本试题 “短文改错。此题要求改正所给短文中的错误。对标题号的每一行做出判断;如有错误(每行只有一个错误),则按下列情况改正:此行多一个词:把多余的词用斜线(...” 主要考查您对可数名词及其单复数
人称代词
反身代词
副词
介词和介词短语
并列连词
过去完成时
状语从句
等考点的理解。关于这些考点您可以点击下面的选项卡查看详细档案。
- 可数名词及其单复数
- 人称代词
- 反身代词
- 副词
- 介词和介词短语
- 并列连词
- 过去完成时
- 状语从句
可数名词:
是指能以数目来计算,可以分成个体的人或东西;因此它有复数形式,当它的复数形式在句子中作主语时,句子的谓语也应用复数形式。
可数名词复数的规则变化:
| 情况 | 构成方法 | 读音 | 例词 |
| 一般情况 | 加 –s | 1.清辅音后读/s/; 2.浊辅音和元音后读/z/; |
map-maps bag-bags car-cars |
| 以s,sh,ch,x等结尾的词 | 加 -es | 读 /iz/ | bus-buses watch-watches |
| 以ce,se,ze,(d)ge等结尾 的词 |
加 -s | 读 /iz/ | license-licenses |
| 以辅音字母+y结尾的词 | 变y 为i再加es | 读 /z/ | baby-babies |
1)以y 结尾的专有名词,或元音字母+y结尾的名词变复数时,直接加s变复数:
如:two Marys the Henrys monkey---monkeys holiday---holidays
比较:层楼:storey---storeys story---stories
2)以o 结尾的名词,变复数时:
a. 加s,如: photo---photos piano---pianos
b. 加es,如:potato--potatoes tomato--tomatoes
c. 均可,如:zero---zeros / zeroes
3)以f或fe 结尾的名词变复数时:
a. 加s,如: belief---beliefs roof---roofs safe---safes gulf---gulfs;
b. 去f, fe 加ves,如:half---halves knife---knives leaf---leaves wolf---wolves wife---wives life---lives thief---thieves;
c. 均可,如:handkerchief: handkerchiefs / handkerchieves
可数名词复数的不规则变化:
1)child---children foot---feet tooth---teeth mouse---mice man---men woman---women
注意:与 man 和 woman构成的合成词,其复数形式也是 -men 和-women。
如:an Englishman,two Englishmen. 但German不是合成词,故复数形式为Germans;Bowman是姓,其复数是the Bowmans。
2)单复同形 如:
deer,sheep,fish,Chinese,Japanese
li,jin,yuan,two li,three mu,four jin
但除人民币元、角、分外,美元、英镑、法郎等都有复数形式。如:
a dollar, two dollars; a meter, two meters
3)集体名词,以单数形式出现,但实为复数。
如:staff people police cattle 等本身就是复数,不能说a staff a people,a police,a cattle,
但可以说a person,a policeman,a head of cattle, the English,the British,the French,the Chinese,the
Japanese, the Swiss 等名词,表示国民总称时,作复数用。
如:The Chinese are industries and brave. 中国人民是勤劳勇敢的。
4)以s 结尾,仍为单数的名词,如:
a. maths,politics,physics等学科名词,为不可数名词,是单数。
b. news 是不可数名词。
c. the United States,the United Nations 应视为单数。
The United Nations was organized in 1945. 联合国是1945年组建起来的。
d. 以复数形式出现的书名,剧名,报纸,杂志名,也可视为单数。
"The Arabian Nights" is a very interesting story-book.
