本试题 “根据短文内容用适当的关系代词或副词填空。The time l. ________ Elias first met Nelson Mandela was a very difficult period in his life. Mandela wasthe...” 主要考查您对关系代词
关系副词
故事类阅读
等考点的理解。关于这些考点您可以点击下面的选项卡查看详细档案。
- 关系代词
- 关系副词
- 故事类阅读
关系代词的概念:
英语中的关系代词有who, whom, whose, that, which, 它们是用来引导定语从句的。关系代词既代表定语从句所修饰的词,又在其所引导的从句中承担一个成分,如主语、宾语、表语、或定语。
如:This is the man who saved your son. (who在从句中作主语,先行词是man)
The man whom I met yesterday is Jim.
A child whose parents are dead is an orphan.
He wants a room whose window looks out over the sea.
关系代词用法:
1、that与which的用法区别:
两者都可指物,常可互换。其区别主要在于:
(1)引导非限制性定语从句时,通常要用which:
如:She received an invitation from her boss, which came as a surprise. 她收到了老板的邀请,这是她意想不到的。
(2)直接放在介词后作宾语时,通常要用which:
如:The tool with which he is working is called a hammer. 他干活用的那个工具叫做锤子。
(3)当先行词是下列不定代词或被它们修饰时much, little, none, all, few, every(thing), any(thing), no(thing)等时,通常用that:
如:There was little that the enemy could do but surrender. 敌人无法,只有投降了。
All[Everything] that can be done must be done. 凡能做的事都必须做。
(4)当先行词有the very, the only, the same等修饰时,通常用that:
如:This is the only example that I know. 我知道的例子只有这一个。
Those are the very words that he used. 那是他的原话。
(5)当先行词有形容词最高级或序数词(包括last, next等)等修饰时,通常用that:
如:This is the best dictionary that I've ever used. 这是我用过的最好的词典。
The first thing that you should do is to work out a plan. 你应该做的第一件事是订个计划。
(6)当关系代词在定语从句中用作表语时,通常用that:
如:China is not the country(that) it was. 中国已不是过去的中国了。
(7)当先行词是一个既指人又指物的并列词组时,通常用that:
如:They talked about the persons and things that most impressed them. 他们谈论了使他们印象最深的人和事。
(8)当要避免重复时:
如:Which is the course that we are to take? 我们选哪门课程?
2、that与who的用法区别:
(1)两者均可指人,有时可互换:
如:All that[who] heard him were delighted. 所有听了他讲话的人都很高兴。
Have you met anybody that[who] has been to Paris? 你遇见过到过巴黎的人吗?
He is the only one among us that[who] knows Russian. 他是我们中间唯一懂俄语的人。
(2)但是在下列情况,通常要用that:
①当先行词是一个既指人又指物的并列词组时:
如:I made a speech on the men and things that I had seen abroad. 我就我在国外所见到的人和事作了报告。
②当先行词是who时(为避免重复):
如:Who was it that won the World Cup in1982? 谁赢得了1982年的世界杯?
