本试题 “短文改错Dear Abby,How are you? I've got a wonderful news to tell you. I have offered a scholarshipat a university in Australia for my further educa...” 主要考查您对不可数名词
基数词
指示代词
副词
情态动词
现在分词
现在完成时的被动语态
同位语从句
等考点的理解。关于这些考点您可以点击下面的选项卡查看详细档案。
- 不可数名词
- 基数词
- 指示代词
- 副词
- 情态动词
- 现在分词
- 现在完成时的被动语态
- 同位语从句
不可数名词的概念:
不可数名词是指不能以数目来计算,不可以分成个体的概念、状态、品质、感情或表示物质材料的东西;它一般没有复数形式,只有单数形式,它的前面不能用不定冠词a / an ,若要表示它的个体意义 时,一般要与一个名词短语连用。
例如: a cup of tea 一杯茶
a piece of news 一则新闻
two pieces of paper 两张纸
不可数名词量的表示:
1)物质名词:
a. 当物质名词转化为个体名词时。
比较:Cake is a kind of food. 蛋糕是一种食物。(不可数)
These cakes are sweet. 这些蛋糕很好吃。(可数)
b. 当物质名词表示该物质的种类时,名词可数。
Thisfactoryproducessteel.(不可数)
如:We need various steels. (可数)
c. 当物质名词表示份数时,可数。
如:Our country is famous for tea. 我国因茶叶而闻名。
Two teas, please. 请来两杯茶。
2)抽象名词有时也可数。
如:four freedoms 四大自由
the four modernizations 四个现代化
注:物质名词和抽象名词可以借助单位词表一定的数量。
如:a glass of water 一杯水
a piece o fadvice 一条建议
不可数名词用法:
1、不可数名词前不能直接加数词或a(an)。切忌犯以下错误: meat, two tea, 应说a piece of meat, two cups oftea。
2、不可数名词无单复数变化,谓语动词一般用单数形式。
如:There is some milk in the glass. 杯里有一些牛奶。
Some food on the table goes bad. 桌子上的食物变质了。
3、能修饰不可数名词的词有:much, a little, little, a bit, some, any, a lot of, plenty of等,以此来表示不确定的数量。如:
much bread 许多面包
a little milk 一点牛奶
a lot of work 许多工作
4、表示具体的数量时应用单位词加of结构。
如:I bought two kilos of meat. 我买了两公斤肉。
He ate three pieces of bread. 他吃了三块面包。
Would you like a cup of coffee? 你想喝杯咖啡吗?
基数词的概念:
数词是指表示数目多少或顺序先后的词。表示数目多少的数词叫基数词,如one, five, ten, thirty, sixty-five等,数词与不定代词用法相似,在现代英语中,它与不定代词、冠词、指示代词、形容词性物主代词等被称之为限定词。数词用法相当于名词和形容词,在句中可用作主语、宾语、表语、定语、同位语等。
时刻的表示法:
①若为整点钟,则直接读相应的基数词;若为非整点钟,则分别以“时”和“分”为单位用相应的基数词读出:
如:twelve (12),
eight twenty (8:20),
nine forty-five (9:45)
②对于带“分”的时间,也可借助past(过)和to(差)这两个介词来表示(在美国英语中用after表示“过”)。
注:这样表示时“分”不能超过30,否则应作处理,如9.38应处理成“10点差22分”:
如:9.18 eighteen minutes past(after)nine(=nine eighteen)
10.46 fourteen minutes to eleven(=ten forty-six)
以上分钟后带了minutes一词。若“分”为5,10,15,20等五的倍数,则可省略minutes:
如:8.05 five(minutes)past[after]eight(=eight five)
9.20 twenty(minutes)past[after]nine(=nine twenty) 若“分”为15或45,可借用quarter一词;若“分”为30,可借用half一词:
如:6.15 a quarter past six
8.45 a quarter to nine
10.30 half past ten
注:时刻表示法分为12小时编时制和24小时编时制。
日期的表示法:
日期的写法(书面语)和读法(口语)稍有不同,如“十月一日”可以写成October1, October 1st, 1October, 1st October, (the)1st of October 等,表示月份的词也可用缩略式,如Oct.1, 1Oct.1,但是在口语中通常只有两种读法October(the)first或the first of October。
注:日期与星期排列时,通常是星期在前,日期在后:
如:He arrived on Friday, May10. 他于5月10日(星期五)到达。
年份的表示法:
通常以“百”为单位来读。如1986年通常读作nineteen(hundredand)eighty-six,除非在正式场合,其中的hundred and通常都省,但在通常情况下不能按普通基数词的读法那样读成one thousand nine hundred and eighty-six。不过,像1500这样的年份可以有两种读法one thousand five hundred和fifteen hundred,而2000年通常读作two thousand,2003年读作two thousand and three。若表示某个某个年代,则按类似以下的读法:1980s读作nineteen-eighties(20世纪80年代),1600s读作sixteen hundreds(17世纪头10年,即1600—1610),比较:1300 thirteen hundred(1300年)。
