本试题 “单句改错。每个句子有且仅有一处错误,或错一词,或多一词,或少一词.如本句多一词,把多余的词用斜线( )划掉;如本句错一词,在错词下划一横线,并在横线下写出改...” 主要考查您对可数名词及其单复数
零冠词
连接代词
形容词
介词和介词短语
过去分词
限制性定语从句
虚拟语气
等考点的理解。关于这些考点您可以点击下面的选项卡查看详细档案。
- 可数名词及其单复数
- 零冠词
- 连接代词
- 形容词
- 介词和介词短语
- 过去分词
- 限制性定语从句
- 虚拟语气
可数名词:
是指能以数目来计算,可以分成个体的人或东西;因此它有复数形式,当它的复数形式在句子中作主语时,句子的谓语也应用复数形式。
可数名词复数的规则变化:
| 情况 | 构成方法 | 读音 | 例词 |
| 一般情况 | 加 –s | 1.清辅音后读/s/; 2.浊辅音和元音后读/z/; |
map-maps bag-bags car-cars |
| 以s,sh,ch,x等结尾的词 | 加 -es | 读 /iz/ | bus-buses watch-watches |
| 以ce,se,ze,(d)ge等结尾 的词 |
加 -s | 读 /iz/ | license-licenses |
| 以辅音字母+y结尾的词 | 变y 为i再加es | 读 /z/ | baby-babies |
1)以y 结尾的专有名词,或元音字母+y结尾的名词变复数时,直接加s变复数:
如:two Marys the Henrys monkey---monkeys holiday---holidays
比较:层楼:storey---storeys story---stories
2)以o 结尾的名词,变复数时:
a. 加s,如: photo---photos piano---pianos
b. 加es,如:potato--potatoes tomato--tomatoes
c. 均可,如:zero---zeros / zeroes
3)以f或fe 结尾的名词变复数时:
a. 加s,如: belief---beliefs roof---roofs safe---safes gulf---gulfs;
b. 去f, fe 加ves,如:half---halves knife---knives leaf---leaves wolf---wolves wife---wives life---lives thief---thieves;
c. 均可,如:handkerchief: handkerchiefs / handkerchieves
可数名词复数的不规则变化:
1)child---children foot---feet tooth---teeth mouse---mice man---men woman---women
注意:与 man 和 woman构成的合成词,其复数形式也是 -men 和-women。
如:an Englishman,two Englishmen. 但German不是合成词,故复数形式为Germans;Bowman是姓,其复数是the Bowmans。
2)单复同形 如:
deer,sheep,fish,Chinese,Japanese
li,jin,yuan,two li,three mu,four jin
但除人民币元、角、分外,美元、英镑、法郎等都有复数形式。如:
a dollar, two dollars; a meter, two meters
3)集体名词,以单数形式出现,但实为复数。
如:staff people police cattle 等本身就是复数,不能说a staff a people,a police,a cattle,
但可以说a person,a policeman,a head of cattle, the English,the British,the French,the Chinese,the
Japanese, the Swiss 等名词,表示国民总称时,作复数用。
如:The Chinese are industries and brave. 中国人民是勤劳勇敢的。
4)以s 结尾,仍为单数的名词,如:
a. maths,politics,physics等学科名词,为不可数名词,是单数。
b. news 是不可数名词。
c. the United States,the United Nations 应视为单数。
The United Nations was organized in 1945. 联合国是1945年组建起来的。
d. 以复数形式出现的书名,剧名,报纸,杂志名,也可视为单数。
"The Arabian Nights" is a very interesting story-book.
<<一千零一夜>>是一本非常有趣的故事书。
5) 表示由两部分构成的东西,如:glasses (眼镜) trousers, clothes ;
若表达具体数目,要借助数量词 pair(对,双); suit(套); a pair of glasses; two pairs of trousers
6)另外还有一些名词,其复数形式有时可表示特别意思,如:goods货物,waters水域,fishes(各种)鱼
复合名词的复数形式:
名词作定语名词作定语一般用单数,但也有以下例外。
1)用复数作定语。
如:sports meeting 运动会
students reading-room 学生阅览室
talks table 谈判桌
the foreign languages department 外语系
2)man, woman, gentleman等作定语时,其单复数以所修饰的名词的单复数而定。
如:men workers
women teachers
gentlemen officials
3)有些原有s结尾的名词,作定语时,s保留。
如:goods train (货车)
arms produce 武器生产
customs papers 海关文件
clothes brush衣刷
4)数词+名词作定语时,这个名词一般保留单数形式。
如:two-dozen eggs 两打/(二十四个鸡蛋)
a ten-mile walk 十里路
two-hundred trees 两百棵树
a five-year plan 一个五年计划
可数名词单复数知识体系:

不同国籍人的单复数:
国籍
总称(谓语用复数)
单数
复数
中国人
the Chinese
a Chinese
two Chinese
瑞士人
the Swiss
a Swiss
two Swiss
澳大利亚人
the Australians
an Australian
two Australians
俄国人
the Russians
a Russian
two Russians
意大利人
the Italians
an Italian
two Italians
希腊人
the Greek
a Greek
two Greeks
法国人
the French
a Frenchman
two Frenchmen
日本人
the Japanese
a Japanese
two Japanese
美国人
the Americans
an American
two Americans
印度人
the Indians
an Indian
two Indians
加拿大人
the Canadians
a Canadian
two Canadians
德国人
the Germans
a German
two Germans
英国人
the English
an Englishman
two Englishmen
瑞典人
the Swedish
a Swede
two Swedes
零冠词的概念:
名词前没有定冠词、不定冠词、或任何限定词的现象。
零冠词的用法:
零冠词是指名词前面没有不定冠词、定冠词,也没有其他限定词的现象,零冠词的用法如下:
1、表示抽象概括意义时,不可数名词和复数名词使用零冠词:
例:Books are my best friends. 书是我的好朋友。
Water boils at 100℃. 水在摄氏100度沸腾。
比较:The water in this river is undrinkable. 这条河的水不可饮用。
2、专有名词通常使用零冠词:
例:Lu Xun is a great Chinese writer. 鲁迅是一位伟大的中国作家。
London is the capital of England. 伦敦是英国的首都。
China is a developing socialist country. 中国是一个发展中的社会主义国家。
3、按照习惯下列各类名词使用零冠词:
1)季节、月份、星期以及节假日等名词:
例:Summer begins in June in this part of the country. 这个地区夏天从六月份开始。
We have no classes on Sunday. 星期日我们不上课。
There are a lot of people shopping at Christmas. 在圣诞节有很多人购买东西。
2)三餐饭菜的名词:
例:have supper 吃晚饭
come to dinner 去吃饭
3)语言、运动、游戏等名词:
例:She speaks Chinese. 她说汉语。
He plays football. 他踢足球。
Let's have a game of chess. 咱俩下盘棋吧。
4)在某些意义有改变的名词前要使用零冠词:
例:He has gone to school. (tolearn) 他去上学了。
They are in church just now. (to worship) 现在他们在做礼拜。
同样,in hospital是“住院(治疗)”,in prison是“服刑”,等等。
注意:如果在这类名词前加冠词,则表示去那里干与之无关的事:
例:go to the school 可理解为去学校看望人,而不是“学习”。
4、在表示职位、头衔、身份等名词前:
例:Professor Wang 王教授
Doctor Tompson 汤普生医生
President Lincoln 林肯总统
Dean of the English Department 英语系主任
零冠词的特殊用法:
1、用于物质名词前。物质名词表示泛指或一般概念时,通常用零冠词:
如:Water boils at 100℃. 水在摄氏100度沸腾。
Blood is thicker than water. 水浓于水(即亲人总比外人亲)。
表示泛指或一般概念的物质名词前,即使有一描绘性修饰语,仍用零冠词:
如:Don't eat rotten food. 不要吃腐烂的食物。
注:(1)若特指,物质名词前可用定冠词:
如:Is the water in the well fit to drink? 这井里的水能喝吗?