<<一千零一夜>>是一本非常有趣的故事书。
5) 表示由两部分构成的东西,如:glasses (眼镜) trousers, clothes ;
若表达具体数目,要借助数量词 pair(对,双); suit(套); a pair of glasses; two pairs of trousers
6)另外还有一些名词,其复数形式有时可表示特别意思,如:goods货物,waters水域,fishes(各种)鱼
复合名词的复数形式:
名词作定语名词作定语一般用单数,但也有以下例外。
1)用复数作定语。
如:sports meeting 运动会
students reading-room 学生阅览室
talks table 谈判桌
the foreign languages department 外语系
2)man, woman, gentleman等作定语时,其单复数以所修饰的名词的单复数而定。
如:men workers
women teachers
gentlemen officials
3)有些原有s结尾的名词,作定语时,s保留。
如:goods train (货车)
arms produce 武器生产
customs papers 海关文件
clothes brush衣刷
4)数词+名词作定语时,这个名词一般保留单数形式。
如:two-dozen eggs 两打/(二十四个鸡蛋)
a ten-mile walk 十里路
two-hundred trees 两百棵树
a five-year plan 一个五年计划
可数名词单复数知识体系:

不同国籍人的单复数:
国籍
总称(谓语用复数)
单数
复数
中国人
the Chinese
a Chinese
two Chinese
瑞士人
the Swiss
a Swiss
two Swiss
澳大利亚人
the Australians
an Australian
two Australians
俄国人
the Russians
a Russian
two Russians
意大利人
the Italians
an Italian
two Italians
希腊人
the Greek
a Greek
two Greeks
法国人
the French
a Frenchman
two Frenchmen
日本人
the Japanese
a Japanese
two Japanese
美国人
the Americans
an American
two Americans
印度人
the Indians
an Indian
two Indians
加拿大人
the Canadians
a Canadian
two Canadians
德国人
the Germans
a German
two Germans
英国人
the English
an Englishman
two Englishmen
瑞典人
the Swedish
a Swede
two Swedes
人称代词的概念:
人称代词是替代我、你、他、她、它、我们、你们、他们、她们、它们等人称的词。
人称代词分为主格和宾格形式,并有人称的单复数形式。按所替代人称的不同分为第一人称、第二人称和第三人称。
人称代词的用法:
人称代词在句中可以用作主语(用主格,如:I,you,he,she,we,they,等)和宾语(用宾格,如 me,you,him,her,us,them等)
如:He loves her, but she hates him. 他爱她,但她却讨厌他。
注:(1)在口语中,当人称代词用作表语、用于than, as之后或用于强调句中被强调时,可以用语。 例如:
"Who is it?" "It's me."“是谁呀?”“是我。”
He sings better than me. 他比我唱得好。
He is as tall as her. 他和她一样高。
It's me who did it. 这是我干的。但是,若than,as后的人称代词后跟有动词,则必须用主格。例如:
He sings better than I do./ He is as tall as she is.
(2)单独使用的人称代词通常用宾格。
"I' m tired.""Me too."“我累了。”“我也累了。”
"Who wants this?" "Me."“谁要这个?”“我要。”
(3)有时用主格或宾格会导致意思的变化。
I like you better than he. 我比他更喜欢你。为 I like you better than he likes you. 之略。
I like you better than him. 我喜欢你胜过喜欢他。为 I like you better than he likes him. 之略。
人称代词主格、宾格、人称、单复数对比:
|
人称代词 |
单数 |
复数 | ||
|
主格 |
宾格 |
主格 |
宾格 | |
|
第一人称 |
I |
me |
we |
us |
|
第二人称 |
you |
you |
you |
you |
|
第三人称 |
he |
him |
they |
them |
|
she |
her |
them | ||
|
it |
it | |||
人称代词的排序:
人称代词的排列顺序为:单数人称代词通常按“二三一”排列,即you, he and I;复数人称代词通常按“一二三”排列,即we, you and they:
You, he and I are of the same age. 你,他和我都是同一年龄。
We, you and they are all good citizens. 我们,你们和他们都是好公民。
但若是用于承担责任或错误等场合,则可把第一人称I置于其他人称代词之前:
I and Tom are to blame. 我和汤姆该受批评。
比较:Tom and I hope to go there. 汤姆和我想去那儿。
注意:you and I 是固定结构,语序通常不宜颠倒。
人称代词知识体系:
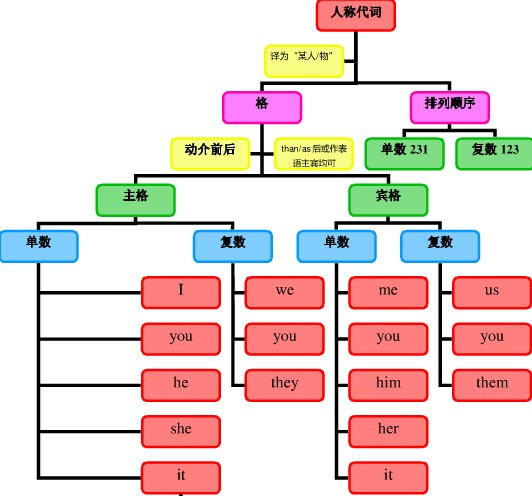
人称代词用法拓展:
1、在通常情况下,人称代词在句子中出现在它所代替的名词之后,即先出现名词,再出现相应的代词。但是,在书面语中,有时也可出现代词,后出现代词所代替的名词。
As soon as it had hopped off, the plane picked up speed.飞机刚一起飞,就加了速。
(比较:As soon as the plane had hopped off, it picked up speed.)