基数词的表示法:
(1)以下是最基本的基数词:
one(1), two(2), three(3), four(4), five(5), six(6), seven(7), eight(8), nine(9), ten(10),
eleven(11), twelve(12), thirteen(13), fourteen(14), fifteen(15), sixteen(16), seventeen(17), eighteen(18), nineteen(19),
twenty(20), thirty(30), forty(40), fifty(50), sixty(60), seventy(70), eighty(80), ninety(90), a hundred(100), a thousand(1000), a million(1000000), a billion(十亿)
(2)21—99的表示法。先说“几十”,再说“几”,中间加连字号:
如:twenty-one(21),
thirty-six(36),
forty-five(45),
ninety-nine(99)等。
(3)101—999的表示法。先说“几百”,后接and,再加末尾两位数(或末位数):
如:one hundred and one(101),
five hundred and thirty(530),
seventy hundred and eighty-nine(789)
(4)1000以上的基数词的表示法。先从右至左数,每三位数加一个逗号(即以此把数目分为若干段)。
第一个逗号前的数为thousand(千),第二个逗号前的数million(百万),第三个逗号前的数为billion(十亿),第四个逗号前的数为trillion(万亿),然后一段一段地数:
如:9,883 nine thousand, eigh thundred and eighty-three
65,359 sixty-five thousand, three hundred and fifty-nine
265,468 two hundred and sixty-five thousand, four hundred and sixty-eight
60,263,150 sixty million, two hundred and sixty-three thousand,one hundred and fifty
注:①英语没有“万”这个单位,要表示“万”须借用thousand,如“一万”用“十千”表示(ten thousand),“十万”用“百千”表示(one hundred thousand)。
②hundred, thousand, million, billion等词在读数时不带复数词尾-s(即用单数形式)。
③在hundred后通常加上连词,不过此and在美国英语中可以省略。若读数中没有hundred,则在thousand后加and。
④一个数的最高位若为“一”,这个“一”可用a或one表示,但在数字中间的“一”,则只能用one,不能用a:
如:1600a[one]thousand and six hundred
6100 six thousand and one hundred (其中的one不可改为a)
⑤在非正式场合,人们也常以hundred为单位来读数
如:It cost fifteen hundred pounds. 这东西花了1500英镑。
基数词知识体系:
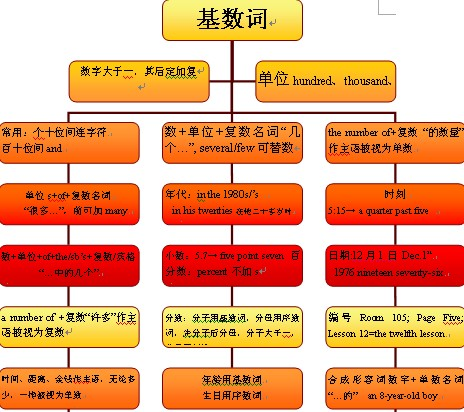
用于复数形式的基数词:
(1)表示整十的基数词用复数形式可以表示人的岁数或年代:
如:in the sixties 在60年代
in one's thirties 在某人30多岁时
(2)基数词转化为名词,可用复数形式:
如:How many twos are there in ten? 10里面有几个2?
Thesoldiersmarchedintens.士兵们10人一排前进。
(3)某些习语中也用复数形式的基数词:
如:in[by] twos and threes 三三两两地
at sixes and sevens 乱其八糟
表示倍数的基数词:
1、倍数+as +形容词/副词(原级)+ as+比较对象。
如: 这座桥是那座桥的三倍长。
This bridge is three times as long as that one.
2. 倍数+形容词或副词的比较级+than+比较对象。
如:这座桥是那座桥的三倍长。
This bridge is three times longer than that one.
3. 倍数+ the size/length/weight…+of+表示比较对象的名词。
如:这座桥是那座桥的三倍长。
This bridge is three times the length of that one.
指示代词的概念:
指示代词是表示指示概念的代词,即用来指示或标识人或事物的代词。主要有this,that,these,those。
this和that用于指代单数,these和those用于指代复数。
指示 代词与定冠词和人称代词一样,都具有指定的含义,用来起指示作用,或用来代替前面已
提到过的名词。
指示代词具有名词和形容词的性质,在句中作主语、宾语、表语、定于等。
指示代词的用法:
指示代词(this, that, these, those)在句中可作主语、宾语、表语、定语:
This is yours and that is mine. 这是你的,那是我的。
I want this book, not that book. 我要这本书,不是那本书。
I like these and he likes those. 我喜欢这些,他喜欢那些。
These computers are cheap. 这些电脑便宜些。
What I want to say is this. 我想说的就是这点。
注:指示代词用作主语和定语时,可指人或物;用作宾语和表语时,只指物。如 This is my father. this 在句中作主语,可以指人,但是在 Do you know this?中,this作宾语,此句只能理解为“你知道这个情况吗?”不能理解为“你认识这个人吗?”