(2)表示一种、一杯、一场、一阵、一份等这样的概念时,可用不定冠词:
如:This is a very good wine. 这是一种很好的酒。
A coffee, please. 请给我来杯咖啡。
It was very cold and a heavy snow was falling. 当时天气很冷,正在下大雪。
2、用于抽象名词前。抽象名词表示泛指或一般概念时,通常用零冠词:
如:Do you like music? 你喜欢音乐吗?
Failure is the mother of success. 失败是成功之母。
表示泛指或一般概念的抽象名词前,即使有一描绘性修饰语,仍用零冠词:
如:I like light music very much. 我非常喜欢轻音乐。
注:(1)若特指,抽象名词前可用定冠词:
如:I like the music of Mozart. 我喜欢莫扎特的曲子。
(2)若表示一种、一类、一方面、那种、这种等这之类的概念时,可用不定冠词:
如:He lives a happy life. 他过着幸福的生活。
Physics is a science. 物理是一门科学。
(3)表示动作的一次、一例、一番等时,可用不定冠词:
如:Let me have a look. 让我看一看。
(4)表示与抽象名词意义相关的具体的人或事,可用不定冠词:
如:The book is a delight to read. 这书读来很有趣。
3、用于专有名词前。在通常情况下,专有名词前用零冠词:
如:Smith lives in London. 史密斯住在伦敦。
注:若特指,专有名词前有时也可用定冠词:
如:The Smith you're looking for no longer lives here. 你找的那个史密斯不住这儿了。
4、用于复数名词前。复数名词表示类别时,通常用零冠词:
如:Teachers should be respected. 教师应该受到尊重。
泛指不定量的人或物,也用零冠词:
如:We are students of ClassFive. 我们是五班的学生。
注:若特指,复数名词前应用定冠词:
如:The teachers should attend the meeting 教师应参加会议。
5、用于单数可数名词前。单数可数名词前用零冠词,主要有以下情况:
(1)用于表示家庭成员或nurse, cook, teacher等名词前:
如:Mother is not at home.妈妈不在家。
Ask nurse to put the child to bed 叫保姆孩子抱到床上去睡觉。
Teacher was satisfied with our work. 老师对我们的工作很满意。
(2)用于动词turn(变成),go(变成)后作表语的名词通常用零冠词:
如:He was a teacher before he turned writer. 他在成为作家之前是教师。
He has gone socialist. 他成了社会主义者。
(3)在让步状语从句的倒装句式中,单数可数名词通常用零冠词:
如:Child as he is, he knows a lot. 他虽然是个孩子,但已经很懂事了。
Teacher though he is, he can't knowe verything. 他虽然是老师,但也不可能什么都懂。
(4)单数可数名词用作呼语,通常用零冠词:
如:How is she, doctor? 医生,她怎么样?
Can you drive me to the station, driver? 司机,请送我去车站,好吗?
(5)在某些独立结构中通常用零冠词:
如:The teacher came in, book in hand. 老师走进教室,手里拿着书。
He was sitting in the chair, pipe in mouth. 他坐在椅子里,嘴里叼着烟斗。
(6)在“kind[sort]of+名词”这一结构中,名词通常用零冠词:
如:This kind of book is very interesting. 这种书很有趣。
He is the sort of person I really dislike. 他这种人我真不喜欢。
注:注意以下两句在含义上的差别:
Whatkindofcarisit?这是什么牌子的车?
Whatkindofacarisit?这种车质量如何?
(7)当单数可数名词含义抽象化具有形容词意味时,通常用零冠词:
如:The man was more animal than man. 那个人与其说是人,不如说是畜生。
I was fool enough to accep this offer. 我接受他的提议真是太傻了。
Are you man enough for this dangerous job? 你有勇气敢做这项危险的工作吗?
零冠词用法口诀:
下列情况应免冠,代词限定名词前;
专有名词不可数,学科球类三餐饭;
复数名词表泛指,两节星期月份前;
颜色语种和国名,称呼习语及头衔。
以上口诀主要概括了一般应“免冠”的几种情况,即:
①名词前已有作定语用的this、that、some、any、my等限定词。
②专有名词和不可数名词前。
③表示学科的(如:maths、Chinese、physics)名词前。
④球类活动的名词前及三餐总称前。
⑤复数名词表示泛指(一类人或事)时。
⑥节日、季节、星期、月份前。
⑦表示颜色(如:It's red/yellow.)、语种(如:speak English/Japanese)和国家的非全称名词(如:We live in China. They come from America.)。
⑧在称呼或表示头衔的名词前。
⑨某些习惯短语中(如:inbed、go to school 等)。
零冠词知识体系:
| 零 冠词 |
名词前面没有定冠词、不定冠词、和其他限定词的现象。 | 1、在某些专有或者抽象物质表示类别前 |
| 2、在表示类别复数名词前 | ||
| 3、在季节、月份、星期、三餐前 | ||
| 4、称呼语或表示头衔,职务的词前 | ||
| 5、学科和球类运动的名称前 | ||
| 6、名词前有代词或所有格 | ||
| 7、在某些固定词组中: at night by bus |
零冠词用法拓展:
(1)节假日、星期、月份、季节等通常用零冠词:
如:We had a good time on Christmas Day. 我们在圣诞节过得很愉快。
Monday comes before Tuesday. 星期二在星期一之后。
He was born in September, 1988. 他出生在1988年9月。
注:①我国用Festival构成的传统节日通常用定冠词:
如:the Spring Festival春节
the Mid-autumn Festival [theMoonFestival]中秋节
②若表示特指或心目中的专指,星期、月份、季节等名词前可用定冠词:
如:He went abroad in the September of 1988. 他于1988年9月出国。
He came on the Sunday and went away on the Monday. 他星期日来,星期一就走了。
③表示“某一个”或受描绘性定语修饰表示“某种”这样的意义时,节日、星期、月份、季节等名词也可用不定冠词:
如:My birthday happened to be on a Saturday. 我的生日碰巧是星期六。
She came round to see me on a sunny Sunday. 她在一晴朗的星期日来看了我。
We had a nice Christmas. 我们过了一个愉快的圣诞节。
④当季节名词不强调时间而强调季节的内涵时,通常用 the:
如:Winter is coming. 冬天要来了。(单纯指冬天的时间)
The winter is coming. 冬天要来了。(暗示寒冷)
(2)某些表示自然界时间变化现象的名词,与某些介词(如at, after, before, till, until, towards, from等) 构成短语时,通常用零冠词:
如:at day-break 在天亮时
before dawn 在天亮前
at dusk 在黄昏时
after sunset 在日落后
after sunrise 在日出前
until sundown 直到日落
towards dark 天快黑时
at midnight 在半夜
from dawn till dusk 从早到晚
当day, night, evening, morning, afternoon 等表示抽象的时间概念时,通常用零冠词:
如:Night fell. 天黑了。
Evening came on. 夜幕来临。
It was late afternoon before he reached home. 傍晚时候他才到家。
(3)球类、三餐、茶点等名词前,通常用零冠词:
如:We play basketball in the afternoon. 我们下午打篮球。
What do you have for breakfast? 你早餐吃什么?
