如a man alive。有些表身体健康状况的形容词如well、faint、ill只作表语。sick既可作表语又可作定语,ill如作定语意为“bad”。
(3)用作定语,修饰由不定代词one、no、any、some和every构成的复合词如anything、something等时,通常后置。
如:I have something important to tell you.
(4)else常用作疑问代词和不定代词的后置定语。
(5)enough、nearby修饰名词前置或后置,程度副词一般位于形容词、副词前面,enough修饰形容词、副词时,必须后置。
(6)几个并列的形容词作定语,其语序通常为:限定语(The、A)+描绘性形容词+size(大小)+shape(形状)+age(年龄、时间)+color(颜色)+origin(国籍、来源)+material(材料)+purpose(目的)+名词。
口诀:
限定描绘大长高,形状年龄和新老;颜色国籍跟材料,作用类别往后靠。
如:a heavy black Chinese steel umbrella,
the man's first tow interesting little red French oil paintings
形容词的用法:
1、形容词修饰名词,说明事物或人的性质或特征。通常,可将形容词分成性质形容词和叙述形容词两类,其位置不一定都放在名词前面:
1)直接说明事物的性质或特征的形容词是性质形容词,它有级的变化,可以用程度副词修饰,在句中可作定语、表语和补语。例如:hot热的。
2)叙述形容词只能作表语,所以又称为表语形容词。这类形容词没有级的变化,也不可用程度副词修饰。
大多数以a开头的形容词都属于这一类。例如:
afraid害怕的。(错)Heisanillman. (对)Themanisill. (错)Sheisanafraidgirl. (对)Thegirlisafraid.
这类词还有:well,unwell,ill,faint,afraid,alike,alive,alone,asleep,awake等。
3)形容词作定语修饰名词时,要放在名词的前边。但是如果形容词修饰以-thing为字尾的词语时,要放在这些词之后。例如:somethingnice
2、用形容词表示类别和整体:
1)某些形容词加上定冠词可以泛指一类人,与谓语动词的复数连接。如:the dead,the living,the rich,the poor,the blind,the hungry The poorarelosinghope.穷人失去了希望。
2)有关国家和民族的形容词加上定冠词指这个民族的整体,与动词的复数连用。如:the British,the English,the French,the Chinese. The English have wonderful senseofhumor.
以-ly结尾的形容词:
1)大部分形容词加-ly可构成副词。但friendly,deadly,lovely,lonely,likely,lively,ugly,brotherly,仍为形容词。改错:
如:(错)She sang lovely.
(错)He spoke to me very friendly.
(对)Her singing was lovely.
(对)He spoke to me in a very friendly way.
2)有些以-ly结尾既为形容词,也为副词。 daily,weekly,monthly,yearly,early .
如:The Times is a daily paper.
The Times is published daily.
形容词知识体系:
复合形容词的构成:
(1)形容词+名词+ed:
如:kind-hearted 好心的,white-haired 白发的
(2)形容词+形容词:
如:red-hot 炽热的,dark-blue 深蓝的
(3)形容词+现在分词:
如:good-looking 好看的,easy-going 随和的
(4)副词+现在分词:
如:hard-working 勤劳的,fast-moving 快速转动的
(5)副词+过去分词:
如:hard-won 得来不易的,newly-made 新建的
(6)名词+形容词:
如:life-long 终生的,world-famous 世界闻名的
(7)名词+现在分词:
如:peace-loving 爱好和平的,fun-loving 爱开玩笑的
(8)名词+过去分词:
如:snow-covered 白雪覆盖的,hand-made 手工的
(9)数词+名词+ed:
如:four-storeyed 4层楼的,three-legged 3条腿的
(10)数词+名词(名词用单数):
如:ten-year 10年的, two-man 两人的
介词和介词短语的概念:
介词是一种用来表示词与词、词与句之间的关系的虚词,在句中不能单独作句子成分。介词后面一般有名词、代词或相当于名词的其他词类,短语或从句作它的宾语。介词和它的宾语构成介词词组,在句中作状语,表语,补语或介词宾语。介词可以分为时间介词、地点介词、方式介词和其他介词。
误用介词的三种情况:
1、多用介词:
多用介词可能是受汉语意思的影响将及物动词误用作不及物动词,也可能是受相关结构的影响而用错:
误:We discussed about the plan.