2、人称代词后跟名词同位语。有些人称代词后有时可跟同位语。
These small desks are forus students.这些小课桌是给我们学生的。
We girls often go to the movies together.我们女孩子常一起去看电影。
He asked you boys to be quiet.他要你们男孩子安静些。
反身代词的定义:
反身代词是一种表示反射或强调的代词。它的基本含义是:
通过反身代词指代主语,使施动者把动作在形式上反射到施动者自己。因此,反身代词与它所指代的名词或代词形成互指关系,在人称、性别、数上保持一致。
反身代词的句法功能:
(1)用作同位语(加强被修饰词的语气,紧放在被修饰名词后,或句末):
如:The box itself is not so heavy.箱子本身并不重。
You yourself said so./ You said so yourself. 你自己是这样说的。
(2)用作宾语(动词或介词的宾语):
Take good care of yourself. 照顾好自己。
She could not make herself understood. 她不能使别人听懂她的话。
(3)用作表语:
The poor boy was myself. 那个可怜的孩子就是我自己。
The ones who really want it are ourselves. 真正想要它的是我们自己。
有时用于be, feel, seem, look 等后作表语表示身体或精神处于正常状态:
I'm not quite myself these days. 我近来身体不大舒服。
I'll be myself again in no time.我过一会儿就会好的。
(4)用作主语:
在现代英语中,反身代词一般不能独立用作主语,但是它却可以借助and,or,nor等连词与其他名词一起构成并列主语(且位于并列主语的后部),以及用于某些特殊结构(如as...as等):
My brother and myself went there yesterday.昨天我兄弟和我一起去了那儿。
Jim's sister and himself get up at six everyday.吉姆的妹妹和他每天6点起床。
He was as anxious as myself. 他和我一样担心。
反身代词人称、单复数对比:
|
|
单数 |
复数 |
|
第一人称 |
myself |
ourselves |
|
第二人称 |
yourself |
yourselves |
|
第三人称 |
himself |
themselves |
|
herself |
themselves | |
|
itself |
themselves |
反身代词的基本形式:
反身代词是oneself 根据所指词的人称、性别、单复数等的变化可以有myself, himself, herself, yourself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves 等形式。
oneself 与 himself:
当one指人时,其相应的反身代词通常用oneself,在美国英语中也可用 himself:One should not praise oneself[himself].一个人不应该自吹自擂。
反身代词知识体系:
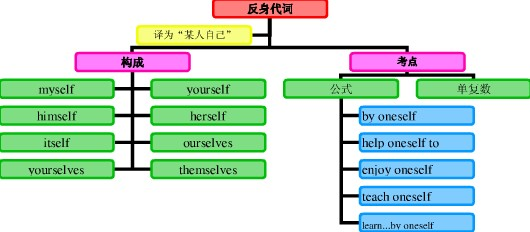
反身代词用法拓展:
1、反身代词不能做主语,但可作主语同位语,放在主语后或句末。
错:Myself went to the cinema.
对:I went to the cinema myself.
2、反身代词可以作宾语的同位语。如:You can go and ask John himself. 你可以去问约翰本人。
3、反身代词可以作介词的宾语,如:by oneself 全靠自己
She learnt swimming all by herself. 她是自学游泳的。
She said to herself,"Who am I?" 她自言自语的说:“我是谁?”
4、反身代词作动词的宾语。如:enjoy oneself 玩得高兴;help oneself (to) 随便用..... hurt oneself 伤害自己;
teach oneself 自学;get dressed oneself 自己穿衣。
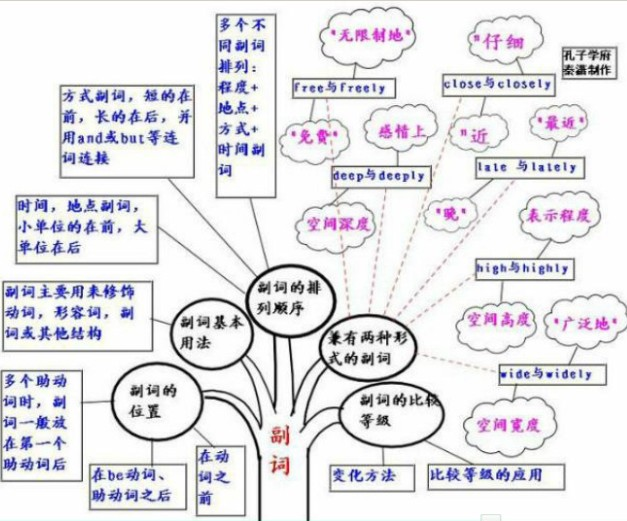
副词的概念:
副词是指在句子中表示行为或状态特征的词,用来修饰动词、形容词、其他副词、介词短语、非谓语动词乃至整个句子,表示时间、地点、程度、方式等概念。
副词的位置:
1)在动词之前。
2)在be动词、助动词之后。
3)多个助动词时,副词一般放在第一个助动词后。
注意:
a. 大多数方式副词位于句尾,但宾语过长,副词可以提前,以使句子平衡。
如:We could see very clearly a strange light ahead of us.
b. 方式副词well,badly糟、坏,hard等只放在句尾。
如:He speaks English well.
副词的排列顺序:
1)时间,地点副词,小单位的在前,大单位在后。
2)方式副词,短的在前,长的在后,并用and或but等连词连接。
如:Please write slowly and carefully.
3)多个不同副词排列:程度+地点+方式+时间副词。
注意:副词very可以修饰形容词,但不能修饰动词。
改错:(错)I very like English.
(对)I like English very much.