指示代词this与that用法比较:
(1)用来回指上文提到的事情时,可用 this 或 that,但是若要指下文叙述的事情,通常要用 this:
She married Jim, and this[that]surprised me. 她嫁给了吉姆,这使我感到很吃惊。
I want to know this: Is he healthy? 我想知道这一点:他是否很健康。
注:回指上文的that在译成汉语时,通常却译为“这”: That's where you are wrong. 这就是你不对的地方。
(2)在打电话时,通常用 this 指自己,用 that 指对方:
Hello. This is Jim. Is that John? 喂,我是吉姆,你是约翰吗? 但在美国英语中指对方时也可用this。
(3)除用作代词外,this 和that 都可用作副词,与形容词或副词连用,其义为“这么”、“那么(=so):
It's about this(that )high. 大约这(那)么高。
Is it this hot every day? 每天都有这么热吗?
指示代词用法特别提示:
1、this (these)与that (those):
this(these)指近的事物,that(those)指远的事物,可以指空间的远近,时间的前后以及叙述事物的先后。
如:This is a new book. That is an old one. 这是一本新书,那是一本旧书。
2、such与same:
前者表示“如此、这样的人或事”,“后者表示同样的人或事”。在句中常用作主语或宾语。
如:Such was Einstein, asimple man of great achievements. 爱因斯坦就是这样一个人,朴实无华,成就非凡。
Read the stories such as you love. 读你喜欢的故事吧。
The same is the case with everyone. 大家的情况也是一样。
指示代词知识体系:
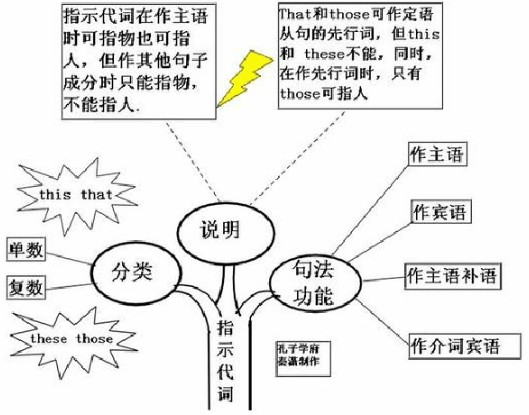
指示代词用法拓展:
1、注意以下各句中this的特殊用法:
如:He will be in Paris this day next week.下个星期的今天他将在巴黎了。
He will come here this day next month.他将在下个月的今天来这儿。
比较:He got married ten years ago today. 他是10年前的今天结婚的。
2、表替代的that与those:
有时为了避免重复,可用that和those 代替前面提到的名词:
如:The population of China is much larger that that of Japan.中国人口比日本人口多得多。(that=the population)
His views are close to those of the Socialist Party. 他的观点接近社会党的观点。(those=the views)
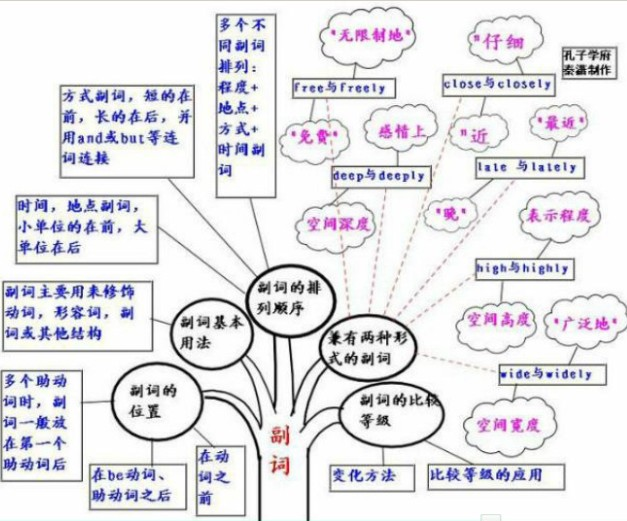
副词的概念:
副词是指在句子中表示行为或状态特征的词,用来修饰动词、形容词、其他副词、介词短语、非谓语动词乃至整个句子,表示时间、地点、程度、方式等概念。
副词的位置:
1)在动词之前。
2)在be动词、助动词之后。
3)多个助动词时,副词一般放在第一个助动词后。
注意:
a. 大多数方式副词位于句尾,但宾语过长,副词可以提前,以使句子平衡。
如:We could see very clearly a strange light ahead of us.
b. 方式副词well,badly糟、坏,hard等只放在句尾。
如:He speaks English well.
副词的排列顺序:
1)时间,地点副词,小单位的在前,大单位在后。
2)方式副词,短的在前,长的在后,并用and或but等连词连接。
如:Please write slowly and carefully.
3)多个不同副词排列:程度+地点+方式+时间副词。
注意:副词very可以修饰形容词,但不能修饰动词。
改错:(错)I very like English.
(对)I like English very much.
注意:副词enough要放在形容词的后面,形容词enough放在名词前后都可。
如:I don't know him well enough.
There is enough food for everyone to eat.
There is food enough for everyone to eat.
兼有两种形式的副词:
1)close与closely:
close意思是“近”;closely意思是“仔细地”。
如: He is sitting close to me.
Watch him closely.
2)late与lately:
late意思是"晚";lately意思是“最近” 。
如:You have come too late.
What have you been doing lately?
3)deep与deeply:
deep意思是“深”,表示空间深度;deeply时常表示感情上的深度,“深深地” 。
如:He pushed the stick deep into the mud.