They were at tea when I called. 我来访时他们正在喝茶(吃茶点)。
注:①球类名词若不是作为一项体育活动看待,而是作为一个实实在在的东西来看待,则可以用冠词:
如:The basketball is mine. 这个篮球是我的。
He bought a basketball. 他买了一个蓝球。
②三餐饭被特指可用定冠词,若受形容词修饰且非特指,可用不定冠词:
如:The supper she cooked was delicious. 她做的晚餐很可口。
We had a good lunch at Uncle's. 我们在叔叔家吃了顿丰盛的午餐。
(4)当名词后接有数词表示顺序时,名词前通常用零冠词:
如:Lesson10 is more interesting than Lesson11. 第10课比第11课更有趣。
There's a picture of a ship on page15. 在第15页有张一艘船的照片。
(5)公园、广场、学校、语言等名词前通常用零冠词:
如:Hyde Park 海德公园
Central Park(纽约) 中内公园
Zhong shan Park中山公园
Tian AnMen Square天安门广场
speak English 说英语
Beijing University 北京大学
注:当语言名词表特指意义或指某一语言中的对应词时,通常用定冠词:
如:the English spoken in America and Canada 在美国和加拿大讲的英语
What's the English for this? 这个东西用英语怎么说?
另外,在语言名词后加上language一词时,也要用冠词:the English language。
(6)表示学习、生活、娱乐等的单数名词,若表示相关的活动时,通常用零冠词:
如:go to school (bed, church, town, class, college, etc)去上学 (睡觉,做礼拜,进城,上课,上大学,等)
in bed (school, class, college, church, prison, hospital,etc) 在睡觉 (上学,上课,上大学,做礼拜,坐牢,住院,等)
be sent to hospital (prison) 被送往医院住院或治疗(关进监狱)
School is over at twelve. 12点放学。
注:①若不是指活动,而是指具体的实物,则要用冠词。比较:
如:go to the bed到床边去 (侧重指“床”这个实体)
go to bed 上床睡觉(侧重指与“床”有关的活动,即睡觉)
be in the school 在这所学校里 (侧重指“学校”这个地点)
be in school 在上学(侧重指与“学校”有关的活动,即读书)
②但是cinema, theatre是例外,它们表示相关活动时,其前要用定冠词:
如:He often goes to the cinema (theatre). 他经常去看电影(看戏)。
I prefer the cinema to the theatre. 我喜欢看电影,不喜欢看戏。
③有时定冠词和零冠词的选择与英美英语的不同习惯有关:
如:in hosptital (英) 住院
in the hospital (美) 住院
go to university (英)上大学
go to the university (美)上大学
at table (英)在吃饭
at the table(美)在吃饭
(7)某些用介词by构成的方式的短语通常用零冠词:
①表示乘坐交通工具:
如:by bus 乘公共汽车
by bike(bicycle) 骑自行车
by plane/byair乘飞机
by ship(boat) 坐船
by land 走陆路
by sea 从海路
②表示用通讯或通信等方式:
如:by phone 用电话
by telegram 用电报
by letter 用信件
by post 用邮寄
by radio 用无线电
by hand 用手工
(8)表示正式的或独一无二的头衔或职位等,在用作宾语、表语、补语或同位语时,通常用零冠词:
如:John is captain of the team. 约翰是足球队的队长。
He is head of the foreign languages department. 他是外语系主任。
注:尽管有时也有用定冠词的现象,但以零冠词为普通。
(9)单数可数名词紧密联系的平行结构,通常用零冠词:
如:They are brother and sister. 他们是兄妹。
Please pass me pencil and paper. 请把纸笔递给我。
Boy and girl came up to me together. 一个男孩和女孩一起向我走来。
(10)有些短语用零冠词和定冠词均可,只是含义不同:
如:out of question 毫无疑问
out of the question 不可能,不值得考虑的
keep house 料理家务
keep the house 呆在家里不外出
in charge of 负责,管理,主管
in the charge of 在…的管理(负责)之下
(11)许多习语用零冠词:
如:catch fire 着火
give way 让路
lose heart 灰心
move hosue 搬家
send word 捎信
take place 发生
by chance 偶然
catch sight of 看见
make use of 利用
连接代词的概念:
连接代词常用来引导一个主语从句、宾语从句和表语从句,在句中可用作主语、宾语、表语、定语等,连接代词主要包括who, whom, what, which, whose, whoever, whatever, whichever, whosever等。
whatever, whoever, whichever 用法说明:
主要用于引导主语从句和宾语从句。
如:He does whatever she asks him to do. 她要他做什么,他就做什么。
Whoever breaks the rules will be punished.谁违反这些规则都将受到处罚。
I'll give the ticket to whoever want sit. 请想要这票,我就把它给谁。
Whichever team gains the most points wins. 哪个队得分最多,哪个队就赢。
注:其中的ever主要用于加强语气,含有“一切”、“任何”、“无论”之义。使用这类词时,注意不要按汉语习惯用错句子结构:
如:任何人(谁)先来都可以得到一张票。
误:Anyone comes first can get a ticket./ Who comes first can get a ticket.
正:Anyone who comes first can get a ticket./ Whoever comes first can get a ticket.
连接代词的用法:
1、连接代词主要包括who, whom, what, which, whose, whoever, whatever, whichever, whosever等,它们在句中可用作主语、宾语、表语、定语等,可以引导主语从句、宾语从句和表语从句:
如:I don't know who he is. 我不知道他是谁。
What he says sounds reasonable. 他说的话听起来很有道理。
The question is who(m) we should trust. 问题是我们该信任谁。
I'll take whoever wants to go. 谁想去我就带谁去。
Take whichever seat you like? 你喜欢坐哪个座位就坐哪个?
I will just say whatever comes into my mind. 我想到什么就说什么。
注:who, whom, whoever等不用于名词前作定语。
2、what的两种用法。请看以下两个句子:
(1)I didn't know what he wanted. 我不知道他想要什么。
(2)I gave her what she wanted. 我给了她想要的一切。
上面第一句中的what表示“什么”,带有疑问的意味;第二句中的what表示“所…的一切事或东西”,其意义上大致相当于that(those) which, the thing(things) that, anything that, all that, as much as等,又如:
What[=That which] you say is quite true. 你说的完全是事实。
He saves what[=all that] he earns. 他赚多少,积蓄多少。
Call it what[=anything that] you please. 你喜欢叫它什么就叫它什么。
这样用的what有时还可后接一个名词:
如:He gave me what money[=all the money that] he had about him. 他把身边带有的钱全给了我。
What friends[=All the friends that] he has are out of the country. 他所有的朋友都在国外。
连接代词知识体系:

whatever, whoever, whichever 用法说明:
主要用于引导主语从句和宾语从句。
如:He does whatever she asks him to do. 她要他做什么,他就做什么。
Whoever breaks the rules will be punished.谁违反这些规则都将受到处罚。
I'll give the ticket to whoever want sit. 请想要这票,我就把它给谁。
Whichever team gains the most points wins. 哪个队得分最多,哪个队就赢。
注:其中的ever主要用于加强语气,含有“一切”、“任何”、“无论”之义。使用这类词时,注意不要按汉语习惯用错句子结构:
如:任何人(谁)先来都可以得到一张票。
误:Anyone comes first can get a ticket./ Who comes first can get a ticket.
