本试题 “In this university a medal with ten thousand dollars ____ gains success in science and technology every twoyears.[ ]A. is given to whoeverB. are gi...” 主要考查您对连接代词
一般现在时的被动语态
主谓一致
等考点的理解。关于这些考点您可以点击下面的选项卡查看详细档案。
- 连接代词
- 一般现在时的被动语态
- 主谓一致
连接代词的概念:
连接代词常用来引导一个主语从句、宾语从句和表语从句,在句中可用作主语、宾语、表语、定语等,连接代词主要包括who, whom, what, which, whose, whoever, whatever, whichever, whosever等。
whatever, whoever, whichever 用法说明:
主要用于引导主语从句和宾语从句。
如:He does whatever she asks him to do. 她要他做什么,他就做什么。
Whoever breaks the rules will be punished.谁违反这些规则都将受到处罚。
I'll give the ticket to whoever want sit. 请想要这票,我就把它给谁。
Whichever team gains the most points wins. 哪个队得分最多,哪个队就赢。
注:其中的ever主要用于加强语气,含有“一切”、“任何”、“无论”之义。使用这类词时,注意不要按汉语习惯用错句子结构:
如:任何人(谁)先来都可以得到一张票。
误:Anyone comes first can get a ticket./ Who comes first can get a ticket.
正:Anyone who comes first can get a ticket./ Whoever comes first can get a ticket.
连接代词的用法:
1、连接代词主要包括who, whom, what, which, whose, whoever, whatever, whichever, whosever等,它们在句中可用作主语、宾语、表语、定语等,可以引导主语从句、宾语从句和表语从句:
如:I don't know who he is. 我不知道他是谁。
What he says sounds reasonable. 他说的话听起来很有道理。
The question is who(m) we should trust. 问题是我们该信任谁。
I'll take whoever wants to go. 谁想去我就带谁去。
Take whichever seat you like? 你喜欢坐哪个座位就坐哪个?
I will just say whatever comes into my mind. 我想到什么就说什么。
注:who, whom, whoever等不用于名词前作定语。
2、what的两种用法。请看以下两个句子:
(1)I didn't know what he wanted. 我不知道他想要什么。
(2)I gave her what she wanted. 我给了她想要的一切。
上面第一句中的what表示“什么”,带有疑问的意味;第二句中的what表示“所…的一切事或东西”,其意义上大致相当于that(those) which, the thing(things) that, anything that, all that, as much as等,又如:
What[=That which] you say is quite true. 你说的完全是事实。
He saves what[=all that] he earns. 他赚多少,积蓄多少。
Call it what[=anything that] you please. 你喜欢叫它什么就叫它什么。
这样用的what有时还可后接一个名词:
如:He gave me what money[=all the money that] he had about him. 他把身边带有的钱全给了我。
What friends[=All the friends that] he has are out of the country. 他所有的朋友都在国外。
连接代词知识体系:

whatever, whoever, whichever 用法说明:
主要用于引导主语从句和宾语从句。
如:He does whatever she asks him to do. 她要他做什么,他就做什么。
Whoever breaks the rules will be punished.谁违反这些规则都将受到处罚。
I'll give the ticket to whoever want sit. 请想要这票,我就把它给谁。
Whichever team gains the most points wins. 哪个队得分最多,哪个队就赢。
注:其中的ever主要用于加强语气,含有“一切”、“任何”、“无论”之义。使用这类词时,注意不要按汉语习惯用错句子结构:
如:任何人(谁)先来都可以得到一张票。
误:Anyone comes first can get a ticket./ Who comes first can get a ticket.
正:Anyone who comes first can get a ticket./ Whoever comes first can get a ticket.
一般现在时的被动语态的概念:
表示的是一般现在时态和被动语态的叠合。构成:(am/is/are +done)
如:This shirt is washed once a week. 这件T恤一周洗一次。
主动语态变被动语态的方法:
1、把主动语态的宾语变为被动语态的主语。
2、把谓语变成被动结构(be+过去分词),根据被动语态句子里的主语的人称和数,以及原来主动语态句子中动词的时态来决定be的形式。
3、把主动语态中的主语放在介词by之后作宾语,将主格改为宾格。
例如:All the people laughed at him.=He was laughed at by all people.
They make the bikes in the factory.=The bikes are made by them in the factory.
记忆歌诀:
宾变主,主变宾,by短语后面跟。
谓语动词变被动,be后“过分”来使用。
含有情态动词的被动语态:
含有情态动词的主动句变成被动句时,由“情态动词+be+过去分词”构成,原来带to的情态动词变成被动语态后“to”仍要保留。
记忆歌诀:
情态动词变动,情态加be加“过分”,原来带to要保留。
例如:We can repair this watch in two days.=This watch can be repaired in two days.
You ought to take it away.=It ought to be taken away.
They should do it at once.=It should be done at once.
