本试题 “-The physics exam is not difficult, is it?-________. Even Tom ________ to the top students failed.[ ]A.Yes; belongsB.No; belongedC.Yes; belongin...” 主要考查您对现在分词
反意疑问句
等考点的理解。关于这些考点您可以点击下面的选项卡查看详细档案。
- 现在分词
- 反意疑问句
现在分词的概念:
现在分词(PresentParticiple)(又称-ing形式),是分词的一种,是非限定动词,即在句子里面不能单独充当谓语,但能充当其它的一些成分(定语,表语,补语和状语)。一般式:doing;一般被动式:being done;完成式:having done;完成被动式:having been done。所有否定式都是在-ing前面加not。
现在分词的用法:
1)做表语:
如:He was very amusing.
That book was rather boring.
很多动词的现在分词都可以作表语:exciting, interesting, encouraging, disappointing, confusing, touching, puzzling.
2)作定语:
上面所出现的现在分词都可以用作定语,修饰一个名词:
如:That must have been a terrifying experience.
I found him a charming person.
现在分词短语还可以放在名词的后面修饰名词,相当于一个定语从句:
如:There are a few boys swimming in the river.
There is a car waiting outside.
3)作状语:
现在分词短语可以表示一个同时发生的次要的或伴随的动作:
如:Following Tom, we started to climb the mountain.
Opening the drawer, he took out a box.
Taking a key out of his pocket, he opened the door.
现在分词短语还可以表示原因,相当于一个原因状语从句:
如:Not knowing her address, we couldn't get in touch with her.
Being unemployed, he hasn't got much money.
现在分词短语还可以表示时间,相当于一个时间状语从句:
如:Hearing the news, they all jumped with joy.
Returning home, he began to do his homework.
Jim hurt his arm while playing tennis.
Be careful when crossing the road.
Having found a hotel, we looked for some where to have dinner.
Having finished her work, she went home.
4)作宾补:
现在分词在一些动词之后可以做宾语的补语:
例如:see, hear, catch, find, keep, have等。
如:I see him passing my house every day.
I caught him stealing things in that shop.
I smelt something burning.
She kept him working all day.
现在分词其他用法解析:
1、现在分词一般式的用法:
现在分词的一般式所表示的动作与主语动作同时发生:
如:When we arrived, we found him sleeping. 我们到达时发现他在睡觉。
Living in the 示的动作也可略早于或迟于谓语动作,但两者之间没有时间间隔:
如:Seeing nobody at home, he decided to leave a note. 发现没有在家,他决定留个字条。
He went home, finding the door locked. 他回到家,发现门是锁着的。当现在分词所表示的动作略迟于谓语动作时,现在分词通常位于句末。
2、现在分词完成式的用法:
现在分词的完成式主要表示发生在谓语动作之前的动作:
如:Having been there once, she knew the place quite well. 由于去过那儿一次,她对那地方很熟悉。
Having failed twice, he didn't want to try again. 他已经失败了两次,不想再试了。
注:(1)现在分词的一般式和完成式均可表示已完成或先于谓语的动作,但有区别:现在分词所表示的动作虽然可以先于谓语动作,但两者之间没有时间间隔,而现在分词的完成式所表示先于谓语的动作则与谓语动作有一定的时间间隔:
如:Locking the door, he went out. 锁好门之后,他就出去了。
Having invited him here to speak, we'd better go to his lecture. 既然我们请了他来作报告,我们最好去听一下。
有时即使是分词动作与谓语动作几乎同时发生,但如果要强调分词动作的完成性,也应用现在分词的完成式:
如:Having bought our tickets, we went into the theatre. 我们买好票后就走进剧场。
(2)现在分词的完成式一般不用作定语:
误:Do you know anyone having lost a cat? 你知道有谁丢了一只猫吗?
误:I want to talk to the person having broken the window. 我想同打破窗户的人谈谈。
若将以上现分词的完成式改为一般式也不可以(因为现在分词作后置定语时通常只表示与谓语动作同时或几乎同时发生的动作,而不能先于谓语动作而发生):
误:I want to talk to the person breaking the window.
3、现在分词被动式的用法:
当要表示一个被动动作时,现在分词就用被动形式。现在分词的一般式和完成式均有被动式形式:
(1)现在分词一般式的被动式:主要表示现在正在进行的动作,也可表示与谓语动作同时发生的动作:
如:Who is the woman being operated on? 正在动手术的女人是谁?