正:We discussed the plan. 我们讨论了计划。
误:Did he mention about the accident?
正:Did he mention the accident? 他提到那次事故了吗?
误:I saw her enter into the bank.
正:I saw her enter the bank. 我看见她进了银行。
误:He married with[to] a nurse.
正:He married a nurse. 他同一位护士结了婚。
误:How can contact with you?
正:How can contact you? 我怎么与你联系?
误:We should serve for the people heart and soul.
正:We should serve the people heart and soul. 我们应该全心全意地为人民服务。
误:Who controls over the factory? (但名词control可接over)
正:Who controls the factory? 谁管理这个工厂?
误:He has a great many of friends here. (比较a great number of)
正:He has a great many friends here. 他在这儿有很多朋友。
2、漏用介词:
漏用介词可能是受汉语意思的影响将不及物动词误用作及物动词,或是受相关结构的影响的影响而用错等:
误:This matter is difficult to deal. (deal with=处理)
正:This matter is difficult to deal with. 这事很难处理。
误:He is not a man to be depended.
正:He is not a man to be depended on. 他不是个可靠的人。
误:He took a cup of tea, and went on the story.
正:He took a cup of tea, and wentonwiththestory.他喝了一口茶,又接着讲故事。
误:My mother still regards me a child. (比较consider…as中的as可省略)
正:My mother still regards me as a child. 我母亲还把我当小孩看。
误:They insisted sending a car over to fetch us.
正:They insisted on sending a car over to fetch us.他们坚持要派车来接我们。
误:What he says is worth listening.
正:What he said is worth listening to.他的话值得一听。
3、错用介词:
错用介词的情况比较复杂,可能是因受汉语意思的而错,也可能是因弄不清搭配关系而错,可能是混淆用法而错,也可能是受相关结构的影响而错,可能是忽略语境而错,也可能是想当然的用错:
误:She called on his office yesterday. (call on+人,call at+地点)
正:She called at his office yesterday. 她昨天去了他办公室拜访。
误:He is engaged with a nurse.
正:He is engaged to a nurse.他与一位护士订了婚。
误:The sun rises from the east.
正:The sun rises in the east.太阳从东方升起。
误:Under his help, I finished it in time.
正:With his help, I finished it in time. 在他的帮助下,我及时做完了。
误:During he was in Japan, he visited many places.
正:During his stay in Japan, he visited many places.他在日本期间,参观过许多地方。
误:We are familiar to his character.
正:We are familiar with his character.我们了解他的性格。
误:Help yourself with the fruit.
正:Help yourself to the fruit.吃点水果吧。
介词的宾语:
1、名词或代词作介词宾语:
如:Are you interested in history? 你对历史感兴趣吗?
Don't worry about it. 别为它担心。
注:若是人称代词用作介词宾语,要注意用宾格。
如:No one can sing like her. 没有人能像她那样唱歌。(不能用like she)
2、动名词作介词宾语:
如:He is good at telling stories. 他善于讲故事。
In crossing the street he was run over. 他在穿过马路时被汽车撞倒。
3、过去分词作介词宾语:
如:We can't regard the matter as settled. 我们不能认为这事已经解决。
I take it for granted you have read the book. 我以为你读过这本书。
注:过去分词用作介词宾语通常只见于某些固定结构中,如上面第1句涉及regard…as(认为…是)结构,第2句涉及take sth for granted(认为某事属实)。在其他情况下,介词后通常不直接跟过去分词作宾语,若语义上需要接过去分词(表被动),可换用“being+过去分词”:
如:He went out without being seen by the others.他出去了,没有被其他人看见。
4、从句作介词宾语:
如:He was not satisfied with what she said. 他对她说的不满意。
I'm worried about where he is. 我担心他上哪儿去了。
注:介词后通常不接that从句,遇此情况需考虑用其他结构:
误:He paid no attention to that she was poor.