被动语态的用法:
1、不知道或没有必要说明动作的执行者是谁。
例如:Some new computers were stolen last night.一些新电脑在昨晚被盗了。(不知道电脑是谁偷的)
This book was published in1981.这 本书出版于1981年。
2、强调动作的承受者,而不强调动作的执行者。
例如:This book was written by him. 这本书是他写的。
Eight hours per day for sleep must be guaranteed. 每天8小时睡眠必须得到保证。
记忆歌诀:
谁做的动作不知道,说出谁做的没有必要;动作承受者需强调,被动语态运用到。
一般现在时的被动语态:
一、被动语态的结构:
主语(动作接受者)+is/am/are+动词的过去分词+(by+动作执行者)
如:Football is played in most countries in the world.
被动语态的句型总结如下:
1、肯定句:主语+be+过去分词+(by~~).
如:The boy is called Jack.
2、否定句:主语+be not+过去分词+(by~~).
如:The baby is not looked after by his father.
3、一般疑问句:Be+主语+过去分词+(by~~)?
如:Is KingLear written by Shakespeare?
4、特殊疑问句:特殊疑词+be+过去分词+(by~~)?
如:What is this kind of sweater made of?
二、被动语态的用法:
1、要表达“被…”、“受…”、“让…”、“遭…”之类的语义。
如:The teachers are well respected.
The child is well loved by people.
2、强调动作承受者。
如:He is known far and wide. 他远近闻名。
3、不知道式没有必要指出动作的执行者。
如: The room is cleaned every day. 房子每天都有人打扫。
4、为礼貌起见避免提及动作执行者。
如:I wonder if I was allowed to introduce myself? 我是否可以做自我介绍?
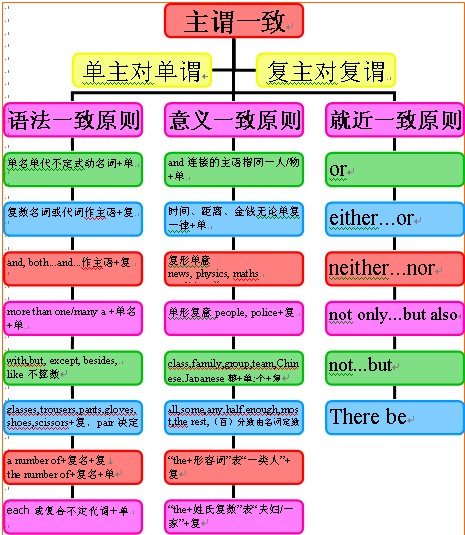
主谓一致的概念:
谓语的数必须和主语的人称和数保持一致,这就叫主谓一致。
主谓一致的基本原则:
1)语法一致原则,即在语法形式上取得一致。例如,主语是单数形式,谓语动词也采取单数形式;主语是复数形式,谓语动词也采取复数形式。
例如:The students are very young.
This picture looks beautiful.
2)意义一致原则,即从意义着眼处理一致关系。例如,主语形式虽是单数但意义是复数,谓语动词也采取复数形式;
而有些主语形式虽是复数但意义上看作单数,谓语动词也采取单数形式。
例如:The people in that country are fighting for independence.
The crowd deeply respect their leader.
Three years in a strange land seems a long time.
3)就近原则,即谓语动词的单数或复数形式取决于最靠近它的词语。
例如:Neither hen or I am going to see the film tonight because we are busy.
几对容易混淆词组的一致用法:
1、由“this/thatkind/typeof+名词”作主语,谓语动词用单数形式;而由"these/thosekind/typeof+复数名词”作主语,谓语动词用复数形式。
例如:This kind of apples is highly priced.
Those kind(s) of tests are good.
2、由“a number of,a totalo f,an average of+复数名词”作主语,谓语动词用复数形式;由“the number of,the total of,the average of+复数名词”作主语,谓语动词用单数形式。
例如:A number of students are waiting for the bus.
The number of the students in this university is increasing yearly.
3、one of,the(only) one of的一致用法
例如:This is one of the books that have been recommended.
This is the(only) one of the books that has been recommended.
主谓一致用法点拨:
1、并列结构作主语谓语用复数:
如:Reading and writing are very important.
注意:当主语由and连结时,如果它表示一个单一的概念,即指同一人或同一物时,谓语动词用单数,and此时连接的两个词前只有一个冠词。
如:The iron and steel industry is very important to our life.
典型例题:
The League secretary and monitor___asked to make a speech at the meeting.
A. is
B. was
C. are
D. were
答案:B.
注:先从时态上考虑。这是过去发生的事情应用过去时,先排除A、C本题易误选D,因为The League secretary and monitor 好象是两个人,但仔细辨别,monitor前没有the,在英语中,当一人兼数职时只在第一个职务前加定冠词。后面的职务用and相连。这样本题主语为一个人,所以应选B。
2、主谓一致中的靠近原则:
1)当there be句型的主语是一系列事物时,谓语应与最邻近的主语保持一致。
例如:There is a pen, a knife and several books on the desk.
There are twenty boy-students and twenty-three girl-students in the class.
2)当either…or…与neither…nor,连接两个主语时,谓语动词与最邻近的主语保持一致。
如果句子是由here, there引导,而主语又不止一个时,谓语通常也和最邻近的主语一致。
例如:Either you or she is to go.
Here is a pen, a few envelops and some paper for you.