Even father was deeply moved by the film.
4)high与highly:
high表示空间高度;highly表示程度,相当于much。
如:The plane was flying high.
I think highly of your opinion.
5)wide与widely:
wide表示空间宽度;widely意思是“广泛地”,“在许多地方”。
如:He opened the door wide.
English is widely used in the world.
6)free与freely:
free的意思是“免费”;freely的意思是“无限制地”。
如:You can eat free in my restaurant whenever you like.
You may speak freely, say what you like.
副词知识体系:
情态动词的概念:
情态动词表示说话人对某一动作或状态的态度。
几组词的辨析:
1、need和dare的用法:
need和dare既可用作情态动词,也可用作实义动词。用作情态动词时,主要用于否定句和疑问句。用作实义动词时,可用于各种句式。
(1)用作情态动词:
如:—Need I come? 我需要来吗?
—Yes, you must. 需要。
You needn′t telephone him now. 你现在不必打电话给他。
I don′t think you need worry. 我想你不必发愁。
She dare not go out alone at night. 她晚上不敢一个人出去。
How dare you say I′m unfair? 你竟敢说我不公平?
Not one of them dared mention this.他们谁也不敢提这件事。
(2)用作实义动词:
如:You don′t need to do it yourself. 你不必亲自做这件事。
We need to tell them the news. 我们需要把这消息告诉他们。
The table needs painting(to be painted.). 桌子需要油漆一下。
We should dare to give our own opinion.我们要敢于提出自己的观点。
He did not dare(to) look up. 他不敢抬头看。
I dare day he′ll come again. 我想他会再来的。
2、can和be able to:
(1)情态动词can只有两种时态形式,现在式can和过去式could,而be able to有多种时态形式。
如:Mary can play the piano. She has been able to play it since she was 5. 玛丽会弹钢琴。她五岁起就会弹了。
(2)用在过去时中,could经常表示能够做某事,事实上不一定去做,而was∕were able to则表示“过去做成了某事”。在否定句中两者可通用。
如:He could swim across the English Channel. But he didn′t feel like it that day.
他能游过英吉利海峡,但那天他不想游。
Yesterday I was able to get home before the heavy rain. 昨天我在下大雨前赶到了家里。
3、must和have to:
must表示主观意志,而have to表示由于客观因素不得不做某事。must没有过去式,除在间接引语中可用于表示过去时间,在直接引语中表示过去时间应该用had to代替。
如:I told her that she must give up smoking. 我叫她必须戒烟。
We had to get everything ready that night. 我们那晚得把一切准备就绪。
4、would和used to:
(1)usedto表示过去与现在或过去某时与后来的情况有不同,而would只表过去的情况。
如:People used to think that the earth was flat. 过去人们认为地球是平的。(现在人们不这么认为。)
She would go out for a walk in the morning when she was in the country.
在乡下时,她总是在早晨去散会儿步。(可能现在仍有散步的习惯。)
(2)used to可表示过去的习惯动作和经常的情况,而would只表示过去的习惯动作。
如:He used to∕would smoke while writing. 过去他写东西时常抽烟。
She used to be fat. 她过去很胖。
情态动词的基本用法:
1、can(could):
1)表示能力,could主要指过去时间。
如:Two eyes can see more than one. 两只眼比一只眼看得清。
Could the girl read before she went to school? 这女孩上学前能识字吗?
2)表示可能(理论上或是逻辑判断上)。
如:The temperature can fall to–60℃, that is 60℃ below freezing. 气温可降至-60℃,也就是零下60℃。
He can′t(couldn′t) have enough money for a new car. 他不可能有足够的钱买新车。
You mustn′t smoke while you′re walking around in the wood. You could start a fire.
在林子里走时勿吸烟,那样可能会引起火灾。
3)表示允许。
如:Can I have a look at your new pen? 我可以看一看你的新钢笔吗?
He asked whether he could take the book out of the reading-room. 他问他可不可以把书带出阅览室。
4)表惊异、怀疑、不相信等态度。主要用于否定句、疑问句或感叹句中。
如:Where can(could) they have gone to? 他们会去哪儿了呢?
He can′t(couldn′t) be over sixty. 他不可能超过六十岁。
How can you be so careless? 你怎么这么粗心?
5)比较委婉客气地提出问题或陈述看法。
如:Can(Could) you lend me a hand? 帮我一把好吗?
I′m afraid we couldn′t give you an answer today. 恐怕我们今天不能给你答复。
2、may(might):
1)表允许,might可以指过去时间,也可指现在时间,语气更委婉。
如:You may take what ever you like. 你喜欢什么就拿什么。
He told me that I might smoke in the room. 他告诉我可以在房间里抽烟。
May(Might) I ask for a photo of your baby? 我可以要一张你宝宝的照片吗?