正:Anyone who comes first can get a ticket./ Whoever comes first can get a ticket.
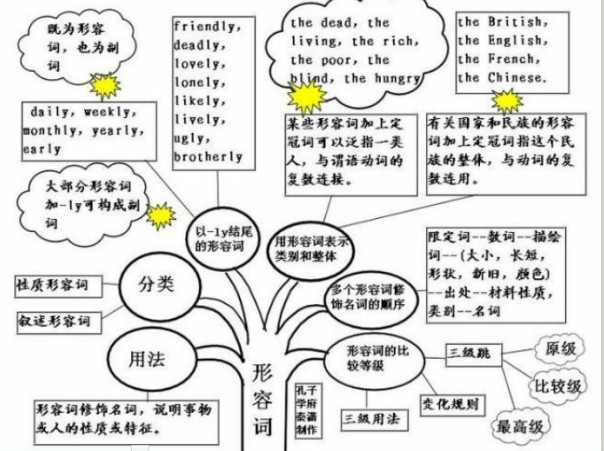
形容词的概念:
形容词(adjective),简称adj.或a,形容词用来修饰名词或代词,表示人或事物的性质、状态,和特征的程度好坏与否,形容词在句中作定语、表语、宾语补足语。通常,可将形容词分成性质形容词和叙述形容词两类,其位置不一定都放在名词前面。
形容词的作用与位置:
形容词是用来修饰名词的,常被放在名词前作定语,或放在系动词后面作表语。以下属几种特殊情况,须牢记;
(1)形容词短语作定语,定语后置。
如:a language difficult to master,
a leaning tower about 180 feet high
(2)表语形容词(afraid、alike、alone、asleep、awake、alive等)作定语,定语后置。如a man alive。有些表身体健康状况的形容词如well、faint、ill只作表语。sick既可作表语又可作定语,ill如作定语意为“bad”。
(3)用作定语,修饰由不定代词one、no、any、some和every构成的复合词如anything、something等时,通常后置。
如:I have something important to tell you.
(4)else常用作疑问代词和不定代词的后置定语。
(5)enough、nearby修饰名词前置或后置,程度副词一般位于形容词、副词前面,enough修饰形容词、副词时,必须后置。
(6)几个并列的形容词作定语,其语序通常为:限定语(The、A)+描绘性形容词+size(大小)+shape(形状)+age(年龄、时间)+color(颜色)+origin(国籍、来源)+material(材料)+purpose(目的)+名词。
口诀:
限定描绘大长高,形状年龄和新老;颜色国籍跟材料,作用类别往后靠。
如:a heavy black Chinese steel umbrella,
the man's first tow interesting little red French oil paintings
形容词的用法:
1、形容词修饰名词,说明事物或人的性质或特征。通常,可将形容词分成性质形容词和叙述形容词两类,其位置不一定都放在名词前面:
1)直接说明事物的性质或特征的形容词是性质形容词,它有级的变化,可以用程度副词修饰,在句中可作定语、表语和补语。例如:hot热的。
2)叙述形容词只能作表语,所以又称为表语形容词。这类形容词没有级的变化,也不可用程度副词修饰。
大多数以a开头的形容词都属于这一类。例如:
afraid害怕的。(错)Heisanillman. (对)Themanisill. (错)Sheisanafraidgirl. (对)Thegirlisafraid.
这类词还有:well,unwell,ill,faint,afraid,alike,alive,alone,asleep,awake等。
3)形容词作定语修饰名词时,要放在名词的前边。但是如果形容词修饰以-thing为字尾的词语时,要放在这些词之后。例如:somethingnice
2、用形容词表示类别和整体:
1)某些形容词加上定冠词可以泛指一类人,与谓语动词的复数连接。如:the dead,the living,the rich,the poor,the blind,the hungry The poorarelosinghope.穷人失去了希望。
2)有关国家和民族的形容词加上定冠词指这个民族的整体,与动词的复数连用。如:the British,the English,the French,the Chinese. The English have wonderful senseofhumor.
以-ly结尾的形容词:
1)大部分形容词加-ly可构成副词。但friendly,deadly,lovely,lonely,likely,lively,ugly,brotherly,仍为形容词。改错:
如:(错)She sang lovely.
(错)He spoke to me very friendly.
(对)Her singing was lovely.
(对)He spoke to me in a very friendly way.
2)有些以-ly结尾既为形容词,也为副词。 daily,weekly,monthly,yearly,early .
如:The Times is a daily paper.
The Times is published daily.
形容词知识体系:
复合形容词的构成:
(1)形容词+名词+ed:
如:kind-hearted 好心的,white-haired 白发的
(2)形容词+形容词:
如:red-hot 炽热的,dark-blue 深蓝的
(3)形容词+现在分词:
如:good-looking 好看的,easy-going 随和的
(4)副词+现在分词:
如:hard-working 勤劳的,fast-moving 快速转动的
(5)副词+过去分词:
如:hard-won 得来不易的,newly-made 新建的
(6)名词+形容词:
如:life-long 终生的,world-famous 世界闻名的
(7)名词+现在分词:
如:peace-loving 爱好和平的,fun-loving 爱开玩笑的
(8)名词+过去分词:
如:snow-covered 白雪覆盖的,hand-made 手工的
(9)数词+名词+ed:
如:four-storeyed 4层楼的,three-legged 3条腿的
(10)数词+名词(名词用单数):
如:ten-year 10年的, two-man 两人的
介词和介词短语的概念:
介词是一种用来表示词与词、词与句之间的关系的虚词,在句中不能单独作句子成分。介词后面一般有名词、代词或相当于名词的其他词类,短语或从句作它的宾语。介词和它的宾语构成介词词组,在句中作状语,表语,补语或介词宾语。介词可以分为时间介词、地点介词、方式介词和其他介词。
误用介词的三种情况:
1、多用介词:
多用介词可能是受汉语意思的影响将及物动词误用作不及物动词,也可能是受相关结构的影响而用错:
误:We discussed about the plan.
正:We discussed the plan. 我们讨论了计划。
误:Did he mention about the accident?
正:Did he mention the accident? 他提到那次事故了吗?
误:I saw her enter into the bank.
正:I saw her enter the bank. 我看见她进了银行。
误:He married with[to] a nurse.
正:He married a nurse. 他同一位护士结了婚。
误:How can contact with you?
正:How can contact you? 我怎么与你联系?
误:We should serve for the people heart and soul.
正:We should serve the people heart and soul. 我们应该全心全意地为人民服务。
误:Who controls over the factory? (但名词control可接over)
正:Who controls the factory? 谁管理这个工厂?