正:He paid no attention to the fact that she was poor. 他根本不注意她很穷这一事实。
但有个别介词(如except)可接that从句。
比较:I know nothing about him except that he lives next door./I know nothing about him except for the fact that he lives next door. 我只知道他住在隔壁,其它的就不知道了。
5、不定式作介词宾语:
如:I had no choice but to wait. 除了等,我没有别的选择。
He wanted nothing but to stay there. 他只想留在那儿。
They did nothing but complain. 他们老是一个劲地抱怨。
He never did anything but watch TV. 除了看电视,他从不干任何事。
注:(1)介词后接不定式的情形通常只见于but, except等极个别个词。该不定式有时带to,有时不带to,其区别是:若其前出现了动词do,其后的不定式通常不带to;
若其前没有出现动词do,则其后的不定式通常带to。
(2)介词后虽然通常不直接跟不定式作宾语,但却可接“连接代词(副词)+不定式”结构:
如:He gave me some advice on how to do it. 对于如何做这事他给我提了些建议。
6、形容词作介词宾语:
如:Her pronunciation is far from perfect. 她的语音远不是完美的。
In short, we must be prepared. 总而言之,我们要有准备。
Things have gone from bad to worse. 事情越来越糟。
注:(1)有些形容词用作介词宾语可视为其前省略了动名词being:
如:He regarded the situationas(being) serious. 他认为形势严重。
His work is far from(being) satisfactory. 他的工作丝毫不令人满意。
(2)有些“介词+形容词”的结构已构成固定搭配:in full全部地,全面地,无省略地; in private私下地,秘密地; in particular特别地;in general一般地,通常地,概括地; in brief 简言之;in short总之,简言之; in vain徒然地,徒劳无益地;for fee免费地,无偿地; for certain肯定地,确切地;for sure肯定地,确切地; for short为了简短,简称;atl arge自由自在地,逍遥法外; by far…得多
7、副词作介词宾语:
如:I can't stay for long. 我不能久呆。
It's too hot in here. 这里面太热了。
I looked every where except there. 除了那儿,我到处都看过了。
8、数词作介词宾语:
如:The city has a population of four million. 这座城市有四百万人口。
He was among the first to arrive. 他是第一批到的。
9、介词短语作介词宾语:
如:Choose a book from among these. 从这些书中选一本吧。
I saw her from across the street. 我从街的对面望见了她。
注:通常可后接介词短语作宾语的介词是from, till, until, since, except, instead of等。
比较:I took it from the bed. 我从床那儿(或床上)拿的。
I took it from under the bed. 我从床下拿的。
10、复合结构用作介词宾语:
如:She had no objection to Mary marrying him. 她不反对玛丽与他结婚。
She came in with a book in her hand. 她手里拿着一本书走了进来。
All the afternoon he worked with the door locked. 整个下午他都锁着门在房里工作。
介词短语的句法功能:
1、表语:
如:He was with a friend. 他和一个朋友在一起。
Health is above wealth. 健康胜过财富。
This knife is for cutting bread. 这把小刀是用于切面包的。
注:有些介词(如because of)引出的短语通常只用作状语,不用作表语:
误:His absence is because of the rain.
正:His absence is due to the rain. 他因雨未来。
但是,若主语是代词(不是名词),becauseof引出的短语可用作表语:
如:It is because of hard work. 那是因为辛苦工作的原因。
2、状语:
如:Don't touch it with your hands. 别用手去摸它。
Did you do this by design or by accident? 你这样做是有意的还是无意的?
3、定语:
如:This is his reply to your letter. 这是他给你的回信。
This is the best way of doing it. 这是做此事最好的方法。
My love for you is deeper than the sea. 我对你的爱比海深。
4、宾语补足语:
如:I found everythingin good condition. 我发现一切正常。
Her illness kept her in bed for a week. 她因生病在床上躺了一星期。
注:用作宾语补足语的介词短语在相应的被动语态中则为主语补足语:
如:He was regarded as a hero. 他被看成是英雄。
5、宾语:
如:A man stepped out from behind the wall. 一个人从墙后走出来。
He cannot spare anytime except on Sunday. 除星期日外,他抽不出时间。
6、主语:
如:Between6 and 7 suits me. 六点到七点对我比较适合。
After the exams is the time to relax. 考试后是轻松一下的时间。
注:介词短语通常不用作主语,尽管有时也像上面这样用作主语,但通常可视为是在一定的上下文中有所省略:
如:—When are we going to have the next meeting? 我们下次什么时候见面?