在回答以may引起的问句时,多避免用这个词,而用其它方式:
如:Yes, please./Certainly. /Please don′t./You′d better not./No, you mustn′t.等,以免显得太严峻或不客气。
2)表可能(事实上)。可以指过去时间,也可以指现在时间,但语气更加不肯定。
如:He may be at home. 他可能在家。
She may not know about it. 她可能不知道这件事。
He was afraid they might not agree with him. 他担心他们可能不同意他的意见。
如:They might be having a meeting, but I′m not sure. 他们有可能在开会,不过我不肯定。
3、must:
1)表示义务。意为“必须”(主观意志)。
如:We must do everything step by step. 我们一切都必须循序渐进地做。
You mustn′t talk to her like that. 你不可能那样对她说话。
—Must we hand in our exercise-books now? 我们现在就要交练习本吗?
—No, you needn′t./No, you don′t have to.不必。(这种情况下,一般不用mustn′t)
2)表示揣测。意为“想必、准是、一定”等,只用于肯定句。
如:He must be ill. He looks so pale. 他准是病了。他的脸色苍白。
如:She′s wearing a diamond necklace. She must have a lot o fmoney. 她戴着钻石项链,一定很有钱。
4、shall:
1)表征询意见,用于第一、第三人称疑问句。
如:Shall I get you some tea? 我给你点茶好吗?
Shall the boy wait outside? 让那男孩在外面等吗?
What shall we do this evening? 我们今晚做什么?
2)表说话人的意愿,有“命令、允诺、警告、决心”等意思,用于第二、第三人称陈述句。
如:You shall do as I say. 按我说的做。(命令)
You shall have my answer tomorrow. 你明天可以得到我的答复。(允诺)
He shall be sorry for it one day, I tell you.有一天他会后悔的,我告诉你。(警告)
如:Nothing shall stop us from carrying out the plan.什么也不能阻止我们执行这项计划。(决心)
5、will:
1)表意愿,用于各种人称陈述句。
如:I will do anything for you. 我愿为你做任何事。
None is so blind as those who won′t see. 不愿看的人眼最瞎。
If you will read the book, I′ll lend it to you. 如果你愿意读这本书,我会把它借给你。
2)表请求,用于疑问句。
如:Will you close the window? It′s a bit cold. 请你把窗户关上好吗?有点冷。
Won′t you drink some more coffee? 再来一点咖啡好吗?
3)表示某种倾向或习惯性动作。
如:Fish will die out of water. 鱼离开水就不能活。
The door won′t open. 这门打不开。
The boy will sit there hour after hour looking at the traffic go by.
那男孩常常坐在那里好几个钟点,看着车辆行人通过。
6、should:
1)表义务。意为“应该”(某件事宜于做),用于各种人称。
如:You should be polite to your teachers. 你对老师应该有礼貌。
You shouldn′t waste anytime. 你不应该浪费时间。
2)表推测,意为“想必一定、照说应该、估计”等。
如:The film should be very good as it is starring first-class actors. 这部新电影是一流演员主演的,估计拍得很好。
They should be home by now. 照说他们现在应当已经到家了。
7、would:
1)表意愿。
如:They would not let him in because he was poorly dressed. 他们不让他进去因为他衣着破旧。
I said I would do anything for you. 我说过我愿意为你做任何事。
2)表委婉地提出请求、建议或看法。
如:Would you like another glass of beer? 再来杯啤酒好吗?
Would you mind cleaning the window? 请把窗户擦一下好吗?
They wouldn′t have anything against it. 他们不会有什么反对意见。
3)表过去反复发生的动作或过去的一种倾向。
如:Every time she was in trouble, she would go to him for help. 她每遇到麻烦都会向她求助。
8、ought to:
1)表义务,意为“应该”(因责任、义务等该做),口气比should稍重。
如:You are his father. You ought to take care of him. 你是他父亲,应当管他。
You oughtn′t to smoke so much. 你不应该抽这么多烟。
2)表推测,暗含很大的可能,语气较弱。
如:Han Mei ought to know his telephone number. 韩梅该知道他的电话号码。
There′s a fine sun set; it ought to be a fine day tomorrow. 今天有晚霞,明天应该是个好天。
9、used to:
表示过去的习惯动作或状态,现在不复发生或存在。疑问式和否定式有两种。
如:He used to live in the countryside, but now he lives in the city. 他过去住在乡下,现在住在城里。
There used to be a building at the street corner, but it has been pulled down. 街道拐角处过去有座楼房,现在拆了。
I usedn′t (didn′t use) to smoke. 我过去不抽烟。
Used you(Did you use) to go to school on foot? 你过去常步行去学校吗?
情态动词的其他用法:
首先它是动词,而且不同于行为动词,行为动词表示的是可以通过行为来表达的动作(如写,读,跑),而情态动词只是表达的一种想法(如能,也许,敢)。
用法是:情态动词+行为动词原形:
句:I can read this sentence in English. 我能用英语读这句话。
情态动词是一种本身有一定的词义,表示说话人的情绪,态度或语气的动词,但不能单独作谓语,只能和其他动词原形构成谓语。
如:We can be there on time tomorrow. 我们明天能按时去那儿。
May I have your name? 我能知道你的名字吗?
Shall we begin now? 我们现在就开始吗?