误:He has a great many of friends here. (比较a great number of)
正:He has a great many friends here. 他在这儿有很多朋友。
2、漏用介词:
漏用介词可能是受汉语意思的影响将不及物动词误用作及物动词,或是受相关结构的影响的影响而用错等:
误:This matter is difficult to deal. (deal with=处理)
正:This matter is difficult to deal with. 这事很难处理。
误:He is not a man to be depended.
正:He is not a man to be depended on. 他不是个可靠的人。
误:He took a cup of tea, and went on the story.
正:He took a cup of tea, and wentonwiththestory.他喝了一口茶,又接着讲故事。
误:My mother still regards me a child. (比较consider…as中的as可省略)
正:My mother still regards me as a child. 我母亲还把我当小孩看。
误:They insisted sending a car over to fetch us.
正:They insisted on sending a car over to fetch us.他们坚持要派车来接我们。
误:What he says is worth listening.
正:What he said is worth listening to.他的话值得一听。
3、错用介词:
错用介词的情况比较复杂,可能是因受汉语意思的而错,也可能是因弄不清搭配关系而错,可能是混淆用法而错,也可能是受相关结构的影响而错,可能是忽略语境而错,也可能是想当然的用错:
误:She called on his office yesterday. (call on+人,call at+地点)
正:She called at his office yesterday. 她昨天去了他办公室拜访。
误:He is engaged with a nurse.
正:He is engaged to a nurse.他与一位护士订了婚。
误:The sun rises from the east.
正:The sun rises in the east.太阳从东方升起。
误:Under his help, I finished it in time.
正:With his help, I finished it in time. 在他的帮助下,我及时做完了。
误:During he was in Japan, he visited many places.
正:During his stay in Japan, he visited many places.他在日本期间,参观过许多地方。
误:We are familiar to his character.
正:We are familiar with his character.我们了解他的性格。
误:Help yourself with the fruit.
正:Help yourself to the fruit.吃点水果吧。
介词的宾语:
1、名词或代词作介词宾语:
如:Are you interested in history? 你对历史感兴趣吗?
Don't worry about it. 别为它担心。
注:若是人称代词用作介词宾语,要注意用宾格。
如:No one can sing like her. 没有人能像她那样唱歌。(不能用like she)
2、动名词作介词宾语:
如:He is good at telling stories. 他善于讲故事。
In crossing the street he was run over. 他在穿过马路时被汽车撞倒。
3、过去分词作介词宾语:
如:We can't regard the matter as settled. 我们不能认为这事已经解决。
I take it for granted you have read the book. 我以为你读过这本书。
注:过去分词用作介词宾语通常只见于某些固定结构中,如上面第1句涉及regard…as(认为…是)结构,第2句涉及take sth for granted(认为某事属实)。在其他情况下,介词后通常不直接跟过去分词作宾语,若语义上需要接过去分词(表被动),可换用“being+过去分词”:
如:He went out without being seen by the others.他出去了,没有被其他人看见。
4、从句作介词宾语:
如:He was not satisfied with what she said. 他对她说的不满意。
I'm worried about where he is. 我担心他上哪儿去了。
注:介词后通常不接that从句,遇此情况需考虑用其他结构:
误:He paid no attention to that she was poor.
正:He paid no attention to the fact that she was poor. 他根本不注意她很穷这一事实。
但有个别介词(如except)可接that从句。
比较:I know nothing about him except that he lives next door./I know nothing about him except for the fact that he lives next door. 我只知道他住在隔壁,其它的就不知道了。
5、不定式作介词宾语:
如:I had no choice but to wait. 除了等,我没有别的选择。
He wanted nothing but to stay there. 他只想留在那儿。
They did nothing but complain. 他们老是一个劲地抱怨。
He never did anything but watch TV. 除了看电视,他从不干任何事。
注:(1)介词后接不定式的情形通常只见于but, except等极个别个词。该不定式有时带to,有时不带to,其区别是:若其前出现了动词do,其后的不定式通常不带to;
若其前没有出现动词do,则其后的不定式通常带to。
(2)介词后虽然通常不直接跟不定式作宾语,但却可接“连接代词(副词)+不定式”结构:
如:He gave me some advice on how to do it. 对于如何做这事他给我提了些建议。
6、形容词作介词宾语:
如:Her pronunciation is far from perfect. 她的语音远不是完美的。
In short, we must be prepared. 总而言之,我们要有准备。
Things have gone from bad to worse. 事情越来越糟。
注:(1)有些形容词用作介词宾语可视为其前省略了动名词being:
如:He regarded the situationas(being) serious. 他认为形势严重。
His work is far from(being) satisfactory. 他的工作丝毫不令人满意。
(2)有些“介词+形容词”的结构已构成固定搭配:in full全部地,全面地,无省略地; in private私下地,秘密地; in particular特别地;in general一般地,通常地,概括地; in brief 简言之;in short总之,简言之; in vain徒然地,徒劳无益地;for fee免费地,无偿地; for certain肯定地,确切地;for sure肯定地,确切地; for short为了简短,简称;atl arge自由自在地,逍遥法外; by far…得多
7、副词作介词宾语:
如:I can't stay for long. 我不能久呆。
It's too hot in here. 这里面太热了。
I looked every where except there. 除了那儿,我到处都看过了。
8、数词作介词宾语:
如:The city has a population of four million. 这座城市有四百万人口。
He was among the first to arrive. 他是第一批到的。
9、介词短语作介词宾语:
如:Choose a book from among these. 从这些书中选一本吧。
I saw her from across the street. 我从街的对面望见了她。
注:通常可后接介词短语作宾语的介词是from, till, until, since, except, instead of等。
比较:I took it from the bed. 我从床那儿(或床上)拿的。
I took it from under the bed. 我从床下拿的。
10、复合结构用作介词宾语:
如:She had no objection to Mary marrying him. 她不反对玛丽与他结婚。
She came in with a book in her hand. 她手里拿着一本书走了进来。
All the afternoon he worked with the door locked. 整个下午他都锁着门在房里工作。
介词短语的句法功能:
1、表语:
如:He was with a friend. 他和一个朋友在一起。
Health is above wealth. 健康胜过财富。
This knife is for cutting bread. 这把小刀是用于切面包的。
注:有些介词(如because of)引出的短语通常只用作状语,不用作表语:
误:His absence is because of the rain.
正:His absence is due to the rain. 他因雨未来。
但是,若主语是代词(不是名词),becauseof引出的短语可用作表语:
如:It is because of hard work. 那是因为辛苦工作的原因。
2、状语:
如:Don't touch it with your hands. 别用手去摸它。
Did you do this by design or by accident? 你这样做是有意的还是无意的?
3、定语:
如:This is his reply to your letter. 这是他给你的回信。
This is the best way of doing it. 这是做此事最好的方法。
My love for you is deeper than the sea. 我对你的爱比海深。
4、宾语补足语:
如:I found everythingin good condition. 我发现一切正常。
Her illness kept her in bed for a week. 她因生病在床上躺了一星期。
注:用作宾语补足语的介词短语在相应的被动语态中则为主语补足语:
如:He was regarded as a hero. 他被看成是英雄。
5、宾语:
如:A man stepped out from behind the wall. 一个人从墙后走出来。
He cannot spare anytime except on Sunday. 除星期日外,他抽不出时间。
6、主语:
如:Between6 and 7 suits me. 六点到七点对我比较适合。
After the exams is the time to relax. 考试后是轻松一下的时间。
注:介词短语通常不用作主语,尽管有时也像上面这样用作主语,但通常可视为是在一定的上下文中有所省略:
如:—When are we going to have the next meeting? 我们下次什么时候见面?