—On Tuesday may be convenient. 星期二可能比较方便。
此句中onTuesday虽用作主语,但可视为是其前省略了meeting一词:
即:Meeting during the vacation may be convenient.
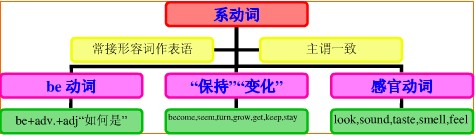
系动词的概念:
连系动词(link verb)是一个表示谓语关系的动词。它必须后接表语(通常为名词或形容词)。连系动词的功能主要是把表语(名词、形容词、某些副词、非谓词、介词短语、从句)和它的主语联系在一起,说明主语的属性、特征或状态。它有自己的但不完全的词义,不能在句中独立作谓语,必须和后面的表语一起构成句子的谓语。它是虚词。
系动词的分类:
1、状态系动词:
用来表示主语状态,只有be一词。
例如:He is a teacher. 他是一名教师。(is与补足语一起说明主语的身份。)
2、持续系动词用来表示主语继续或保持一种状况或态度,主要有keep, rest, remain, stay, lie, stand:
例如:The weather will continue cold and wet.
He remained poor after 20years.
The shop will stay open at 11:00p.m.
He stood/sat silent there.
3、表像系动词:
用来表示"看起来像"这一概念,主要有seem, appear, look。
例如:She appears to have know this thing.
She seems a student.
4、感官系动词:
感官系动词主要有feel, smell, sound, taste。
例如:The silk feels soft.
Your idea sounds a good one.
He looked like his mother.
The mixture tasted terrible.
The flower smells sweet.
5、变化系动词:
这些系动词表示主语变成什么样,变化系动词主要有become, grow, turn, fall, get, go, come, run。
例如:My dream o fcoming to China has come true.
In summer food often goes bad.
He turned doctor./ He became a doctor.
He fell asleep as soon as he went to bed.
6、终止系动词表示主语已终止动作,主要有prove, turn out,表达"证实","变成"之意。
例如:The truth he stuck to proved true.
系动词基本用法:
连系动词是表示不完全谓语关系的动词,它与其后的表语一起构成谓语。
常见的连系动词有be(是),become(成为),get(变成),remain(还是),seem(似乎是),look(看上去),feel(感觉)等。
连系动词后的表语通常是名词和形容词,有时也可以是代词、数词、副词、介词短语、不定式、动名词、从句等:
如:His English is excellent. 他的英语很棒。(跟形容词)
He is a famous poet. 他是著名诗人。(跟名词)
Money isn't everything. 金钱不是一切。(跟代词)
She was the first to arrive. 她是第一个到达的人。(跟数词)
Who is up stairs? 谁在楼上?(跟副词)
He is with his friends. 他和朋友在一起。(跟介词短语)
He seems to be ill.他似乎病了。(跟不定式)
Seeing is believing. 眼见为实。(跟动名词)
This is what you need. 这就是你需要的。(跟从句)
注:有些系动词又是实义动词,该动词表达实义时,有词义,可单独作谓语。
例如:1、She tasted①the soup to see if it tasted②too salty. 她尝了一口汤,看是否太咸。
2、The doctor is feeling①his pulse because he feels②sick. 因为身体不舒服,医生正在给他切脉。
3、The mother looked①at the sick child sadly and she looked②sad. 母亲难过地看着生病的孩子。
4、She smelled①the meat to make sure it still smelled②good. 她闻了闻肉,看看是否还新鲜。
5、The teacher asked the students to keep②quite when they were keeping①everything in order. 当学生整理东西时,老师让他们保持安静。