注意:副词enough要放在形容词的后面,形容词enough放在名词前后都可。
如:I don't know him well enough.
There is enough food for everyone to eat.
There is food enough for everyone to eat.
兼有两种形式的副词:
1)close与closely:
close意思是“近”;closely意思是“仔细地”。
如: He is sitting close to me.
Watch him closely.
2)late与lately:
late意思是"晚";lately意思是“最近” 。
如:You have come too late.
What have you been doing lately?
3)deep与deeply:
deep意思是“深”,表示空间深度;deeply时常表示感情上的深度,“深深地” 。
如:He pushed the stick deep into the mud.
Even father was deeply moved by the film.
4)high与highly:
high表示空间高度;highly表示程度,相当于much。
如:The plane was flying high.
I think highly of your opinion.
5)wide与widely:
wide表示空间宽度;widely意思是“广泛地”,“在许多地方”。
如:He opened the door wide.
English is widely used in the world.
6)free与freely:
free的意思是“免费”;freely的意思是“无限制地”。
如:You can eat free in my restaurant whenever you like.
You may speak freely, say what you like.
副词知识体系:
介词和介词短语的概念:
介词是一种用来表示词与词、词与句之间的关系的虚词,在句中不能单独作句子成分。介词后面一般有名词、代词或相当于名词的其他词类,短语或从句作它的宾语。介词和它的宾语构成介词词组,在句中作状语,表语,补语或介词宾语。介词可以分为时间介词、地点介词、方式介词和其他介词。
误用介词的三种情况:
1、多用介词:
多用介词可能是受汉语意思的影响将及物动词误用作不及物动词,也可能是受相关结构的影响而用错:
误:We discussed about the plan.
正:We discussed the plan. 我们讨论了计划。
误:Did he mention about the accident?
正:Did he mention the accident? 他提到那次事故了吗?
误:I saw her enter into the bank.
正:I saw her enter the bank. 我看见她进了银行。
误:He married with[to] a nurse.
正:He married a nurse. 他同一位护士结了婚。
误:How can contact with you?
正:How can contact you? 我怎么与你联系?
误:We should serve for the people heart and soul.
正:We should serve the people heart and soul. 我们应该全心全意地为人民服务。
误:Who controls over the factory? (但名词control可接over)
正:Who controls the factory? 谁管理这个工厂?
误:He has a great many of friends here. (比较a great number of)
正:He has a great many friends here. 他在这儿有很多朋友。
2、漏用介词:
漏用介词可能是受汉语意思的影响将不及物动词误用作及物动词,或是受相关结构的影响的影响而用错等:
误:This matter is difficult to deal. (deal with=处理)
正:This matter is difficult to deal with. 这事很难处理。
误:He is not a man to be depended.
正:He is not a man to be depended on. 他不是个可靠的人。
误:He took a cup of tea, and went on the story.
正:He took a cup of tea, and wentonwiththestory.他喝了一口茶,又接着讲故事。
误:My mother still regards me a child. (比较consider…as中的as可省略)
正:My mother still regards me as a child. 我母亲还把我当小孩看。
误:They insisted sending a car over to fetch us.
正:They insisted on sending a car over to fetch us.他们坚持要派车来接我们。
误:What he says is worth listening.
正:What he said is worth listening to.他的话值得一听。
3、错用介词:
错用介词的情况比较复杂,可能是因受汉语意思的而错,也可能是因弄不清搭配关系而错,可能是混淆用法而错,也可能是受相关结构的影响而错,可能是忽略语境而错,也可能是想当然的用错:
误:She called on his office yesterday. (call on+人,call at+地点)
正:She called at his office yesterday. 她昨天去了他办公室拜访。
误:He is engaged with a nurse.
正:He is engaged to a nurse.他与一位护士订了婚。
误:The sun rises from the east.
正:The sun rises in the east.太阳从东方升起。
误:Under his help, I finished it in time.
正:With his help, I finished it in time. 在他的帮助下,我及时做完了。
误:During he was in Japan, he visited many places.
正:During his stay in Japan, he visited many places.他在日本期间,参观过许多地方。
误:We are familiar to his character.
正:We are familiar with his character.我们了解他的性格。
误:Help yourself with the fruit.
正:Help yourself to the fruit.吃点水果吧。
介词的宾语:
1、名词或代词作介词宾语:
如:Are you interested in history? 你对历史感兴趣吗?