—On Tuesday may be convenient. 星期二可能比较方便。
此句中onTuesday虽用作主语,但可视为是其前省略了meeting一词:
即:Meeting during the vacation may be convenient.
过去分词的概念:
过去分词一般表示完成和被动的动作,只有一种形式。即:动词原形加-ed构成。
如:fallen leaves 落叶
boiled water 开水
I heard the door closed. 我听见门被关上了。
过去分词与现在分词被动式的区别:
两者均可表示被动,其区别主要在于它们所表示的时间概念不同,但有时它们也可表示相同的意思。
如:Written in haste, the book has many mistakes. 这书因写得仓促,所以错误不少。
Being written in haste, the book has many mistakes. 这书因写得仓促,所以错误不少。
Having been written in haste, the book has many mistakes. 这书因写得仓促,所以错误不少。
有时虽然所表示的时间概念相同,但有细微区别:
如:Having been show the lab, we left. 被领着看了实验室后,我们就离开了。
过去分词的句法功能:
1、作定语:
如:I don't like the book written by Martin.
Our class went on an organized trip last Monday. 上周一我们班开展了一次有组织的旅行。
注意:当过去分词是单词时,一般用于名词前,如果是过去分词短语,就放在名词的后面。过去分词做定语相当于一个被动语态的定语从句。
2、过去分词作表语:
如:They were very excited at the news. 听到这个消息,他们非常激动。
The window is broken. 窗户破了。
They were frightened at the sad sight. 他们对眼前悲惨的景象感到很害怕。
注意:be+过去分词,如果表示状态是系表结构,如果表示被动的动作是被动语态。
区别:The window is broken.(系表)
The window was broken by the boy.(被动)
有些过去分词是不及物动词构成的,不表示被动,只表示完成。
如:boiled water(开水) fallen leaves(落叶) newly arrived goods(新到的货) the risen sun(升起的太阳) the changed world(变了的世界)
这类过去分词有:gone, come, fallen, risen, changed, arrived, returned, passed等。
3、过去分词作宾语补足语:
如:I heard the song sung several times last week. 上周我听见这首歌被唱了好几次。
有时过去分词做with短语中的宾语补足语:
如:With the work done, they went out to play. 工作做完了,他们出去玩去了。
4、过去分词作状语:
如:Praised by the neighbours, he became the pride of his parents. 受到邻居们的表扬,他成为父母的骄傲。(表示原因)
Onceseen, it can never be forgotten. 一旦它被看见,人们就忘不了。(表示时间)
Given more time, I'll be able to do it better. 如果给予更多的时间,我能做得更好。(表示条件)
Though told of the danger, he still risked his life to save the boy. 虽然被告之危险,他仍然冒生命危险去救那个孩子。(表示让步)
Filled with hopes and fears, he entered the cave. 心中充满了希望与恐惧,他走进山洞。
5、过去分词与逻辑主语构成独立主格:
如:All books returned at the end of the term, the library assistant was satisfied. 所有的书期末时都还了,图书管理员很高兴。
The field ploughed, he began to spread seed. 地耕好了,他开始撒种子。
现在分词与过去分词的区别:
1、分词作表语:
分词做表语有两种情况,一种是现在分词做表语,一种是过去分词做表语,这两者区别是考试中经常考到的地方。一般来说,表示心理状态的动词如excite,interest等都是及物动词,汉语意思不是“激动”,“高兴”,而是“使激动”、“使高兴”,因而现在分词应该是“令人激动的”、“令人高兴的”,过去分词则是“感到激动的”和“感到高兴的”。所以,凡表示“令人……的”都是-ing形式,凡是表示“感到……”都用-ed形式。换句话说,若人对……感兴趣,就是somebody is in terestedi n...,若人/物本身有兴趣时,就是说sb./sth. is interesting。这类词常见的有:
interesting 使人感到高兴—interested感到高兴的
exciting令人激动的—excited感到激动的
delighting令人高兴的—delighted感到高兴的
disappointing令人失望的—disappointed感到失望的
encouraging令人鼓舞的—encouraged感到鼓舞的
pleasing令人愉快的—pleased感到愉快的
puzzling令人费解的—puzzled感到费解的
satisfying令人满意的—satisfied感到满意的
surprising令人惊异的—surprised感到惊异的
worrying令人担心的—worried感到担心的
如:Travelling is interesting but tiring. 旅行是有趣的,但是使人疲劳。
The pupils will get confused if they are made to learn too much. 如果要学生学得太多,他们会感到糊涂的。
The game is exciting. (现在分词作表语)
We were excited at the news. (过去分词作表语)
2、分词作定语:
分词作定语时有下面几个特点:
1)现在分词表示主动意义,过去分词一般表示被动含意。
2)现在分词表示正在进行,过去分词表示状态或做完(完成)的事。
如:He rushed into the burning house. 他冲进了正在燃烧着的房子。
The child standing over there is my brother. 站在那儿的男孩子是我弟弟。
The room facing south is our classroom. 朝南的房间是我们的教室。
He is an advanced teacher. 他是个先进教师。
3)下列不及物动词也以过去分词形式做定语或表语,但不具有被动意义,这点要注意:
departed, elapsed, faded, fallen, gone, frown-up, retired, returned, risen, set, vanished, much-traveled, newly-arrived, recently-come
3、分词作状语:
现在分词做状语与过去分词做状语的最主要区别在于两者与所修饰的主语的主动与被动关系的区别。
1)现在分词作状语时,现在分词的动作就是句子主语的动作,它们之间的关系是主动关系。
如:He went out shutting the door behind him. 他出去后将门随手关上。
Not knowing what to do, he went to his parents for help. 由于不知如何办是好,他去找父母帮忙。
Smiling, they came in.
2)过去分词作状语时,过去分词表示的动作是句子主语承受的动作,它们之间的关系是被动关系。
如:Cleaned, the room looks nice.