3、谓语动词与前面的主语一致:
当主语后面跟有with, together with, like, except, but, no less than, as well as等词引起的短语时,谓语动词与前面的主语一致。
例如:The teacher together with some students is visiting the factory.
He as well as I wants to go boating.
4、谓语需用单数:
1)代词each和由every, some, no, any等构成的复合代词作主语,或主语中含有each,every,谓语需用单数。
例如:Each of us has a tape-recorder.
2)当主语是一本书或一条格言时,谓语动词常用单数。
例如:The Arabian Night is a book known to lovers of English.
3)表示金钱,时间,价格或度量衡的复合名词作主语时,通常把这些名词看作一个整体,谓语一般用单数。(用复数也可,意思不变。)
例如:Three weeks was allowed for making the necessary preparations.
Ten yuan is enough.
5、指代意义决定谓语的单复数:
1)在代词what, which, who, none, some, any, more, most, all等词的单复数由其指代的词的单复数决定。
例如:All is right. (一切顺利。)
All are present. (所有人都到齐了。)
2)集体名词作主语时,谓语的数要根据主语的意思来决定。
例如:family, audience, crew, crowd, class, company, committee等词后用复数形式时,意为这个集体中的各个成员,用单数时表示该个集体。
例如:His family isn't very large. 他家不是一个大家庭。
His family are music lovers. 他的家人都是音乐爱好者。
但集合名词people, police, cattle, poultry等在任何情况下都用复数形式。
例如:Are there any police around?
3)有些名词,如variety, number, population, proportion, majority等有时看作单数,有时看作复数。
A number of+名词复数+复数动词。 The number of+名词复数+单数动词。
例如:A number of books have lent out.
The majority of the students like English.
6、与后接名词或代词保持一致:
1)用half of, part of, most of, a portion of等词引起主语时,动词通常与of后面的名词,代词保持一致。
例如:Most of his money is spent on books.
Most of the students are taking an active part in sports.
2)在一些短语,如many a或more than one所修饰的词作主语时,谓语动词多用单数形式。
但由more than…of作主语时,动词应与其后的名词或代词保持一致。
例如:Many a person has read the novel. 许多人都读过这本书。
More than 60percent of the students are from the city. 百分之六十多的学生都来自这个城市
主谓一致知识体系:
主谓一致用法拓展:
1)当everyone,everybody,noone,nobody,anyone,anybody,someone,somebody,everything,anything,something,nothing等用作主语时,其相应的代词一般用单数形式。
例如:If anybody calls, tell him that I'm out.
Something strange happened, didn't it?
2)人称代词与名词的呼应:人称代词I(me),he(him),she(her),it(it) 都是代替前面的单数名词,而they(them),we(us)则是代替复数名词的,you既可以代表单数,也可以代表复数。但表示泛指的时候,用he或one来表示。
例如:If a young person enters a classical music field only for money, he is in the wrong profession.
3)物主代词与名词的呼应:my,our,his,her,its,their要与代替的名词在数上一致。
例如:The welfare department,as well as the other social services,will have its budget cut.
4)反身代词与其所代成分间的呼应。
例如:Many primitive people believed that by eating ananimal they could get some of the good qualities of that animal for themselves.
5)指示代词与所代名词间的呼应:this和that指代单数名词或不可数名词,these和those指代复数名词(those还可以用作先行词,引导定语从句,表示“那些人”)。
例如:She invited all those who had been her former colleagues.
6)much和muchof后接不可数名词,而many和manyof后接可数名词的复数。
例如:There is not much coal left.
A great many of the houses were knocked down by the earthquake.
7)表示量的词后面有的接可数名词,有的接不可数名词。
接可数名词的有:a number of,a rangeof,a series of十复数名词;
接不可数名词的有:a great deal of,an amount of十不可数名词;
既可接可数又可接不可数名词的有:a lot of,a variety of。
例如:1.The government attached a great deal of importance to education.
2.Quiteanumberofwomenappliedforthisjob.
3.The college library has avariety of books.
4.An apple is avariety off ruit.
与“In this university a medal with ten thousand dollars ____...”考查相似的试题有:
- Playing QQ's "Happy Farm" by planting, watering, fertilizing, harvesting and selling virtual (虚拟的)vegetables, frui...
- The poor ______ living in the mountain ____ top is covered with green trees.A.are; whichB. are; of whichC.is; whos...
- No worker and no engineer who it is that is for the explosion of the chemical factory.A.know; to blameB.would know;...
- The majority of doctors ______ smoking is harmful to health.A.are believedB.had believedC.has believedD.believe
- Twenty years _____ passed since I came to this school, but I feel twenty years _____a short time in my life.A.has; a...
- A professor and a writer present at the meeting. A.wasB.isC.wereD.had been
- . Many a student ______ the importance of learning a foreign language.A.have realizedB.has realizeC.have been real...
- 短文改错。假定英语课上老师要求同桌之间交换修改作文,请你修改你同学写的以下作文。文中共有10处语言错误,每句中最多有两处...
- Every student as well as some teachers who _________to visit the Forbidden City_________asked to be at school gate be...
- One-third of the country ______ covered with trees and the majority of the citizens black people.A. is; are B is; is ...