本试题 “The last letter ____ arrived yesterday morning left him______ very sad.[ ]A. which; feelB. which; to feelC. that; feelingD. /; felt” 主要考查您对关系代词
动名词
等考点的理解。关于这些考点您可以点击下面的选项卡查看详细档案。
- 关系代词
- 动名词
关系代词的概念:
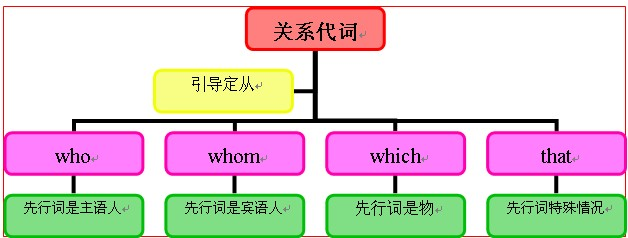
英语中的关系代词有who, whom, whose, that, which, 它们是用来引导定语从句的。关系代词既代表定语从句所修饰的词,又在其所引导的从句中承担一个成分,如主语、宾语、表语、或定语。
如:This is the man who saved your son. (who在从句中作主语,先行词是man)
The man whom I met yesterday is Jim.
A child whose parents are dead is an orphan.
He wants a room whose window looks out over the sea.
关系代词用法:
1、that与which的用法区别:
两者都可指物,常可互换。其区别主要在于:
(1)引导非限制性定语从句时,通常要用which:
如:She received an invitation from her boss, which came as a surprise. 她收到了老板的邀请,这是她意想不到的。
(2)直接放在介词后作宾语时,通常要用which:
如:The tool with which he is working is called a hammer. 他干活用的那个工具叫做锤子。
(3)当先行词是下列不定代词或被它们修饰时much, little, none, all, few, every(thing), any(thing), no(thing)等时,通常用that:
如:There was little that the enemy could do but surrender. 敌人无法,只有投降了。
All[Everything] that can be done must be done. 凡能做的事都必须做。
(4)当先行词有the very, the only, the same等修饰时,通常用that:
如:This is the only example that I know. 我知道的例子只有这一个。
Those are the very words that he used. 那是他的原话。
(5)当先行词有形容词最高级或序数词(包括last, next等)等修饰时,通常用that:
如:This is the best dictionary that I've ever used. 这是我用过的最好的词典。
The first thing that you should do is to work out a plan. 你应该做的第一件事是订个计划。
(6)当关系代词在定语从句中用作表语时,通常用that:
如:China is not the country(that) it was. 中国已不是过去的中国了。
(7)当先行词是一个既指人又指物的并列词组时,通常用that:
如:They talked about the persons and things that most impressed them. 他们谈论了使他们印象最深的人和事。
(8)当要避免重复时:
如:Which is the course that we are to take? 我们选哪门课程?
2、that与who的用法区别:
(1)两者均可指人,有时可互换:
如:All that[who] heard him were delighted. 所有听了他讲话的人都很高兴。
Have you met anybody that[who] has been to Paris? 你遇见过到过巴黎的人吗?
He is the only one among us that[who] knows Russian. 他是我们中间唯一懂俄语的人。
(2)但是在下列情况,通常要用that:
①当先行词是一个既指人又指物的并列词组时:
如:I made a speech on the men and things that I had seen abroad. 我就我在国外所见到的人和事作了报告。
②当先行词是who时(为避免重复):
如:Who was it that won the World Cup in1982? 谁赢得了1982年的世界杯?