I saw him being taken away by the police. 我看见他被警察带走。
注:有时现在分词一般式的被动式所表示的动作也可发生在谓语动作之前(此时的现在分词通常用于表示原因,且多为状态动词):
如:Not having a car, he finds it difficult to get around. 由于没车,她感到行动很困难。
(2)现在分词完成式的被动式:主要表示发生在谓语动词之前且已经完成的动作。
如:The subject having been opened, he had to go on with it. 话题已经开始了,他不得不谈下去。
Having been written inhaste, the book has many mistakes. 这书因写得仓促,所以错误不少。
比较:Being so ill, she can't go to school. 由于病得那么严重,她不能去上学。
Having been ill for a long time, he needed time to recover. 由于病了很长时间,他需要一段恢复的时间。
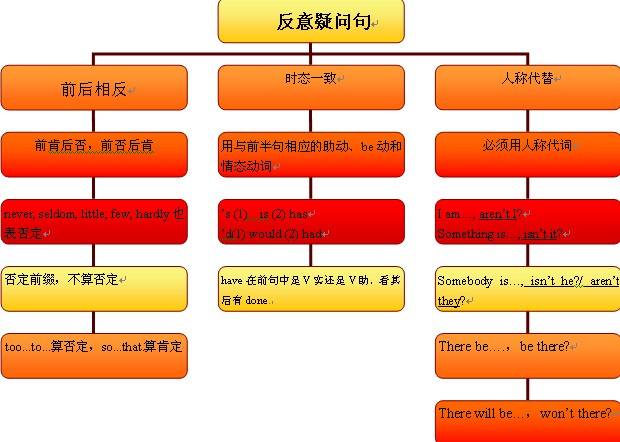
反意疑问句的概念:
表示提问人的看法,没有把握,需要对方证实。
反意疑问句由两部分组成:前一部分是一个陈述句,后一部分是一个简短的疑问句,两部分的人称时态应保持一致。
1、陈述部分肯定式+疑问部分否定式,可记为前肯后否。
2、陈述部分否定式+疑问部分肯定式,可记为前否后肯。
例如:This pencil is red, isn't it? Yes, it is. / No, it isn't.
This pencil isn't red, is it? Yes, it is. / No, it isn't.
反意疑问句类型:
1)陈述部分的主语是I,疑问部分要用aren't I.
如:I'm as tall as your sister, aren't I?
2)陈述部分的谓语是wish,疑问部分要用may+主语。
如:I wish to have a word with you, may I?
3)陈述部分用no, nothing, nobody, never, few, seldom, hardly, rarely, little等否定含义的词时,疑问部分用肯定含义。
如:The Swede made no answer, did he/she?
Some plants never blown(开花), do they?
4)含有oughtto的反意疑问句,陈述部分是肯定的,疑问部分用shouldn't/oughtn't+主语。
如:He ought to know what to do,oughtn't he?/shouldn't he?
5)陈述部分有have to+v.(had to+v.),疑问部分常用don't+主语(didn't+主语)。
如:We have to get there at eight tomorrow, don't we?
6)陈述部分的谓语是usedto时,疑问部分用didn't+主语或usedn't+主语。
如:He used to take pictures there, didn't he?/usedn't he?
7)陈述部分有had better+v. 疑问句部分用hadn't you?
如:You'd better read it by yourself, hadn't you?
8)陈述部分有would rather+v.,疑问部分多用wouldn't+主语。
如:He would rather read it ten times than recite it, wouldn't he?
9)陈述部分有You'd like to+v.疑问部分用wouldn't+主语。
如:You'd like to go with me, wouldn't you?
10)陈述部分有must的疑问句,疑问部分根据实际情况而定。
如:He must be a doctor, isn't he?
You must have studied English for three years, haven't you?/didn't you?
He must have finished it yesterday, didn't he?
反意疑问句用法总结:
| 陈述部分的谓语 | 疑问部分 |
| I' | aren’t I |
| wish | may + 主语 |
| no, nothing, nobody, never, few, seldom, hardly, rarely, little等否定含义的词 | 肯定含义 |
| ought to(肯定的) | shouldn't/ oughtn't +主语 |
| have to+v.(had to+v.) | don't +主语(didn't +主语) |
| used to | didn't +主语或 usedn't +主语 |
| had better + v. | hadn't you |
| would rather + v. | wouldn't +主语 |
| you'd like to + v. | wouldn't +主语 |
| must | 根据实际情况而定 |
| 感叹句中 | be +主语 |
| neither…nor, either…or 连接的并列主语 | 根据其实际逻辑意义而定 |
| 指示代词或不定代词everything, that, nothing, this | 主语用it |
| 并列复合句 | 谓语根据邻近从句的谓语而定 |
| 定语从句,宾语从句的主从复合句 | 根据主句的谓语而定 |
| think, believe, expect, suppose, imagine等引导 | 与宾语从句相对应的从句 |
| everybody, anyone, somebody, nobody, no one | 复数they, 单数he |
|
情态动词dare或need dare, need 为实义动词 |
need (dare ) +主语 do +主语 |
|
省去主语的祈使句 Let's 开头的祈使句 |
will you?shall we? |
| there be | 相应的谓语动词+there(省略主语代词) |
| 否定前缀不能视为否定词 | 仍用否定形式 |
| must表"推测" | 根据其推测的情况来确定反意疑问句 |
反意疑问句特殊用法点拨:
1、感叹句中,疑问部分用be+主语。
如:What colours, aren't they?