You must obey the school rules. 你必须遵守校规。
情态动词知识体系:

情态动词表推测的三种句式:
1、在肯定句中一般用must(一定),may(可能),might/could(也许,或许)。
如:He must/may/might know the answer to this question? 他一定/可能/也许知道这个问题的答案。
It is cold in the room. They must have turned off the heating. 屋里很冷,他们肯定把暖气关了。
2、否定句中用can't/couldn't (不可能), may not/might not(可能不)。
如:It can't/couldn't be the headmaster. He has gone to America. 这不可能是校长,他去美国了
He may not/might not know the scientist. 他也许不认识那位科学家。
3、疑问句中用can/could(能……?)。
如:Could he have finished the task? 他可能把任务完成了吗?
Can he be at home now? 他现在能在家吗?
注:以上三种句式中情态动词的语气按程度都是依次递减的。Might, could并非may, can的过去式,而表示语气较为委婉或可能性较小。
情态动词表推测的三种时态:
1、对将来情况的推测,用“情态动词+动词原形”。
如:She must/may/might/could arrive before 5. 5:00前她一定/可能/也许到。
She must/may/might/could walk miles and miles among the hills without meeting anyone.
她一定/可能/也许会在山里一连走好几英里而遇不到一个人。
2、对现在或一般情况的推测,用“情态动词+be”,“情态动词+bedoing”或“情态动词+动词原形”。
如:He must/may/might/could be listening to the radio now. 他一定/可能/也许正在听收音机。
He can't(couldn't)/may(might) not be at home at this time. 这个时候他不可能/可能不在家。
Mr. Bush is on time for everything. How can(could) he be late for the opening ceremony?
布什先生一向准时,这次开幕式他怎么可能迟到呢?
3、对过去情况的推测,用“情态动词+have+过去分词”。
如:It must/may/might/ could have rained last night. The ground is wet. 地湿了,昨晚肯定/可能/也许下雨了。
The door was locked. He can(could) not/may(might) not have been at home. 门锁着,他不可能/可能不在家。
Can/Could he have gotten the book?难道他找到书了吗?
注:情态动词should/ought to表推测时,意为“想必会,理应……”但与“have+过去分词”连用时,则又可构成虚拟语气意为“本应该做某事却没做”。
如:It's seven o'clock. Jack should/ought to be here at any moment.
现在七点钟了,杰克理应随时到达。(推测)
She should/ought to have attended your birthday party, but she had to look after her mother in hospital.(虚拟)
她本该出席你的生日晚会的,可是她得在医院照顾她妈妈。
Tom should not/ought not to have told me your secret, but he meant no harm.(虚拟)
汤姆本不该告诉我你的秘密,可是他并无恶意。
现在分词的概念:
现在分词(PresentParticiple)(又称-ing形式),是分词的一种,是非限定动词,即在句子里面不能单独充当谓语,但能充当其它的一些成分(定语,表语,补语和状语)。一般式:doing;一般被动式:being done;完成式:having done;完成被动式:having been done。所有否定式都是在-ing前面加not。
现在分词的用法:
1)做表语:
如:He was very amusing.
That book was rather boring.
很多动词的现在分词都可以作表语:exciting, interesting, encouraging, disappointing, confusing, touching, puzzling.
2)作定语:
上面所出现的现在分词都可以用作定语,修饰一个名词:
如:That must have been a terrifying experience.
I found him a charming person.
现在分词短语还可以放在名词的后面修饰名词,相当于一个定语从句:
如:There are a few boys swimming in the river.
There is a car waiting outside.
3)作状语:
现在分词短语可以表示一个同时发生的次要的或伴随的动作:
如:Following Tom, we started to climb the mountain.
Opening the drawer, he took out a box.
Taking a key out of his pocket, he opened the door.
现在分词短语还可以表示原因,相当于一个原因状语从句:
如:Not knowing her address, we couldn't get in touch with her.
Being unemployed, he hasn't got much money.
现在分词短语还可以表示时间,相当于一个时间状语从句:
如:Hearing the news, they all jumped with joy.
Returning home, he began to do his homework.
Jim hurt his arm while playing tennis.
Be careful when crossing the road.
Having found a hotel, we looked for some where to have dinner.
Having finished her work, she went home.
4)作宾补:
现在分词在一些动词之后可以做宾语的补语:
例如:see, hear, catch, find, keep, have等。
如:I see him passing my house every day.
I caught him stealing things in that shop.
I smelt something burning.
She kept him working all day.
现在分词其他用法解析:
1、现在分词一般式的用法:
现在分词的一般式所表示的动作与主语动作同时发生:
如:When we arrived, we found him sleeping. 我们到达时发现他在睡觉。
Living in the 示的动作也可略早于或迟于谓语动作,但两者之间没有时间间隔:
如:Seeing nobody at home, he decided to leave a note. 发现没有在家,他决定留个字条。
He went home, finding the door locked. 他回到家,发现门是锁着的。当现在分词所表示的动作略迟于谓语动作时,现在分词通常位于句末。
2、现在分词完成式的用法:
现在分词的完成式主要表示发生在谓语动作之前的动作:
如:Having been there once, she knew the place quite well. 由于去过那儿一次,她对那地方很熟悉。
Having failed twice, he didn't want to try again. 他已经失败了两次,不想再试了。
注:(1)现在分词的一般式和完成式均可表示已完成或先于谓语的动作,但有区别:现在分词所表示的动作虽然可以先于谓语动作,但两者之间没有时间间隔,而现在分词的完成式所表示先于谓语的动作则与谓语动作有一定的时间间隔:
如:Locking the door, he went out. 锁好门之后,他就出去了。
Having invited him here to speak, we'd better go to his lecture. 既然我们请了他来作报告,我们最好去听一下。
有时即使是分词动作与谓语动作几乎同时发生,但如果要强调分词动作的完成性,也应用现在分词的完成式:
如:Having bought our tickets, we went into the theatre. 我们买好票后就走进剧场。
(2)现在分词的完成式一般不用作定语:
误:Do you know anyone having lost a cat? 你知道有谁丢了一只猫吗?