③当关系代词在定语从句中作表语时(可省略):
如:Tom is not the boy(that) he was. 汤姆这孩子已不是以前那个样子了。
关系代词知识体系:
关系代词用法拓展:
1、as与which的用法区别:
(1)引导限制性定语从句时,在such,as,thesame后只能用as,其他情况用which:
如:I never heard such stories as he tells. 我从未听过他讲那样的故事。
It's the same story as I heard yesterday. 这故事跟我昨天听到的一样。
This is the photo which shows my house. 这张照片拍的是我的住宅。
(2)引导非限制性定语从句时,有时两者可互换:
如:I live a long way from work, as [which] you know. 我住得离工作单位很远,这你是知道的。
(3)但在,在以下情况引导非限制性定语从句时,两者不可换用:
①当从句位于主句前面时,只用as:
如:As is known to everybody, the moon travels round the earth once every month. 月球每月绕地球转一周,这是每个人都清楚的。
②as引导的非限制性定语从句应与主句在意义上和谐一致,which无此限制:
如:He went abroad, as[which] was expected. 他出国了,这是大家预料到的。
He went abroad, which was unexpected. 他出国了,这让大家感到很意外。(不用as)
③as引导非限制性定语从句时,先行词通常不能是主句中某个具体的词,而应是整个句子、整个短语或某个短语推断出来的概念,而which则无此限制:
如:The river, which flows through London, is called the Thames. 这条流经伦敦的河叫泰晤士河。(不用as)
④当as引导非限制性定语从句作主语时,其谓语通常应是连系动词,而不宜是其他动词,而which则无此限制:
如:She has married again, as[which] seemed natural. 她又结婚了,这似乎很自常。
She has married again, which delighted us.她又结婚了,这使我们很高兴。(不用as)
2、who与whom的用法区别:
两者均只用于人,从理论上说,who为主格,whom为宾格:
如:Where's the girl who sells the tickets? 卖票的女孩在哪里?
The author whom you criticized in your view has written a letter in reply. 你在评论中批评的那个作者已写了一封回信。
但实际上,除非在正式文体中,宾格关系代词whom往往省略不用,或用who或that代之:
如:The man(that, who, whom) you met just now is called Jim. 你刚遇见的那个人叫吉姆。
不过,在以下几种情况值得注意:
(1)直接跟在介词后面作宾语时,只能用whom,而且不能省略:
如:She brought with her three friends, none of whom I had ever met before. 她带了3个朋友来,我以前都没见过。
(2)引导非限制性定语从句且作宾语时,who和whom均可用,但以用whom为佳,此时也不能省略:
如:This is Jack, who[whom] you haven't met before. 这是杰克,你以前没见过。
动名词概念:
动名词是一种兼有动词和名词特征的非限定动词。它可以支配宾语,也能被副词修饰,动名词有时态和语态的变化。
现在分词和动名词用法比较:
动词的-ing形式包括现在分词和动名词两种形式。他们的句法功能如下:
动词的-ing形式如果作句子的主语或者宾语时,应该是动名词形式;如果作补语或者状语时,应该是现在分词形式。那么作表语或者定语的动名词和现在分词又该怎样区分呢?
1、动名词与现在分词作表语时的比较:
(1)动名词作表语说明主语的内容,回答what的问题;现在分词作表语相当于形容词作表语,说明主语的性质、特征等,回答how的问题。
如:One of the best exercises is swimming. 游泳是最好的运动项目之一。
What pleases him most is bathing in the sea. 最使他高兴的事是在海中沐浴。
The situation both at home and abroad is very in-spiring. 国内外的形势都很鼓舞人心。
The color is pleasing to the eye. 颜色悦目。
(2)动名词作表语,表语和主语几乎处于同等地位,可以互换位置,其句意不变;现在分词作表语,表语和主语则不能互换位置。
如:Our work is serving the people.
(=Serving the people is our work.)我们的工作是为人民服务。
The news was disappointing. 那消息令人失望。
(3)作表语的现在分词前可以用very,quite,rather,greatly等副词修饰,而动名词则不可以。
如:What he said was very encouraging. 他的话很鼓舞人心。
Our goal is realizing the four modernizations in the near future. 我们的目标是在不久的将来实现四个现代化。
(4)现在分词与形容词一样可以和more,the most构成形容词的比较级和最高级,而动名词则不可以。
如:The story is the most fascinating. 那个故事最迷人。
(5)作表语用的现在分词除了和be连用以外,还可以和其它的系动词连用;而作表语的动名词则通常只能和be连用。
如:His speech seems inspiring.他的演讲似乎很鼓舞人心。
His interest is writing for the news papers. 他的爱好是给报社写文章。
(6)有些用作表语的现在分词已经形容词化了。常见的有:exciting,moving,inspiring,missing,interesting,disappointing等。
2、动名词与现在分词作定语时的比较:
(1)动名词作定语时,表示它所修饰的名词的性能和用途,和它所修饰的名词在逻辑上没有主谓关系;