Given more attention, the trees could have grown better. 如果对这些树多关心一些,它们本来会长得更好。
Faced with difficulties, we must try to overcome them. 在遇到困难的时候,我们必须设法克服。
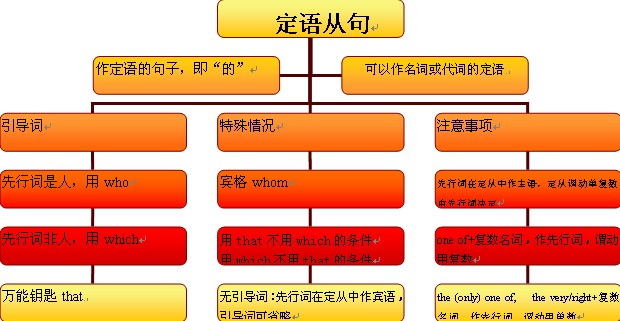
限制性定语从句的概念:
限制性定语是指对被修饰名词或代词的必需修饰,是被修饰名词或代词不可缺少的修饰语,如果去掉它句子意思往往会不明确或会发生变化。
如:The travellers knowing about the floods took another road. 知道发大水的那些游客改道走了。
The boys wanting to play football were disappointed when it rained. 想踢足球的那些男孩子因为下雨而感到失望。
关系代词引导的定语从句:
关系代词所代替的先行词是人或物的名词或代词,并在句中充当主语、宾语、定语等成分。关系代词在定语从句中作主语时,从句谓语动词的人称和数要和先行词保持一致。
1)who, whom, that 这些词代替的先行词是人的名词或代词,在从句中所起作用如下:
例:Is he the man who/that wants to see you? 他就是你想见的人吗?(who/that在从句中作主语)
He is the man whom/that I saw yesterday. 他就是我昨天见的那个人。(whom/that在从句中作宾语)
2)Whose用来指人或物,(只用作定语,若指物,它还可以同ofwhich互换)
例:They rushed over to help the man whose car had broken down. 那人车坏了,大家都跑过去帮忙。
Please pass me the book whose(of which) coverisgreen. 请递给我那本绿皮的书。
3)which, that 它们所代替的先行词是事物的名词或代词,在从句中可作主语、宾语等。
例如:A prosperity which/that had never been seen before appears in the countryside. 农村出现了前所未有的繁荣。(which/that在句中作宾语)
The package(which/that) you are carrying is about to come unwrapped.你拿的包快散了。(which/that在句中作宾语)
关系副词引导的定语从句:
关系副词可代替的先行词是时间、地点或理由的名词,在从句中作状语。
1)when, where, why 关系副词when, where, why的含义相当于“介词+which”结构,因此常常和“介词+which”结构交替使用。
例如:There are occasions when(on which) one must yield.任何人都有不得不屈服的时候。
Beijing is the place where(inwhich) I was born. 北京是我的出生地。
Is this the reason why(for which) he refused our offer? 这就是他拒绝我们帮助他的理由吗?
2)that代替关系副词 that可以用于表示时间、地点、方式、理由的名词后取代when, where, why和“介词+which”引导的定语从句,在口语中that常被省略,
例如:His father died the year(that/when/in which) he was born. 他父亲在他出生那年逝世了。
He is unlikely to find the place(that/where/in which) he lived forty years ago. 他不大可能找到他四十年前居住过的地方。
限定性定语与非限定性定语的区别:
1、形式不同:
限定性定语从句主句和从句之间不用逗号隔开,口语中使用时也不停顿;而非限定性定语从句与主句之间通常有逗号隔开,口语中使用时有停顿。
2、功能不同:
限定性定语从句用于对先行词的意义进行修饰、限制和识别,如果去掉,就会造成句意不完整或概念不清;而非限定性定语从句用于对先行词起补充说明作用,如果省略,句意仍然清楚、完整:
如:People who take physical exercise live longer. 进行体育锻炼的人活得长些。(若把从句去掉句子就失去意义)
His daughter, who is in Boston now, is coming home next week. 他女儿现在在波士顿,下星期回来。(若把从句去句子意义仍然完整)
3、翻译不同:
在翻译定语从句时,一般把限定性定语从句翻译在它所修饰的先行词之前,而把非限定性定语从句与主句分开:
如:He is the man whose car was stolen. 他就是汽车被窃的那个人。
I've invited Jim, who lives in the next flat. 我邀请了吉姆,他就住在隔壁。
4、含义不同:
如:I have a sister who is a doctor. 我有一个医生的姐姐。(姐姐不止一个)
I have a sister, who is a doctor. 我有一个姐姐,她是当医生的。(只有一个姐姐)
5、先行词不同限定性定语从句的先行词只能是名词或代词,而非限定性定语从句的先行词则可以是名词或代词,也可以是短语或句子;
另外,当先行词为专有名词或其他具有独一无二性的普通名词时,通常要用非限制性定语从句,而不用限制性定语从句:
如:Peter drove too fast, which was dangerous. 彼得开车很快,这是很危险的。(which指drive too fast)
He changed his mind, which made me very angry. 他改变了主意,这使我很生气。(which指整个主句)
Mr.Smith, who is our boss, will leave for Japan next week. 我们的老板史密斯先生下周要去日本。(先行词为专有名词,要用非限制性定语从句修饰)
Her father, who has a lot of money, wishes her to study abroad. 她父亲很有钱,希望她出国学习。(先行词为表独一无二意义的普通名词,要用非限制性定语从句修饰)
6、关系词不同:
关系词that和why可用于限制性定语从句中,通常不用于非限制性定语从句;另外,在限制性定语从句中,关系词有时可以省略,而在非限制性定语从句中关系词一律不省略。
判断关系代词与关系副词方法:
一:用关系代词,还是关系副词完全取决于从句中的谓语动词。及物动词后面无宾语,就必须要求用关系代词;而不及物动词则要求用关系副词。
例如:This is the mountain village where I stayed last year.
I'll never forget the days when I worked together with you.
判断改错
(错)This is the mountain village where I visited last year.
(错)I will never forget the days when I spent in the countryside.
(对)This is the mountain village(which) I visited last year.
(对)I'll never forget the days(which) I spent in the countryside.
注:习惯上总把表地点或时间的名词与关系副词where, when联系在一起。此两题错在关系词的误用上。
二:准确判断先行词在定语从句中的成分(主、谓、宾、定、状),也能正确选择出关系代词/关系副词。
例1. Is this museum ___ you visited a few days age?
A. where
B. that
C. on which
D. the one
例2. Is this the museum ____ the exhibition was held.
A. where
B. that
C.on which
D. the one
答案:例1:D,例2:A
例1变为肯定句:This museum is___ you visited a few days ago.
例2变为肯定句:This is the museum ___ the exhibition was held.
注:在句1中,所缺部分为宾语,而where, that, on which都不能起到宾语的作用,只有the one既做了主句的表语,又可做从句的宾语,可以省略关系代词,所以应选D。
而句2中,主、谓、宾俱全,从句部分为句子的状语表地点,既可用副词where,又因in the museum词组,可用介词in+which引导地点状语。
而此题中,介词on用的不对,所以选A。关系词的选择依据在从句中所做的成分,先行词在从句中作主、定、宾语时,选择关系代词(who,whom,that,which,whose);
先行词在从句中做状语时,应选择关系副词(where地点状语,when时间状语,why原因状语)。
定语从句知识体系:
关系代词that的用法:
1)不用that的情况:
a)在引导非限定性定语从句时。
如:(错)The tree, that is four hundred years old, is very famous here.
b)介词后不能用:
如:We depend on the land from which we get our food.
We depend on the land that/which we get our food from.
2)只能用that作为定语从句的关系代词的情况
a)在there be句型中,只用that,不用which。
b)在不定代词,如:anything, nothing, the one, all, much, few, any, little等作先行词时,只用that,不用which。
c)先行词有the only, the very修饰时,只用that。
d)先行词为序数词、数词、形容词最高级时,只用that。.
e)先行词既有人,又有物时。
例:All that is needed is a supply of oil. 所需的只是供油问题。
Finally, the thief handed everything that he had stolen to the police. 那贼最终把偷的全部东西交给了警察。
虚拟语气的概念:
虚拟语气用来表示说话人的主观愿望或假想,所说的是一个条件,不一定是事实,或与事实相反。在条件句中的应用条件句可分为两类,一类为真实条件句,一类为非真实条件句。非真实条件句表示的是假设的或实际可能性不大的情况,故采用虚拟语气。
虚拟语气在条件句中的应用:
一、真实条件句:
真实条件句真实条件句用于陈述语气,假设的情况可能发生,其中if是如果的意思。
时态关系句型:条件从句:一般现在时;主句:shall/will+动词原形
如:If he comes, he will bring his violin.