从以例子不难出,标①的动词为实义动词,他们后跟有宾语;标②的动词为系动词,其后往往跟形容词、名词、不定式等作表语。
系动词知识体系:
连系动词使用应注意的两点:
1、关于连系动词后接副词作表语:
连系动词后通常可接形容词作表语,一般不接副词:
误:His English is very well. 他的英语很好。(应将well改为good)
误:Be carefully. 小心点。(应将carefully改为careful)
误:The soup tastes nicely. 这汤味道不错。(应将nicely改为nice)
但是,有时连系动词后也可接副词作表语,不过这主要限于in, on, off, out, away, behind, up, down, over, through, around, round, below, inside, outside等少数副词小品词以及here, there, upstairs, downstairs等少数表示地点或方位的副词:
如:Mother wasn't in last night. 母亲昨晚不在家。
The meeting was over at five. 会议五点结束。
Come along. The taxi is outside. 来吧,出租车在外面。
Mother is downstairs waiting for you. 母亲在楼下等你。
2、关于连系动词后接不定式:
(1)连系动词be后根据情况可自由地接不定式作表语:
如:My dream is to be a scientist. 我的梦想是当一名科学家。
All I could do was to wait. 我只能等。
My plan was to go from London to Paris. 我计划从伦敦去巴黎。
I was to have seen Mr Kay. 我本要去见凯先生的。
(2)seem, appear, prove, continue, turn out, get, grow, come等连系动词后也可接不定式(尤其是to be)作表语:
如:She always seems to be sad. 她常常显得很忧伤。
My advice proved to be wrong. 我的意见证明是错的。
She appears to have many friends. 他好像有很多朋友。
The weather turned out to be fine. 天气结果很好。
Circumstances continue to be favorable. 情况仍然是有利的。
He has grown to like studying English. 他渐渐喜欢学英语了。
【注】
若所接不定式为to be,通常可以省略。不过,若其后接的是表语形容词,则to be通常不宜省略。
另外,连系动词look后能否接tobe似乎尚有争论,不过,在现代英语中接to be的现象已较普遍。
(3)sound, smell, feel, taste, become等连系动词后通常不能接不定式:
误:These oranges taste to be good. (应去掉to be)
误:The roses smell to be nice.(应去掉to be)
(4)有的连系动词后接的从句可用不定式来改写:
如:It seems that she's right./ She seems to be right. 她似乎是对的。
It appears that you have made a mistake./You appear to have made a mistake. 似乎你弄错了。
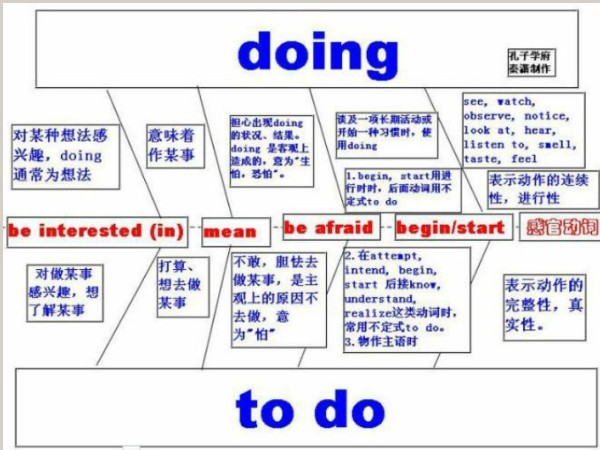
动名词概念:
动名词是一种兼有动词和名词特征的非限定动词。它可以支配宾语,也能被副词修饰,动名词有时态和语态的变化。
现在分词和动名词用法比较:
动词的-ing形式包括现在分词和动名词两种形式。他们的句法功能如下:
动词的-ing形式如果作句子的主语或者宾语时,应该是动名词形式;如果作补语或者状语时,应该是现在分词形式。那么作表语或者定语的动名词和现在分词又该怎样区分呢?
1、动名词与现在分词作表语时的比较:
(1)动名词作表语说明主语的内容,回答what的问题;现在分词作表语相当于形容词作表语,说明主语的性质、特征等,回答how的问题。
如:One of the best exercises is swimming. 游泳是最好的运动项目之一。
What pleases him most is bathing in the sea. 最使他高兴的事是在海中沐浴。
The situation both at home and abroad is very in-spiring. 国内外的形势都很鼓舞人心。
The color is pleasing to the eye. 颜色悦目。
(2)动名词作表语,表语和主语几乎处于同等地位,可以互换位置,其句意不变;现在分词作表语,表语和主语则不能互换位置。
如:Our work is serving the people.