现在分词作定语时,表示它所修饰的名词正在进行的动作,和它所修饰的名词在逻辑上有主谓关系,常可以扩展成一个定语从句。
如:a swimming girl=a girl who is swimming 一个在游泳的姑娘
a walking stick=a stick that is used for walking 一根拐杖
(2)现在分词作定语有时可以后置,而动名词则通常只能放在它所修饰的名词之前。
如:The girl wearing glasses is one of his students. 戴眼镜的那个女孩是他的一个学生。
I bought some reading materials. 我买了一些阅读材料。
动名词的用法:
1、作主语:
例如:Fighting broke out between the South and the North. 南方与北方开战了。
2、作宾语:
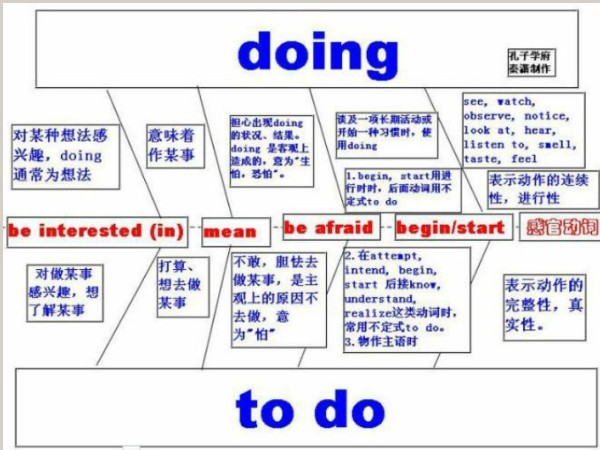
a. 有些动词可以用动名词作宾语。
例如:admit承认 appreciate感激 avoid避免 complete完成 consider认为 delay耽误 deny否认 detest讨厌 endure忍受 enjoy喜欢 escape逃脱 fancy想象 finish完成 imagine想象 mind介意 miss想念 postpone推迟 practice训练 recall回忆 resent讨厌 resume继续 resist抵抗 risk冒险 suggest建议 face面对 include包括 stand忍受 understand理解 forgive宽恕 keep继续
例如:Would you mind turning down your radio a little, please? 你把收音机音量调小一点,好吗?
The squirrel was lucky that it just missed being caught. 这松鼠幸运得很,刚逃避了被逮住的厄运。
b. 有些结构后面可以用动名词作宾语或其他成分。
例如:admit to prefer...to burst out keep on insist on count on set about put off be good at take up give up be successful in be used to lead to devote oneself to object to stick to no good no use be fond of look forward to be proud of be busy can't help be tired of be capable of be afraid of think of
3、作表语,对主语说明、解释:
例如:Her job is washing, cleaning and taking care of the children. 她的工作是洗刷、清扫和照顾孩子。
比较:She is washing, cleaning and taking care of the children.
4、作定语,一般表示所修饰名词事物的用途:
例如:a writing desk=a desk for writing 写字台
a swimming pool=a pool swimming 游泳池
有些动名词作定语,与所修饰的名词关系比较复杂。
例如:boiling point=a temperature point at which something begins to boil 沸点
a walking tractor=a tractor which a driver can operate while he or she is walking behind it 手扶拖拉机
动名词知识体系:

动名词与不定式用法对比:
与“The last letter ____ arrived yesterday morning left him__...”考查相似的试题有:
- I shall never forget the day _____ Shenzhou Ⅵ was launched, _____ has a great effect on my life.[ ]A. when; whichB. t...
- He said ______ at the meeting and just sat there silently.A.somethingB.anythingC.nothingD.everything
- Do you prefer_____when your boss takes an interest in your personal life?A.thisB.不填C.thatD.it
- ---- What about the two MP3s? ---- Sorry, but I don’t like _____ of them. Would you please show me a third one?A.non...
- Li Lei has been to __________ many times this month.A.her uncleB.her uncle’sC.her unclesD.aunt’s
- The father and the son entered the tiger area _______ two doors were open at the time.Suddenly five tigers appeared, ...
- Now there is a system ______ the waste is disposed of using the principles of ecology.[ ]A. whenB. thatC. whereD. what
- ——Your coffee smells great!——It’s from Mexico. Would you like ____ ?A.itB.someC.thisD.little
- ..Though he _________ the danger of drinking and driving ,he will have a couple of glasses of wine every day .A scare...
- There is a widespread belief among the science world ____ we keep on _____ the earth as we are doing today,the exist ...