Don't worry about it. 别为它担心。
注:若是人称代词用作介词宾语,要注意用宾格。
如:No one can sing like her. 没有人能像她那样唱歌。(不能用like she)
2、动名词作介词宾语:
如:He is good at telling stories. 他善于讲故事。
In crossing the street he was run over. 他在穿过马路时被汽车撞倒。
3、过去分词作介词宾语:
如:We can't regard the matter as settled. 我们不能认为这事已经解决。
I take it for granted you have read the book. 我以为你读过这本书。
注:过去分词用作介词宾语通常只见于某些固定结构中,如上面第1句涉及regard…as(认为…是)结构,第2句涉及take sth for granted(认为某事属实)。在其他情况下,介词后通常不直接跟过去分词作宾语,若语义上需要接过去分词(表被动),可换用“being+过去分词”:
如:He went out without being seen by the others.他出去了,没有被其他人看见。
4、从句作介词宾语:
如:He was not satisfied with what she said. 他对她说的不满意。
I'm worried about where he is. 我担心他上哪儿去了。
注:介词后通常不接that从句,遇此情况需考虑用其他结构:
误:He paid no attention to that she was poor.
正:He paid no attention to the fact that she was poor. 他根本不注意她很穷这一事实。
但有个别介词(如except)可接that从句。
比较:I know nothing about him except that he lives next door./I know nothing about him except for the fact that he lives next door. 我只知道他住在隔壁,其它的就不知道了。
5、不定式作介词宾语:
如:I had no choice but to wait. 除了等,我没有别的选择。
He wanted nothing but to stay there. 他只想留在那儿。
They did nothing but complain. 他们老是一个劲地抱怨。
He never did anything but watch TV. 除了看电视,他从不干任何事。
注:(1)介词后接不定式的情形通常只见于but, except等极个别个词。该不定式有时带to,有时不带to,其区别是:若其前出现了动词do,其后的不定式通常不带to;
若其前没有出现动词do,则其后的不定式通常带to。
(2)介词后虽然通常不直接跟不定式作宾语,但却可接“连接代词(副词)+不定式”结构:
如:He gave me some advice on how to do it. 对于如何做这事他给我提了些建议。
6、形容词作介词宾语:
如:Her pronunciation is far from perfect. 她的语音远不是完美的。
In short, we must be prepared. 总而言之,我们要有准备。
Things have gone from bad to worse. 事情越来越糟。
注:(1)有些形容词用作介词宾语可视为其前省略了动名词being:
如:He regarded the situationas(being) serious. 他认为形势严重。
His work is far from(being) satisfactory. 他的工作丝毫不令人满意。
(2)有些“介词+形容词”的结构已构成固定搭配:in full全部地,全面地,无省略地; in private私下地,秘密地; in particular特别地;in general一般地,通常地,概括地; in brief 简言之;in short总之,简言之; in vain徒然地,徒劳无益地;for fee免费地,无偿地; for certain肯定地,确切地;for sure肯定地,确切地; for short为了简短,简称;atl arge自由自在地,逍遥法外; by far…得多
7、副词作介词宾语:
如:I can't stay for long. 我不能久呆。
It's too hot in here. 这里面太热了。
I looked every where except there. 除了那儿,我到处都看过了。
8、数词作介词宾语:
如:The city has a population of four million. 这座城市有四百万人口。
He was among the first to arrive. 他是第一批到的。
9、介词短语作介词宾语:
如:Choose a book from among these. 从这些书中选一本吧。
I saw her from across the street. 我从街的对面望见了她。
注:通常可后接介词短语作宾语的介词是from, till, until, since, except, instead of等。
比较:I took it from the bed. 我从床那儿(或床上)拿的。
I took it from under the bed. 我从床下拿的。
10、复合结构用作介词宾语:
如:She had no objection to Mary marrying him. 她不反对玛丽与他结婚。
She came in with a book in her hand. 她手里拿着一本书走了进来。
All the afternoon he worked with the door locked. 整个下午他都锁着门在房里工作。
介词短语的句法功能:
1、表语:
如:He was with a friend. 他和一个朋友在一起。
Health is above wealth. 健康胜过财富。
This knife is for cutting bread. 这把小刀是用于切面包的。
注:有些介词(如because of)引出的短语通常只用作状语,不用作表语:
误:His absence is because of the rain.
正:His absence is due to the rain. 他因雨未来。
但是,若主语是代词(不是名词),becauseof引出的短语可用作表语:
如:It is because of hard work. 那是因为辛苦工作的原因。
2、状语:
如:Don't touch it with your hands. 别用手去摸它。
Did you do this by design or by accident? 你这样做是有意的还是无意的?
3、定语:
如:This is his reply to your letter. 这是他给你的回信。
This is the best way of doing it. 这是做此事最好的方法。
My love for you is deeper than the sea. 我对你的爱比海深。
4、宾语补足语:
如:I found everythingin good condition. 我发现一切正常。
Her illness kept her in bed for a week. 她因生病在床上躺了一星期。
注:用作宾语补足语的介词短语在相应的被动语态中则为主语补足语:
如:He was regarded as a hero. 他被看成是英雄。
5、宾语:
如:A man stepped out from behind the wall. 一个人从墙后走出来。
He cannot spare anytime except on Sunday. 除星期日外,他抽不出时间。
6、主语:
如:Between6 and 7 suits me. 六点到七点对我比较适合。
After the exams is the time to relax. 考试后是轻松一下的时间。
注:介词短语通常不用作主语,尽管有时也像上面这样用作主语,但通常可视为是在一定的上下文中有所省略:
如:—When are we going to have the next meeting? 我们下次什么时候见面?