(=Serving the people is our work.)我们的工作是为人民服务。
The news was disappointing. 那消息令人失望。
(3)作表语的现在分词前可以用very,quite,rather,greatly等副词修饰,而动名词则不可以。
如:What he said was very encouraging. 他的话很鼓舞人心。
Our goal is realizing the four modernizations in the near future. 我们的目标是在不久的将来实现四个现代化。
(4)现在分词与形容词一样可以和more,the most构成形容词的比较级和最高级,而动名词则不可以。
如:The story is the most fascinating. 那个故事最迷人。
(5)作表语用的现在分词除了和be连用以外,还可以和其它的系动词连用;而作表语的动名词则通常只能和be连用。
如:His speech seems inspiring.他的演讲似乎很鼓舞人心。
His interest is writing for the news papers. 他的爱好是给报社写文章。
(6)有些用作表语的现在分词已经形容词化了。常见的有:exciting,moving,inspiring,missing,interesting,disappointing等。
2、动名词与现在分词作定语时的比较:
(1)动名词作定语时,表示它所修饰的名词的性能和用途,和它所修饰的名词在逻辑上没有主谓关系;
现在分词作定语时,表示它所修饰的名词正在进行的动作,和它所修饰的名词在逻辑上有主谓关系,常可以扩展成一个定语从句。
如:a swimming girl=a girl who is swimming 一个在游泳的姑娘
a walking stick=a stick that is used for walking 一根拐杖
(2)现在分词作定语有时可以后置,而动名词则通常只能放在它所修饰的名词之前。
如:The girl wearing glasses is one of his students. 戴眼镜的那个女孩是他的一个学生。
I bought some reading materials. 我买了一些阅读材料。
动名词的用法:
1、作主语:
例如:Fighting broke out between the South and the North. 南方与北方开战了。
2、作宾语:
a. 有些动词可以用动名词作宾语。
例如:admit承认 appreciate感激 avoid避免 complete完成 consider认为 delay耽误 deny否认 detest讨厌 endure忍受 enjoy喜欢 escape逃脱 fancy想象 finish完成 imagine想象 mind介意 miss想念 postpone推迟 practice训练 recall回忆 resent讨厌 resume继续 resist抵抗 risk冒险 suggest建议 face面对 include包括 stand忍受 understand理解 forgive宽恕 keep继续
例如:Would you mind turning down your radio a little, please? 你把收音机音量调小一点,好吗?
The squirrel was lucky that it just missed being caught. 这松鼠幸运得很,刚逃避了被逮住的厄运。
b. 有些结构后面可以用动名词作宾语或其他成分。
例如:admit to prefer...to burst out keep on insist on count on set about put off be good at take up give up be successful in be used to lead to devote oneself to object to stick to no good no use be fond of look forward to be proud of be busy can't help be tired of be capable of be afraid of think of
3、作表语,对主语说明、解释:
例如:Her job is washing, cleaning and taking care of the children. 她的工作是洗刷、清扫和照顾孩子。
比较:She is washing, cleaning and taking care of the children.
4、作定语,一般表示所修饰名词事物的用途:
例如:a writing desk=a desk for writing 写字台
a swimming pool=a pool swimming 游泳池
有些动名词作定语,与所修饰的名词关系比较复杂。
例如:boiling point=a temperature point at which something begins to boil 沸点
a walking tractor=a tractor which a driver can operate while he or she is walking behind it 手扶拖拉机
动名词知识体系:

动名词与不定式用法对比:
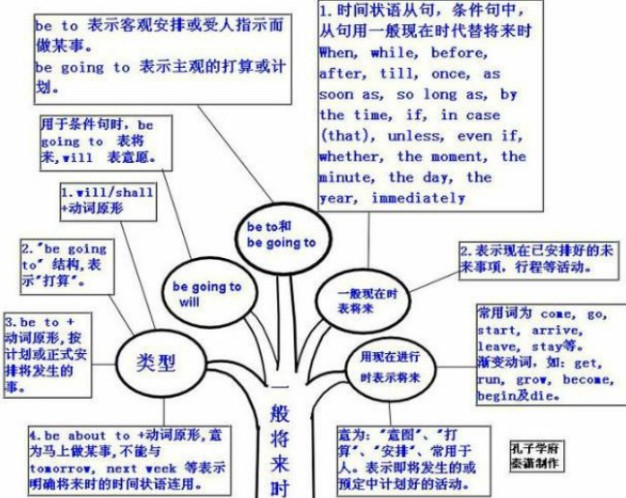
一般将来时的概念:
一般将来时表示将来某一时刻的发生动作或状态,或将来某一段时间内经常的动作或状态。常与表示将来的时间状语连用。
一般将来时用法:
1)shall用于第一人称,常被will所代替。will在陈述句中用于各人称,在征求意见时常用于第二人称。
例如:Which paragraph shall I read first?我先读哪一段呢?