误:I want to talk to the person having broken the window. 我想同打破窗户的人谈谈。
若将以上现分词的完成式改为一般式也不可以(因为现在分词作后置定语时通常只表示与谓语动作同时或几乎同时发生的动作,而不能先于谓语动作而发生):
误:I want to talk to the person breaking the window.
3、现在分词被动式的用法:
当要表示一个被动动作时,现在分词就用被动形式。现在分词的一般式和完成式均有被动式形式:
(1)现在分词一般式的被动式:主要表示现在正在进行的动作,也可表示与谓语动作同时发生的动作:
如:Who is the woman being operated on? 正在动手术的女人是谁?
I saw him being taken away by the police. 我看见他被警察带走。
注:有时现在分词一般式的被动式所表示的动作也可发生在谓语动作之前(此时的现在分词通常用于表示原因,且多为状态动词):
如:Not having a car, he finds it difficult to get around. 由于没车,她感到行动很困难。
(2)现在分词完成式的被动式:主要表示发生在谓语动词之前且已经完成的动作。
如:The subject having been opened, he had to go on with it. 话题已经开始了,他不得不谈下去。
Having been written inhaste, the book has many mistakes. 这书因写得仓促,所以错误不少。
比较:Being so ill, she can't go to school. 由于病得那么严重,她不能去上学。
Having been ill for a long time, he needed time to recover. 由于病了很长时间,他需要一段恢复的时间。
现在完成时的被动语态概念:
现在完成时被动语态的结构就是现在完成时态和被动语态结构的叠合,即“have+been+动词过去分词”。
现在完成时态的被动语态的构成:
1、现在完成时的被动语态的肯定式为:have/has+been+done。
如:The new schools have been set up. 新学校都已经建成了。
The experiment has been done successfully. 这个实验做得很成功。
2、现在完成时的被动语态的否定式为:have/has+not+been+done。
如:The books have not been borrowed by the teacher. 那些书还没有被老师借走了。
Tom's novel has not been published. 汤姆的小说还没有被出版。
3、现在完成时的被动语态的一般疑问句需将have/has提到主语的前面。
如:—Have the letters been posted? 信已经寄出去了吗?
—Yes, they have. 是的,已寄出了。
—Has his bike been repaired? 他的自行车修好了吗?
—No, it hasn't. 不,还没有被修好。
4、现在完成时的被动语态的特殊疑问句为:疑问词+have/has+been+done。
如:How long have the machine been repaired?这些机器已被修好多长时间了?
Who has been invited? 谁受到了邀请?
现在完成时态的被动语态的用法:
1、现在完成时的被动语态同它的主动语态一样,强调过去的动作对现在造成的影响或结果,通常与 already, yet, just, never, recently等副词连用。
如:The room has already been cleaned. 房间已经被清扫干净了。(含现在已不用清扫房间了)
The doctor hasn't been sent for yet. 还没有派人去请医生。(含现在应派人去请医生)
The office looks nice. It has just been cleaned. 办公室看起来很干净。它刚被打扫过。(含现在已不用清扫房间了)
Such a thing has never been heard of before. 这样的事以前从未听说过。(含现在才听说过)
Recently the price of TV sets has been cut. 近来电视机降价了. (含电视机的价格现在比以前低了)
2、表示一个被动的动作或状态开始于过去,持续到现在,并可能持续下去,常与for或since等引导的时间状语连用,或用与How long…?的句型中。
如:The machine has been repaired for two hours. 这台机器已修了两小时了。
They have been helped by us for two weeks. 他们得到我们帮助有两周了。
How long has the project been carried out? 这项工程已被实施多长时间了?