—On Tuesday may be convenient. 星期二可能比较方便。
此句中onTuesday虽用作主语,但可视为是其前省略了meeting一词:
即:Meeting during the vacation may be convenient.
并列连词的概念:
连词是一种虚词,它不能独立担任句子成分而只起连接词与词,短语与短语以及句与句的作用。连词主要可分为两类:并列连词和从属连词。并列连词用来连接平行的词、词组和分句。如:and, but, or, nor, so, therefore, yet, however, for, hence, as well as, both...and, notonly...butalso, either...or, neither...nor, (and)then 等等。
并列连词与并列结构:
并列连词引导两个并列的句子。
1)and与or:
判断改错:
(错) They sat down and talk about something.
(错) They started to dance and sang.
(错) I saw two men sitting behind and whisper there.
(对) They sat down and talked about something.
(对) They started to dance and sing.
(对) I saw two men sitting behind and whispering there.
解析:第一句:and连接两个并列的谓语,所以talk应改为talked。
第二句:and连接两个并列的动词不定式,第二个不定式往往省略to,因此sang应改为sing。
第三句:and连接感观动词saw后面的用作的宾补的两个并列分词结构,因此whisper应改为whispering。
注意:and还可以和祈使句或名词词组连用表示条件。(or也有此用法)
如:Make up your mind, and you'll get the chance.=If you make up your mind, you'll get the chance.
One more effort, and you'll succeed.=If you make one more effort, you'll succeed.
2)both...and 两者都
如:She plays(both) the piano and the guitar.
3)not only...but(also), as well as 不但…而且
如:She plays not only the piano, but(also) the guitar.
注意:not only…but also关联两个分句时,一个分句因有否定词not而必须倒装。
如:Not only does he like reading stories, but also he can even write some.
4)neither...nor 意思为“既不……也不……”谓语动词采用就近原则,与nor后的词保持一致。
如:Neither you nor he is to blame.
比较so和such :
so与such的用法由不同词性决定。such是形容词,修饰名词或名词词组,so是副词,只能修饰形容词或副词。so还可与表示数量的形容词many,few,much,little连用,形成固定搭配。
构成:so+adj.
such+a(n)+n.
so+adj.+a(n)+n.
such+n.(pl.)
so+adj.+n.(pl.)
such+n.(pl.)
so+adj.+n.[不可数]
such+n.[不可数]
如:so foolish
such a fool
so nice a flower
such a nice flower
so many/few flowers
such nice flowers
so much/ little money.
such rapid progress
so many people
such a lot of people
注:so many 已成固定搭配,a lot of 虽相当于many,但a lot of为名词性的,只能用such搭配。 so...that与such...that之间的转换既为so与such之间的转换。
并列连词用法点拨:
1、表示并列关系:
1)or意思为“否则”。
如:I must work hard, or I'll fail in the exam.
2)either...or意思为“或者……或者……”。注意谓语动词采用就近原则。
如:Either you or I am right.
2、表示转折或对比关系:
1)but表示转折,while表示对比。
如:Some people love cats, while others hate them.
典型例题:
—Would you like to come to dinner tonight?
—I'd like to, ___ I'm too busy.
A. and
B. so
C. as
D. but
答案:D。but与前面形成转折,符合语意。而表并列的and,结果的so,原因的as都不符合句意。
2)not...but...意思为“不是……而是……” not和but后面的用词要遵循一致原则。
如:They were not the bones of an animal, but(the bones) of a human being.
3、表示原因关系:
1)for 判断改错:
(错)For he is ill, he is absent today.
(对)He is absent today, for he is ill. for是并列连词,不能置于含两个并列分句的句子的句首,只能将其放在两个分句中间。
并列连词知识体系:
| 种类 | 用法 | 举例 |
| 并列连词 | 表示转折关系 | yet, but等 |
| 表示并列关系 | and, or, either...or..., as welll as等 | |
| 表示因果关系 | for, so等 |
比较and和or的用法:
1)并列结构中,or通常用于否定句,and用于肯定句。
2)但有时and也可用于否定句。请注意其不同特点:
如:There is no air or water in the moon.
There is no air and no water on the moon.
在否定中并列结构用or连接,但含有两个否定词的句子实际被看作是肯定结构,因此要用and。
典型例题:
—I don't like chicken___fish.
—I don't like chicken, ___I like fish very much.
A. and;and
B. and;but
C. or;but
D. or;and
答案:C。否定句中表并列用or,but表转折。
判断改错:
(错)We will die without air and water.
(错)We can't live without air or water.
(对)We will die without air or water.
(对)We can't live without air and water.