Will you be at home at seven this evening? 今晚七点回家好吗?
2)be going to+不定式,表示将来。
a. 主语的意图,即将做某事。
例如:What are you going to do tomorrow? 明天打算作什么呢?
b. 计划,安排要发生的事。
例如:The play is going to be produced next month。这出戏下月开播。
c. 有迹象要发生的事。
例如:Look at the dark clouds, there is going to be a storm. 看那乌云,快要下雨了。
3)be+不定式表将来,按计划或正式安排将发生的事。
例如:We are to discuss the report next Saturday. 我们下星期六讨论这份报告。
4)be about to+不定式,意为马上做某事。
例如:He is about to leave for Beijing. 他马上要去北京。
注意:be about to do不能与tomorrow, next week 等表示明确将来时的时间状语连用。
一般将来时知识体系:
一般现在时表将来:
1)下列动词come, go, arrive, leave, start, begin, return的一般现在时可以表示将来,主要用来表示在时间上已确定或安排好的事情。
例如:The train leaves a tsix tomorrow morning. 火车明天上午六点开。
—When does the bus star? 汽车什么时候开?
—It stars in ten minutes. ?十分钟后。
2)以here, there等开始的倒装句,表示动作正在进行。
例如:Here comes the bus.=The bus is coming. 车来了。
There goes the bell.=The bell is ringing. 铃响了。
3)在时间或条件句中。
例如:When Bill comes(不是will come), ask him to wait for me. 比尔来后,让他等我。
I'll write to you as soon as I arrive there. 我到了那里,就写信给你。
4)在动词hope, take carethat,makesurethat等的宾语从句中。
例如:I hope they have a nice time next week. 我希望他们下星期玩得开心。
Make sure that the windows are closed before you leave the room. 离开房间前,务必把窗户关了。
现在进行时表示将来:
下列动词come, go, arrive, leave, start, begin, return等现在进行时可以表示将来。
例如:I'm leaving tomorrow. 明天我要走了。
Are you staying here till next week? 你会在这儿呆到下周吗?
与“短文改错。此题要求改正所给短文中的错误。对标有题号的每一...”考查相似的试题有:
- (2013·陕西宝鸡高三第一次联考)Jogging every morning is ________ good habit. Stick to it, and you'll make ________ grea...
- Although ____ badminton is my favorite sport, I am not _____ very good player.A.the ; aB.the ; theC./ ; aD./ ; the
- _______ his scientific work, he has no time to care for his family affairs, _______, of course, his wife always compl...
- Now ________ tents and medicine are needed in the quake-stricken area.[ ]A. a great deal of B. a large amount of C. a...
- 27.After the adventure, the children returned home, ______.A.safe but tiredB.safely but tiredlyC.safely but tired...
- Nanjing is a beautiful city and it _____ again.[ ]A. is worth being visitedB. is worthy of visitingC. is worthy to vi...
- I can't give my son the leading position.________, he is too young; secondly, I want Mr Smith to havethe job.[ ]A. Af...
- Mr Black was driving fast to take his wife to a nearby hospital because their baby was ________.A.on its wayB.in th...
- One day Chuck is ______ a flight ______ the Pacific Ocean suddenly ______ his plane crashes.[ ]A. in; over; whileB. o...
- I desire to make friends with him, but ________ I am worried that I can't get along well with him.[ ]A. on the wholeB...