What a smell, isn't it?
2、陈述部分由neither...nor, either...or 连接的并列主语时,疑问部分根据其实际逻辑意义而定。
如:Neither you nor I am engineer, are we?
3、陈述部分主语是指示代词或不定代词everything, that, nothing, this,疑问部分主语用it。
如:Everything is ready, isn't it?
4、陈述部分为主语从句或并列复合句,疑问部分有三种情况:
a.并列复合句疑问部分,谓语动词根据邻近从句的谓语而定。
如:Mr. Smith had been to Bei jing for several times, he should have been in China now, shouldn't he?
b.带有定语从句,宾语从句的主从复合句,疑问部分谓语根据主句的谓语而定。
如:He is not the man who gave us a talk, is he?
He said he wanted to visit Japan, didn't he?
c.上述部分主句谓语是think, believe, expect, suppose, imagine等引导的定语从句,疑问部分与宾语从句相对应构成反意疑问句。
如:I don't think he is bright, is he?
We believe she can do it better, can't she?
5、陈述部分主语是不定代词everybody, anyone, somebody, nobody, noone等,疑问部分常用复数they,有时也用单数he。
如:Everyone knows the answer, don't they?(doeshe?)
Nobody knows about it, do they?(doeshe?)
6、带情态动词dare或need的反意疑问句,疑问部分常用need(dare)+主语。
如:We need not do it again, need we?
He dare not say so,dare you? 当dare, need为实义动词时,疑问部分用助动词do+主语。
如:She doesn't dare to go home alone, does she?
7、省去主语的祈使句的反意疑问句,疑问部分用will you。
如:Don't do that again, will you?
Go with me, will you/won't you? 注意:Let's开头的祈使句,后用shall we? Let us开头的祈使句,后用will you?
如:Let's go and listen to the music, shall we?
Let us wait for you in the reading-room, will you?
8、陈述部分是"therebe"结构的,疑问部分用there省略主语代词。
如:There is something wrong with your watch, isn't there?
There will not be any trouble, will there?
9、否定前缀不能视为否定词,其反意疑问句仍用否定形式。
如:It is impossible, isn't it?
He is not unkind to his classmates, is he?
10、must在表"推测"时,根据其推测的情况来确定反意疑问句。
如:He must be there now, isn't he?
It must be going to rain tomorrow, won't it?
反意疑问句知识体系:
复合句的反意疑问句:
1、当陈述部分是一个(带that引导宾语从句的)主从复合句时,附加疑问句的主谓要和主句的主谓保持对应关系。但是,当陈述部分的主语是:I suppose, I think, I believe, I imagine, I expect等结构时,附加疑问句的主语和谓语要和从句的主语,谓语保持一致关系。而且要注意到否定的转移问题。
如:I think there is something wrong with the washer, isn't there?
We don't suppose he cares, does he?
2、当陈述部分是I'm sure that;we are sure;I'm afraid that;We are sure that;I feel sure that等后面跟宾语从句时,反意疑问句与后面的宾语从句一致。
3、当陈述部分是并列句时,附加疑问句的主谓语要和离它最近的句子的主谓保持对应关系。
如:We must redouble our efforts, or we'll not be able to catch up with the others, will we?
与“-The physics exam is not difficult, is it?-________. Even...”考查相似的试题有:
- Born in 1976 in Taiwan, Liu Qian found himself _____ to a magic toy in a shop when he was seven years old.A.attracti...
- The two elderly sisters, ____ so long, held each other.A.being separatedB.having been separatedC.to be separatedD...
- Many students, ________ some pocket money and social experience, work during their holidays.A.to getB.having gotC....
- All the staff in our company are considering _________ to the city center for the fashion show.A.to goB.to have gon...
- 11. Mrs. White found her husband surrounded by letters and papers and _________ very worriedA.lookedB.looksC.looki...
- There are many reasons for animals _____ but the most important one is the part _____ humans have played.[ ]A. die ou...
- _____ to get there before noon, the postman set off in spite of the heavy fog.A.PromisingB.To promiseC.Having prom...
- 34.Zhou Yang didn't want to let anyone overtake her.She wanted to be the first ______ that finishing line.A.cross...
- The film TROY is______worth______.A.well;being seeing B.well;seeingC.much;watching D.greatly;being watched
- Go straight into the cave and find out what's in it, ________?[ ]A. can't youB. don't youC. are youD. will you