过去完成时的概念:
过去完成时既可表示过去某个时间或动作之前所发生的事情,也可表示过去某个时间或动作之 前所发生的动作一直持续到过去某个时间。过去完成时由“had+过去分词”构成。
如:She had leant 2000 English words by the end of last month.
过去完成时的应用:
(1)与过去完成时连用的时间状语可以多种多样,使用它的主要依据是看其是否发生在“过去的过去”。
如:He had learnt some English before I went here. 在来这儿之前我学过一些英语。
He had written three stories by last year.到去年他已经写了三篇故事。
We had cleaned the room when he got there. 当他到那儿时,我们已经把房子弄干净了。
He went there after he had finished his work. 他把事做完之后,就去哪儿了。
注意:当主句跟由before, after, as soon as所引导的时间从句的动作连接很紧密时,从句也可用一般过去时。
如:He went there after he read the letter. 他看了那封信后就去那儿了。
(2)过去完成时还经常用于主句为过去时的宾语从句中。
如:He said he had been a soldier. 他说他当过兵。
They said they had seen the film. 他们说这幕电影他们看过。
(3)在hardly/scarcely…when…,nosooner…than…两个结构中的主句通常要用过去完成时。
如:Hardly had I told her the news when she began to cry out. 她一听到这一消息就大哭了起来。
Scarcely had he finished his supper when he went out. 他已吃完晚饭就出去了。
No sooner had he fallen asleep than he lay down on the bed. 他一躺倒床上就睡着了。
(4)动词expect, hope, suppose, think, want等的过去完成时可用来表示未实现的计划、打算或希望。
如:I had hoped to see you. 我本希望来看你。
He had wanted to buy a house in Beijing. 他本想在北京买栋房子。
过去完成时与一般过去时:
(1)过去完成时表示以过去某时间为起点以前所发生的动作或存在的状态,即:过去完成时强调“过去的过去”,而一般过去时只表示以现在时间为起点以前所发生的事情或存在的状态。
如:He studied there two years ago. 他在那儿学习了两年。(离现在两年)
He said he had studied there two years ago. 他说他在那儿学习了两年。(离他说话时两年)
(2)表示过去某个时间以前所连续发生的两个或两个以上的动作时,一般用and, then, but按照动作的先后顺序连接,此时通常用一般过去时而不用过去完成时。
如:He said he went the shop and bought some food. 他说他去商店买了一些食品。
(3)两个动作相继发生,可用一般过去时;如第一个动作需要若干时间完成,用过去完成时。
如:When I heard the news, I was very excited.
(4)叙述历史事实,可不用过去完成时,而只用一般过去时。
如:Our teacher told us that Columbus discovered America in1492.
状语从句的概念:
状语从句指句子用作状语时,起副词作用的句子。它可以修饰谓语、非谓语动词、定语、状语或整个句子。根据其作用可分为时间、地点、原因、条件、目的、结果、让步、方式和比较等从句。状语从句一般由连词(从属连词)引导,也可以由词组引起。从句位于句首或句中时通常用逗号与主句隔开,位于句尾时可以不用逗号隔开。
比较while/as/when:
1、as/when引导短暂性动作的动词例句:
如:Just as/Just when/When I stopped my car, a man came up to me.
2、当从句的动作发生于主句动作之前,只能用when引导这个从句,不可用as或while。
如:When you have finished your work, you may have a rest.
3、从句表示“随时间推移”连词能用as,不用when或while。
如:As the day went on, the weather got worse.
比较untill/till:
两个连词意义相同,肯定形式表示的意思是“做某事直至某时”,动词必须是延续性的。否定形式表达的意思是“直至某时才做某事”,动词为延续性或非延续性都可以。
正确使用这两个连词的关键之一就在于判断句中的动词该用肯定式还是否定式。
肯定句例句:I slept until midnight. 我一直睡到半夜时醒了。
Wait till I call you. 等着我叫你。
注意:在肯定句中可用before代替:Let's get in the wheat before the sunsets.
否定句例句:She didn't arrive until 6o'clock.
I didn't manage to do it until you had explained how.
1、Until可用于句首,而till通常不用于句首。
例句:Until you told me, I had heard nothing of what happened.
2、Untilwhen疑问句中,until要放在句首。
例句:Until when are you staying? 你呆到什么时候?
注意:否定句可用另外两种句式表示。
1)Not until…在句首,主句用倒装。
例句:Not until the early years of the19th century did man know what heat is.
2)It is not until…that…
状语从句的用种类:
1、时间状语从句:
表示时间的状语从句可由when, as, while, whenever, after, before, till(until), since, once, as soon as(或the moment), by the time, no sooner…than, hardly(scarcely)… when, everytime等引导。
e.g. When I came into the office, the teachers were having a meeting.
He started as soon as he received the news.
Once you see him, you will never forget him.
No sooner had I gone to bed than I went to sleep.
2、原因状语从句:
原因状语从句是表示原因或理由的,引导这类从句的最常用的连词是because, since, as, nowthat(既然)等,for表示因果关系时(它引导的不是从句)为并列连词,语气不如because强。 e.g. He is disappointed because he didn't get the position.