同位语从句的概念:
在复合句中充当同位语的名词性从句称为同位语从句。同位语从句是名词性从句(主语从句、表语从句、宾语从句、同位语从句)中的主要从句之一,从句作同位语表示与之同位的名词(短语)的实际内容,它的作用相当于名词,对前面的名词(短语)加以补充说明或进一步解释,相当于一个表语从句,它们之间的关系是同位关系,即主表关系。
同位语从句的用法:
1、同位语从句的引导:
词引导同位语从句的词语通常有连词that,whether,连接代词和连接副词等:
如:We heard the news that our team had won. 我们听到消息说我们队赢了。
They were worried over the fact that you were sick. 他们为你生病发愁。
I have no idea when he will come back. 我不知道他什么时候回来。
There is some doubt whether he will come. 他是否会来还不一定。
The question whether it is right or wrong depends on the result. 这个是对还是错要看结果。
注:whether可引导同位语从句,但if不能引导同位语从句。
2、同位语从句与定语从句的区别:
(1)意义的不同:
同位语从句是用于说明所修饰名词的具体内容的,它与被修饰词语通常可以划等号;而定语从句是限制所修饰名词的,它的作用是将所修饰的名词与其他类似的东西区别开来:
如:We are glad at the news that he will come. 听到他要来这个消息我们很高兴。
(news的内容就是that he will come,故that引导的是同位语从句)
We are glad at the news that he told us. 听到他告诉我们的这个消息我们很高兴。
(that从句是限制thenews的内容的,即我们高兴只是因为他告诉的这个news而不是其他的news,故that从句为定语从句)
(2)引导词的不同:
what, how, if, whatever等可引导名词性从句,但不引导定语从句。
(3)引导词的功能上的不同:
that引导同位语从句时,它不充当句子成分,而引导定语从句时,它作为关系代词,要么充当定语从句的主语,要么充当定语从句的宾语。
如上例that he told us中的that就充当told的宾语。
(4)被修饰词语的区别:
同位语从句所修饰的名词比较有限,通常有hope, wish, idea, news, fact, promise, opinion, suggestion, truth等,而定语从句所修饰的名词则非常广泛。
另外,when和where引导定语从句时,通常只修饰表示时间和地点的名词,而它们引导同位语从句时却不一定;又如why引导定语从句,它通常只修饰名词thereason,而它引导同位语从句时则不一定:
如:I have no idea when they will come. 我不知道他们什么时候来。(同位语从句)
I'll never forget the days when I lived there. 我永远不会忘记我住在那儿的日子。(定语从句)
We don't understand the problem why this is the best choice. 我们不明白这个问题,为什么这是最好的选择。(同位语从句)
There a son why he didn't come to the meeting is that he is ill. 他未能来开会,原因是他生病了。(定语从句)
同位语从句用法解析:
一、理解同位语从句的含义,把握同位语从句的实质:
在主从复合句中作同位语的从句称为同位语从句。同位语从句一般用that, whether, what, which, who, when, where, why, how等词引导,常放在fact, news, idea, truth, hope, problem, information, wish, promise, answer, evidence, report, explanation, suggestion, conclusion, word, possibility等抽象名词后面,说明该名词的具体内容。换言之,同位语从句和所修饰的名词在内容上为同一关系,对其内容作进一步说明。
例:The news that they had won the game soon spread over the whole school. 他们比赛获胜的消息很快传遍了整个学校。
析:they had won the game说明the news的全部内容,因此该句为同位语从句。
二、正确运用同位语从句的引导词,准确把握同位语从句:
1、如同位语从句意义完整,应用that引导同位语从句。(即that不充当任何成分,只起连接作用,不可省略)
例:The general gave the order that the soldiers should cross the river at once. 将军下达了战士们立即过河的命令。
析:the soldiers should cross the river at once是the order的全部内容,且意义完整,因此应用that引导同位语从句。
2、如同位语从句意义不完整,需增加"是否"的含义,应用whether引导同位语从句。(if不能引导同位语从句)
例:We'll discuss the problem whether the sports meeting will be held on time. 我们将讨论运动会是否会如期举行的问题。
析:the sports meeting will be held on time 意义不完整,应加“是否”的含义才能表达the problem的全部内容,因此应用whether引导同位语从句。
3、如同位语从句意义不完整,需增加"什么时候"、"什么地点"、"什么方式"等含义,应用when, where, how等词引导同位语从句。
例1:I have no idea when he will be back.
析:he will be back 意义不完整,应加"什么时候"的含义才能表达idea的全部内容,因此应用when引导同位语从句。
例2:I have no impression how he went home, perhaps by bike.
析:he went home 意义不完整,应加"如何"的含义才能表达impression的全部内容,因此应用how引导同位语从句。
4、当主句的谓语较短,而同位语从句较长时,同位语从句常后置。
如:The thought came to him that may be the enemy had fled the city.
与“短文改错Dear Abby,How are you? I've got a wonderful news ...”考查相似的试题有:
- 看下图回答问题
- The traffic problems have severely affected economic development. ________, we must spare no efforts to solve them.A...
- Tom insisted what he said ____ true and we insisted that he____ and have a look.A.be;should goB.should be;would goC...
- 33. He sat _______ notes of everything ________ was said.A.taken; thatB.taking; whatC.taking; thatD.taken; what
- --- _______ made her ashamed of herself?--- ______ the lowest mark in her class.A.What; Because she gotB.Was it wha...
- _____ in a poor family made Jack very hardworking when he was still young.A.Brought upB.Bringing upC.Having brough...
- 36.Surveys demonstrate that a majority of urban residents nowadays in the mainland of China rate ___________a perfec...
- The situation is hard to _______, because he isn’t a man easy to _______.A.be dealt; communicateB.be dealt with; be...
- From the situation in this financial crisis,you can see China is totally not she used to be a century ago.A./:tha...
- The treatment will continue until the patient reaches the point ________ he can walk correctly and safely.A.whenB.w...