典型例题:
The volleyball match will be put off if it___.
A. will rain
B. rains
C. rained
D. is rained
答案:B。真实条件句主句为将来时,从句用一般现在时。
注意:1)在真实条件句中,主句不能用be going to表示将来,该用shall, will。
如: (错) If you leave now, you are never going to regret it.
(对) If you leave now, you will never regret it.
2)表示真理时,主句谓语动词便不用shall(will)+动词原形,而直接用一般现在时的动词形式。
二、非真实条件句:
非真实条件句表示的是假设的或实际可能性不大的情况,故采用虚拟语气。
1)时态:可以表示过去,现在和将来的情况。它的基本特点是时态退后。
a. 同现在事实相反的假设。
句型:从句:一般过去时;主句:should(would)+动词原形
如:If they were here, they would help you.
b.表示于过去事实相反的假设。
句型:条件从句:过去完成时;主句:should(would)have+过去分词
如:If she had worked harder, she would have succeeded.
The rice would not have been burnt if you had been more careful.
If my lawyer had been here last Saturday, he would have prevented me from going.
c.表示对将来的假想句型:
条件从句:一般过去时;主句:should+动词原形
从句: were+不定式;主句:would+动词原形 should+动词原形
如:If you succeeded, everything would be all right.
If you should succeed, everything would be all right.
If you were to succeed, everything would be all right.
三、混合条件句:
主句与从句的动作发生在不同的时间,这时主,从句谓语动词的虚拟语气形式因时间不同而不同,这叫做混合条件句。
如:If you had asked him yesterday, you would know what to do now. (从句与过去事实相反,主句与现在事实相反。)
If it had rained last night (过去), it would be very cold today (现在).
比较if only与only if:
only if表示“只有”;if only则表示“如果……就好了”。If only也可用于陈述语气。
如:I wake up only if the alarm clock rings. 只有闹钟响了,我才会醒。
If only the alarm clock had rung. 当时闹钟响了,就好了。
If only he comes early. 但愿他早点回来。
It is(high) time that It is(high) time that 后面的从句谓语动词要用过去式或用should加动词原形,但should不可省略。
如:It is time that the children went to bed.
It is high time that the children should go to bed.
need“不必做”和“本不该做"”
didn't need to do表示:过去不必做某事,事实上也没做。
needn'thavedone表示:过去不必做某事,但事实上做了。
如:John went to the station with the car to meet Mary, so she didn't need to walk back home.
约翰开车去车站接玛丽,所以她不必步行回家了。
John went to the station with the car to meet Mary, so she needn't have walked back home.
约翰开车去车站接玛丽,所以她本不必步行回家了。(Mary步行回家,没有遇上John的车。)
典型例题:
There was plenty o ftime. She___.
A. mustn't have hurried
B. couldn't have hurried
C. must not hurry
D. needn't have hurried
答案:D。needn't havedone. 意为"本不必",即已经做了某事,而时实际上不必要。 Mustn't have done用法不正确,对过去发生的事情进行否定性推断应为couldn't have done,“不可能已经”。must not do不可以(用于一般现在时)
特殊的虚拟语气词should 的用法:
1)It is demanded/necessary/a pity+that…结构中的主语从句的谓语动词要用should加动词原形,should可省略。
句型:
如:It is suggested that we(should) hold a meeting next week.
It is necessary that he(should) come to our meeting tomorrow.
2)在宾语从句中的应用在表示命令、建议、要求等一类动词后面的从句中。order, suggest, propose, require, demand, request, insist, command, insist+(should)do
如:I suggest that we(should) hold a meeting next week.
He insisted that he(should) be sent there.
注意:如suggest, insist不表示“建议”或“坚持要某人做某事时”,即它们用于其本意“暗示、表明”、“坚持认为”时,宾语从句用陈述语气。
如:The guard at gate insisted that everybody obey the rules.
判断改错:(错)You pale face suggests that you(should) be ill.
(对)Your pale face suggests that you are ill.
(错)I insisted that you(should) be wrong.
(对)I insisted that you were wrong.
3)在表语从句,同位语从句中的应用在suggestion, proposal, idea, plan, order, advice等名词后面的表语从句、同位语从句中要用虚拟语气,即(should)+动词原形。
如:My idea is that we(should) get more people to attend the conference.
I make a proposal that we(should) hold a meeting next week.
虚拟语气知识体系:
| 条件从句中的谓语动词形式 | 主句中的谓语动词形式 | |
| 与过去事实相反 | had+过去分词 | should/would+have+过去分词 |
| 与现在事实相反 | 过去式 | should/would+动词原形 |
| 与将来事实相反 | 1、过去式 | should/would+动词原形 |
| 2、should+动词原形 | should/would+动词原形 | |
| 3、were to+动词原形 | should/would+动词原形 |
虚拟条件句的倒装:
虚拟条件句的从句部分如果含有were, should, 或had, 可将if省略,再把were, should或had移到从句句首,实行倒装。
如:Were they here now, they could help us.=If they were here now, they could help us.
Had you come earlier, you would have met him=If you had come earlier, you would have met him.
Should it rain, the crops would be saved.=Were it to rain, the crops would be saved.
注意:在虚拟语气的从句中,动词“be”的过去时态一律用“were”,不用was,即在从句中be用were代替。
如:If I were you, I would go to look for him. 如果我是你,就会去找他。
If he were here, everything would be all right. 如果他在这儿,一切都会好的。
典型例题:_____to do the work, I should do it some other day.
A. If were I
B. I were
C. Were I
D. Was I
答案:C. 在虚拟条件状语中如果有were, should, had这三个词,通常将if省略,主语提前,变成were, should, had+主语的形式。
但要注意,在虚拟条件状语从句中,省略连词的倒装形式的句首不能用动词的缩略形式。如我们可说Were I not to do.,而不能说Weren't I to do。
与“单句改错。每个句子有且仅有一处错误,或错一词,或多一词,或少...”考查相似的试题有:
- You can try to guess the meaning of ______ words you don't know from ______ passage.A.the; 不填B.the; theC.不填;...
- They prepared manmade rubber as a substitute________ the natural rubber that they could no longer obtain.
- What a victory ________ those rich and proud women![ ]A.to envy atB.to be envied atC.to envy byD.to be envied by
- Keep me _____of the latest news.A.informB.to informC.informedD.informing
- .The jewelry shop is reported in the local newspaper ___ last night.A.to have robbedB.having been robbedC.to be ro...
- All the staff in our company are considering ___ to the city center for the fashion show.A.to goB.having goneC.to ...
- .Tony was very unhappy for to the party.A.having not been invitedB.not having invitedC.having not invitedD.not ha...
- When I drove to the school gate, I found myself __________in the traffic jam.A.catchingB.to catchC.caughtD.to be ...
- --Where do you suggest_________?--Downtown in Quanzhou, of course.A.will we locate the museumB.the museum must be l...
- Michael______be a policeman, for he’s much too short.A.needn’tB.can’tC.shouldD.may