③当关系代词在定语从句中作表语时(可省略):
如:Tom is not the boy(that) he was. 汤姆这孩子已不是以前那个样子了。
关系代词知识体系:
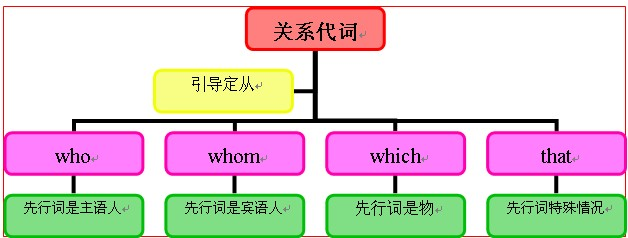
关系代词用法拓展:
1、as与which的用法区别:
(1)引导限制性定语从句时,在such,as,thesame后只能用as,其他情况用which:
如:I never heard such stories as he tells. 我从未听过他讲那样的故事。
It's the same story as I heard yesterday. 这故事跟我昨天听到的一样。
This is the photo which shows my house. 这张照片拍的是我的住宅。
(2)引导非限制性定语从句时,有时两者可互换:
如:I live a long way from work, as [which] you know. 我住得离工作单位很远,这你是知道的。
(3)但在,在以下情况引导非限制性定语从句时,两者不可换用:
①当从句位于主句前面时,只用as:
如:As is known to everybody, the moon travels round the earth once every month. 月球每月绕地球转一周,这是每个人都清楚的。
②as引导的非限制性定语从句应与主句在意义上和谐一致,which无此限制:
如:He went abroad, as[which] was expected. 他出国了,这是大家预料到的。
He went abroad, which was unexpected. 他出国了,这让大家感到很意外。(不用as)
③as引导非限制性定语从句时,先行词通常不能是主句中某个具体的词,而应是整个句子、整个短语或某个短语推断出来的概念,而which则无此限制:
如:The river, which flows through London, is called the Thames. 这条流经伦敦的河叫泰晤士河。(不用as)
④当as引导非限制性定语从句作主语时,其谓语通常应是连系动词,而不宜是其他动词,而which则无此限制:
如:She has married again, as[which] seemed natural. 她又结婚了,这似乎很自常。
She has married again, which delighted us.她又结婚了,这使我们很高兴。(不用as)
2、who与whom的用法区别:
两者均只用于人,从理论上说,who为主格,whom为宾格:
如:Where's the girl who sells the tickets? 卖票的女孩在哪里?
The author whom you criticized in your view has written a letter in reply. 你在评论中批评的那个作者已写了一封回信。
但实际上,除非在正式文体中,宾格关系代词whom往往省略不用,或用who或that代之:
如:The man(that, who, whom) you met just now is called Jim. 你刚遇见的那个人叫吉姆。
不过,在以下几种情况值得注意:
(1)直接跟在介词后面作宾语时,只能用whom,而且不能省略:
如:She brought with her three friends, none of whom I had ever met before. 她带了3个朋友来,我以前都没见过。
(2)引导非限制性定语从句且作宾语时,who和whom均可用,但以用whom为佳,此时也不能省略:
如:This is Jack, who[whom] you haven't met before. 这是杰克,你以前没见过。
关系副词的概念:
关系副词兼有副词与连接词两种作用,在不及物动词的连接中要求用关系副词。关系副词有when, where, why。
关系副词的特点:
关于副词用于引出定语从句,主要有when, where, why:
如:Sunday is the day when very few people go to work. 星期日是没什么人上班的日子。
That's the reason why he dislikes me. 这就是他不喜欢我的原因。
Do you know a shop where I can find sandals? 你知道哪家商店我能找到凉鞋吗?
注:关系副词用于引出定语从句,且在从句中用作状语。关系副词when表示时间,where表示地点,why表示原因。
使用关系副词应注意的几点:
(1)how不能用作关系副词,不要想当然地将how用作关系副词置于theway后表示方式:他说话就是那个样子。
误:This is the way how he spoke.
正:This is how he spoke./ This is the way(that, in which)he spoke.
(2)关系副词when和where既可引导限制性定语从句,也可引导非限制性定语从句,但why只能引导限制性定语从句,不能引导非限制性定语从句(若引导非限制性定语从句,可用for which reason)。
(3)引导定语从句时,when的先行词为时间,where的先行词为地点,why的先行词为原因(主要是the reason),但是反过来却不一定:
如:Don't forget the time(that) I've toldyou.不要忘记我告诉你的时间。
Do you know the house(that) he bought recently? 你知道他最近买的那座房子吗?
Please tell me there as on(that) you know. 请告诉我你所知道的原因吧。
关系副词的用法:
关系副词有when, where, why,作用有三个:
1、连接主句与从句;
2、代替先行词;
3、在从句中作状语,不可省略。
When和where既可引导限制性定语从句,也可引导非限制性定语从句。Why只能引导限制性定语从句。这些关系副词在意义上都相当于一定得“介词+which”结构。
1)when=at/in/on/during,在定语从句中作时间状语。
例如:Tell me the time when(at which) the train leaves.
注意:
①当表示时间的先行词在从句中中作主语或宾语时,不能用when。
例如:I will never forget the days I spent with your family.