As it is raining, I will not go out.
Now that you mention it, I do remember.
3、地点状语从句:
引导地点状语从句的连词是where和wherever等。
e.g. Sit wherever you like.
Make a mark where you have a question.
4、目的状语从句:
引导目的状语从句最常用的词(组)是so, so that(从句谓语常有情态动词), in order that, in case(以防,以免)等。
e.g. Speak clearly, so that they may understand you.
She has bought the book in order that she could follow the TV lessons.
He left early in case he should miss the train.
5、结果状语从句:
结果状语从句是表示事态结果的从句,通常主句是原因,从句是结果。由so that(从句谓语一般没有情态动词),so…that, such…that等引导。
e.g. She was ill, so that she didn't attend the meeting.
He was so excited that he could not say a word.
She is such a good teacher that everyone admires her.
6、条件状语从句:
条件状语从句分真实性(有可能实现的事情)与非真实性(条件与事实相反或者在说话者看来不大可能实现的事情)条件句。
引导条件状语从句的词(组)主要有if, unless, so(as)long as, on condition that, so(as) far as, if only(=if)。
注意:条件从句中的if不能用whether替换。
e.g. If he is not in the office, he must be out for lunch.
You may borrow the book so long as you keep it clean.
So far as I know(据我所知), he will be away for three months.
You can go swimming on condition that(=if) you don't go too far away from the river bank.
If he had come a few minutes earlier, he could have seen her.
7、让步状语从句:
让步状语从句可由although, though, as, even if(though), however, whatever, whether…or, no matter who(when, what,…)等引导。
注意:as引导的让步状语从句一般是倒装的。
e.g. Though he is a child, he knows a lot.
Child a she is, he knows a lot.
Whatever(=No matter what) you say, I'll never change my mind.
8、方式状语从句:
方式状语从句常由as, as if(though), the way, rather than等引导。
e.g.You must do the exercise as I show you.
He acted as if nothing had happened.
9、比较状语从句:
比较状语从句常用than, so(as)…as, the more…the more等引导。
e.g. I have made a lot more mistakes than you have.
He smokes cigarettes as expensive as he can afford.
The busier he is, the happier he feels.
使用状语从句时要注意的几个问题:
1、在时间和条件(有时也在方式、让步等)从句中,主句是一般将来时,从句通常用一般现在时表示将来。
e.g. We'll go outing if it doesn't rain tomorrow.
I'll write to you as soon as I get to Shanghai.
2、有些时间、地点、条件、方式或让步从句,如果从句的主语与主句主语一致(或虽不一致,是it),从句的谓语又包含动词be,就可省略从句中的“主语+be”部分。
e.g. When(hewas) still a boy of ten, he had to work day and night.
If(you are) asked you may come in.
If(it is) necessary I'll explain to you again.
3、注意区分不同从句:引导的是什么从句,不仅要根据连词,还要根据句子结构和句意来判别。以where为例,能引导多种从句。
e.g. You are to find it where you left it.(地点状语从句)
Tell me the address where he lives.(定语从句,句中有先行词)
I don't know where he came from.(宾语从句)
Where he has gone is not known yet.(主语从句)
This place is where they once hid.(表语从句)
注意:表示“一…就…”的结构 hardly/scarcely…when/before/no sooner…than和as soon as都可以表示“一…就…”的意思。
例句:I had hardly/scarcely got home when it began to rain.
I had no sooner got home than it began to rain.
As soon as I got home, it began to rain.
注意:如果hardly/scarcely或nosooner置于句首,句子必须用倒装结构:
例句:Hardly/Scarcely had I got home when it began to rain.
No sooner had I got home than it began to rain.
与“短文改错。此题要求改正所给短文中的错误。对标题号的每一行...”考查相似的试题有:
- All parents love their children, ______ they make mistakes.A.becauseB.ifC.even ifD.as if
- James took the magazines off the little table to make_______for the television.A.roomB.areaC.fieldD.position
- To come back before Sunday, I have made a few minor ________ to the schedule of my trip.A.adjustmentsB.arrangementC...
- Why don’t you bring ______ to his attention that you are too ill to go on working?A.itB.thatC.thisD.them
- Please admire the ___decorated rooms where King HenryⅤⅢ met kings from other countries.A.beautifullyB.beautifulC.b...
- The person who was taking photos asked the family to sit ______ and listen ______ to his order.[ ]A. closely; closeB....
- 19.From this year’s poor results, one can see ______ many changes have been made in the football team and that, sadl...
- Our class discussed the question of __________it is necessary for us students to use mobile phones on campus.A.ifB....
- The place was flooded ________ it had been raining for several weeks.A.becauseB.because ofC.ever sinceD.as a resu...
- I don’t like _________ you speak to her.A.the wayB.the way in thatC.the way whichD.the way of which