本试题 “A warm thought suddenly ____ to me ____ I might use the pocket money to buy some flowers formy mother's birthday.[ ]A. occurred, ifB. crossed, when...” 主要考查您对动词
同位语从句
等考点的理解。关于这些考点您可以点击下面的选项卡查看详细档案。
- 动词
- 同位语从句
动词的定义:
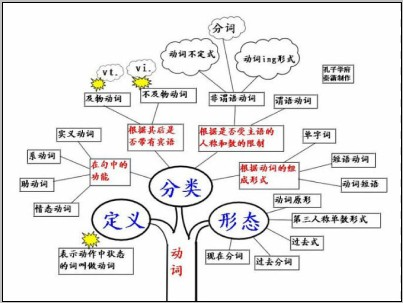
表示动作中状态的词叫做动词。根据其在句中的功能,动词可分为行为动词、系动词、助动词和情态动词四类,有些动词是兼类词。
例如:We have lunch at 12. (have是行为动词)
We have been to NewYork. (have是助动词)
I am hungry. (am是系动词)
You need not have waited for me. (need是情态动词)
The door needs painting. (need是兼类词)
动词的分类:
1)表示动作中状态的词叫做动词。
2)根据其在句中的功能,动词可分为四类,分别是:
实义动词(Notional Verb)、系动词(Link Verb)、助动词(Auxiliary Verb)、情态动词(Modal Verb)。
说明:有些情况下,有些动词是兼类词。
例如:We are having a meeting. 我们正在开会。(having是实义动词。)
He has gone to NewYork.他已去纽约。(has是助动词。)
3)动词根据其后是否带有宾语,可分为两类,分别是:
及物动词(Transitive Verb)、不及物动词(Intransitive Verb),缩写形式分别为vt.和vi.。
说明:同一动词有时可用作及物动词,有时可用作不及物动词。
例如:She can dance and sing. 她能唱歌又能跳舞。(sing在此用作不及物动词。)
She can sing many English songs. 她能唱好多首英文歌曲。(sing用作及物动词。)
4)根据是否受主语的人称和数的限制,可分两类,分别是:
限定动词(Finite Verb)、非限定动词(Non-finite Verb)。
例如:She sings very well. 她唱得很好。(sing受主语she的限制,故用第三人称单数形式sings。)
She wants to learn English well. 她想学好英语。(to learn不受主语she的限制,没有词形变化,是非限定动词。
说明:英语中共有三种非限定动词,分别是:动词不定式(Infinitive)、动名词(Gerund)、分词(Participle)。
5)根据动词的组成形式,可分为三类,分别是:
单字词(One-Word Verb)、短语动词(Phrasal Verb)、动词短语(Verbal Phrase)
例如:The English language contains many phrasal verbs and verbal phrases. 英语里有许多短语动词和动词短语。(contains是单字动词。)
Students should learn to look up new words in dictionaries. 学生们学会查字典。(look up是短语动词。)
The young ought to take care of the old. 年轻人应照料老人。(takecareof是动词短语。)
6)动词有五种形态,分别是:
原形(OriginalForm)、第三人称单数形式(Singular From in Third Personal)、过去式(Past Form)、过去分词(Past Participle)、现在分词(Present Participle)。
动词知识体系:
同位语从句的概念:
在复合句中充当同位语的名词性从句称为同位语从句。同位语从句是名词性从句(主语从句、表语从句、宾语从句、同位语从句)中的主要从句之一,从句作同位语表示与之同位的名词(短语)的实际内容,它的作用相当于名词,对前面的名词(短语)加以补充说明或进一步解释,相当于一个表语从句,它们之间的关系是同位关系,即主表关系。
同位语从句的用法:
1、同位语从句的引导:
词引导同位语从句的词语通常有连词that,whether,连接代词和连接副词等:
如:We heard the news that our team had won. 我们听到消息说我们队赢了。
They were worried over the fact that you were sick. 他们为你生病发愁。
I have no idea when he will come back. 我不知道他什么时候回来。
There is some doubt whether he will come. 他是否会来还不一定。
The question whether it is right or wrong depends on the result. 这个是对还是错要看结果。
注:whether可引导同位语从句,但if不能引导同位语从句。
2、同位语从句与定语从句的区别:
(1)意义的不同:
同位语从句是用于说明所修饰名词的具体内容的,它与被修饰词语通常可以划等号;而定语从句是限制所修饰名词的,它的作用是将所修饰的名词与其他类似的东西区别开来:
如:We are glad at the news that he will come. 听到他要来这个消息我们很高兴。
(news的内容就是that he will come,故that引导的是同位语从句)
We are glad at the news that he told us. 听到他告诉我们的这个消息我们很高兴。
(that从句是限制thenews的内容的,即我们高兴只是因为他告诉的这个news而不是其他的news,故that从句为定语从句)
(2)引导词的不同:
what, how, if, whatever等可引导名词性从句,但不引导定语从句。
(3)引导词的功能上的不同:
that引导同位语从句时,它不充当句子成分,而引导定语从句时,它作为关系代词,要么充当定语从句的主语,要么充当定语从句的宾语。
如上例that he told us中的that就充当told的宾语。
(4)被修饰词语的区别:
同位语从句所修饰的名词比较有限,通常有hope, wish, idea, news, fact, promise, opinion, suggestion, truth等,而定语从句所修饰的名词则非常广泛。
另外,when和where引导定语从句时,通常只修饰表示时间和地点的名词,而它们引导同位语从句时却不一定;又如why引导定语从句,它通常只修饰名词thereason,而它引导同位语从句时则不一定:
如:I have no idea when they will come. 我不知道他们什么时候来。(同位语从句)
I'll never forget the days when I lived there. 我永远不会忘记我住在那儿的日子。(定语从句)
We don't understand the problem why this is the best choice. 我们不明白这个问题,为什么这是最好的选择。(同位语从句)
There a son why he didn't come to the meeting is that he is ill. 他未能来开会,原因是他生病了。(定语从句)
同位语从句用法解析:
一、理解同位语从句的含义,把握同位语从句的实质:
在主从复合句中作同位语的从句称为同位语从句。同位语从句一般用that, whether, what, which, who, when, where, why, how等词引导,常放在fact, news, idea, truth, hope, problem, information, wish, promise, answer, evidence, report, explanation, suggestion, conclusion, word, possibility等抽象名词后面,说明该名词的具体内容。换言之,同位语从句和所修饰的名词在内容上为同一关系,对其内容作进一步说明。
例:The news that they had won the game soon spread over the whole school. 他们比赛获胜的消息很快传遍了整个学校。
析:they had won the game说明the news的全部内容,因此该句为同位语从句。
二、正确运用同位语从句的引导词,准确把握同位语从句:
1、如同位语从句意义完整,应用that引导同位语从句。(即that不充当任何成分,只起连接作用,不可省略)
例:The general gave the order that the soldiers should cross the river at once. 将军下达了战士们立即过河的命令。
析:the soldiers should cross the river at once是the order的全部内容,且意义完整,因此应用that引导同位语从句。
2、如同位语从句意义不完整,需增加"是否"的含义,应用whether引导同位语从句。(if不能引导同位语从句)
例:We'll discuss the problem whether the sports meeting will be held on time. 我们将讨论运动会是否会如期举行的问题。
析:the sports meeting will be held on time 意义不完整,应加“是否”的含义才能表达the problem的全部内容,因此应用whether引导同位语从句。
3、如同位语从句意义不完整,需增加"什么时候"、"什么地点"、"什么方式"等含义,应用when, where, how等词引导同位语从句。
例1:I have no idea when he will be back.
析:he will be back 意义不完整,应加"什么时候"的含义才能表达idea的全部内容,因此应用when引导同位语从句。
例2:I have no impression how he went home, perhaps by bike.
析:he went home 意义不完整,应加"如何"的含义才能表达impression的全部内容,因此应用how引导同位语从句。
4、当主句的谓语较短,而同位语从句较长时,同位语从句常后置。
如:The thought came to him that may be the enemy had fled the city.
与“A warm thought suddenly ____ to me ____ I might use the p...”考查相似的试题有:
- Everyone should learn something about first aid, because every second ____ in an emergency.[ ]A. urgesB. costsC. need...
- The attack by terrorists has been _________by the entire world.[ ]A. condemnedB. scoldedC. criticizedD. blamed
- I wonder how it ____ that Chinese climbers successfully finished the torch relay on the Mount Qomolangma, where the a...
- As the famous saying _____, two heads are better than one.A. mentionsB. goesC. tellsD. instructs
- In order to ___ consumers, it’s extremely important to consider what information should be included in the advertisem...
- Don’t _____me. What I really mean is that he is smart and can deal with each situation well.A. believeB. refuseC. mis...
- He was born and________up in this town,________he left at the age of 16.[ ]A.grew;whereB.grew;whichC.brought;w...
- The way ______ was thought of by him ______ the experiment was similar to the way _____ you carried it out.A.that, d...
- Many people wrote articles on ___Liu Xiang had failed to compete in the event ..A.whyB.whatC.whoD.that
- Evidence has been piled up ______ drinking water before breakfast is good for our health.[ ]A. whatB. whichC. ifD. that