②It/This/That+be+the first/second/last time that…句型中,that是习惯用法,不能用 when代替,that还可以省略。从句中使用与“be动词”呼应的完成形式。
例如:It is the first time that I have been to the Great Wall.
2)where表地点,只能跟在表示地点的名词后,它在定语从句中作地点状语。
例如:This is the second school where I used to teach.
注意:
①引导词where可用that替换,并经常可以省略。
例如:That's the place(where/that) we went before.
②当表示地点的先行词在句中作主语或宾语时,不用where,用关系代词that或which。
例如:The factory that/which we visited yesterday was built last year.
③where可与from连用。
例如:His head soon appeared out of the second story windows, from where he could see nothing but rees.
3)why表原因,引导的从句修饰名词reason。Why可用that或forwhich替换或省略。
例如:I don't know the reason(why/for which/that) he left here.
故事类阅读概念:
这类文章一般描述的是某一件具体事情的发生发展或结局,有人物、时间、地点和事件。命题往往从故事的情节、人物或事件的之间的关系、作者的态度及意图、故事前因和后果的推测等方面着手,考查学生对细节的辨认能力以及推理判断能力。
故事类阅读应试技巧:
1、抓住文章的6个要素:
阅读时要学会从事情本身的发展去理解故事情节而不要只看事件在文中出现的先后顺序。因此,无论是顺叙还是倒叙,阅读此类文章时,必须要找到它结构中的5个W(when, where, who, why, what)和1个H(how),不过不是每篇都会完整地交待六个要素。毫无疑问,寻出这些元素是能够正确快速解题的一个先决条件。
2、注意作者的议论和抒情:
高考英语阅读理解故事类文章常伴随着作者思想情感的流露和表达,因此议论和抒情往往夹杂其中。行文时或按事情发生发展的先后时间进行或按事情发生发展的地点来转换,也可能按事情发展的阶段来布局。在引出话题,讲完一件事情后,作者往往会表达个人感悟或提出建议等。这些体现作者观点或思想的语句在阅读时可以划线,它们往往体现文章中心或者写作意图,属于必考点,所以要仔细体会。
3、结合前两点归纳文章中心,把握作者态度:
故事类文章是通过记叙一件事来表达中心思想的,它是文章的灵魂。归纳文章中心思想时,尤其要分析文章的结尾,因为很多文章卒章显志,用简短的议论、抒情揭示文章中心;文章中议论抒情的句子往往与中心密切相关;也有的文章需要在结合概括各段大意的基础上归纳中心。另外,叙述一件事必有其目的,或阐明某一观点,或赞美某种品德,或抨击某种陋习,这就要求我们在阅读时,通过对细节(第1点中的六要素)的理解,把握作者的态度。
4、有章有据进行解题判断:
分析文章,归纳主题,属于分析、概括、综合的表述能力的考查。切忌脱离文章,架空分析,一定让分析在文章中有依据。
与“根据短文内容用适当的关系代词或副词填空。The time l. _____...”考查相似的试题有:
- Some people like living abroad, while others think there is ______ like home.A.somethingB.anythingC.nothingD.ever...
- It was evening _____ we reached the little town of Win Chester.[ ]A. thatB. untilC. whenD. since
- Mark was a student at this university from 1999 to 2003, _____ he studied very hard and was madechairman of the Stude...
- One day the employees of a large company in St Louis, Missouri returned from their lunch break and were greeted with ...
- I was the middle child of three, but there was a gap of five years on either side, and I hardly saw my father before ...
- 完形填空。 Jean's father was a farm plane pilot in the little farming community in Northern California where shewas r...
- 阅读下面的短文,然后以约30个词概括故事的主要情节。An old man went to live with his son, daughter-in-law, and four-yea...
- 阅读理解。Introductory Chemistry was taught at Duke University for many years by professor Bonk.One year, two guys to...
- 第三部分阅读理解(共15小题,每小题2分,满分30分)阅读下列短文,从每题所给的四个选项中,选出最佳选项,并在答题卡上将该项...
- 完形填空(共20题,每小题1.5分,满分30分)阅读下面短文,掌握其大意,然后从36—55各题所给的四个选项(A、B、C和D)中,选...