本试题 “The football match was really _______. No one was sure which side ________ until the last moment.[ ]A. firm; would winB. exciting; was winningC. ti...” 主要考查您对形容词
过去将来时
等考点的理解。关于这些考点您可以点击下面的选项卡查看详细档案。
- 形容词
- 过去将来时
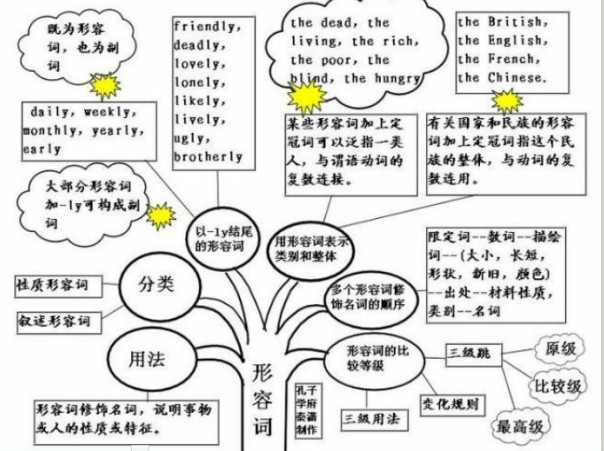
形容词的概念:
形容词(adjective),简称adj.或a,形容词用来修饰名词或代词,表示人或事物的性质、状态,和特征的程度好坏与否,形容词在句中作定语、表语、宾语补足语。通常,可将形容词分成性质形容词和叙述形容词两类,其位置不一定都放在名词前面。
形容词的作用与位置:
形容词是用来修饰名词的,常被放在名词前作定语,或放在系动词后面作表语。以下属几种特殊情况,须牢记;
(1)形容词短语作定语,定语后置。
如:a language difficult to master,
a leaning tower about 180 feet high
(2)表语形容词(afraid、alike、alone、asleep、awake、alive等)作定语,定语后置。如a man alive。有些表身体健康状况的形容词如well、faint、ill只作表语。sick既可作表语又可作定语,ill如作定语意为“bad”。
(3)用作定语,修饰由不定代词one、no、any、some和every构成的复合词如anything、something等时,通常后置。
如:I have something important to tell you.
(4)else常用作疑问代词和不定代词的后置定语。
(5)enough、nearby修饰名词前置或后置,程度副词一般位于形容词、副词前面,enough修饰形容词、副词时,必须后置。
(6)几个并列的形容词作定语,其语序通常为:限定语(The、A)+描绘性形容词+size(大小)+shape(形状)+age(年龄、时间)+color(颜色)+origin(国籍、来源)+material(材料)+purpose(目的)+名词。
口诀:
限定描绘大长高,形状年龄和新老;颜色国籍跟材料,作用类别往后靠。
如:a heavy black Chinese steel umbrella,
the man's first tow interesting little red French oil paintings
形容词的用法:
1、形容词修饰名词,说明事物或人的性质或特征。通常,可将形容词分成性质形容词和叙述形容词两类,其位置不一定都放在名词前面:
1)直接说明事物的性质或特征的形容词是性质形容词,它有级的变化,可以用程度副词修饰,在句中可作定语、表语和补语。例如:hot热的。
2)叙述形容词只能作表语,所以又称为表语形容词。这类形容词没有级的变化,也不可用程度副词修饰。
大多数以a开头的形容词都属于这一类。例如:
afraid害怕的。(错)Heisanillman. (对)Themanisill. (错)Sheisanafraidgirl. (对)Thegirlisafraid.
这类词还有:well,unwell,ill,faint,afraid,alike,alive,alone,asleep,awake等。
3)形容词作定语修饰名词时,要放在名词的前边。但是如果形容词修饰以-thing为字尾的词语时,要放在这些词之后。例如:somethingnice
2、用形容词表示类别和整体:
1)某些形容词加上定冠词可以泛指一类人,与谓语动词的复数连接。如:the dead,the living,the rich,the poor,the blind,the hungry The poorarelosinghope.穷人失去了希望。
2)有关国家和民族的形容词加上定冠词指这个民族的整体,与动词的复数连用。如:the British,the English,the French,the Chinese. The English have wonderful senseofhumor.
以-ly结尾的形容词:
1)大部分形容词加-ly可构成副词。但friendly,deadly,lovely,lonely,likely,lively,ugly,brotherly,仍为形容词。改错:
如:(错)She sang lovely.
(错)He spoke to me very friendly.
(对)Her singing was lovely.
(对)He spoke to me in a very friendly way.
2)有些以-ly结尾既为形容词,也为副词。 daily,weekly,monthly,yearly,early .
如:The Times is a daily paper.
The Times is published daily.
形容词知识体系:
复合形容词的构成:
(1)形容词+名词+ed:
如:kind-hearted 好心的,white-haired 白发的
(2)形容词+形容词:
如:red-hot 炽热的,dark-blue 深蓝的
(3)形容词+现在分词:
如:good-looking 好看的,easy-going 随和的
(4)副词+现在分词:
如:hard-working 勤劳的,fast-moving 快速转动的
(5)副词+过去分词:
如:hard-won 得来不易的,newly-made 新建的
(6)名词+形容词:
如:life-long 终生的,world-famous 世界闻名的
(7)名词+现在分词:
如:peace-loving 爱好和平的,fun-loving 爱开玩笑的
(8)名词+过去分词:
如:snow-covered 白雪覆盖的,hand-made 手工的
(9)数词+名词+ed:
如:four-storeyed 4层楼的,three-legged 3条腿的
(10)数词+名词(名词用单数):
如:ten-year 10年的, two-man 两人的
过去将来时的概念:
过去将来时表示从过去的某一时间来看将来要发生的动作或存在的状态。过去将来时常用于宾语从句和间接引语中。过去将来时的出发点是过去,即从过去某一时刻看以后要发生的动作或状态。
过去将来时的结构:
(1)would+动词原形:
如:She told us that she would try her best to catch up with other classmates this term. 她告诉我们说她将一切努力在本期赶上其他同学们。
When you asked Li Lei for help, he would never refuse you. 过去当你请她帮忙时,他绝不会拒绝。
(2)was/were going to+动词原形:
如:He told us that he was going to attend the meeting. 他告诉我说他要参加那次会议。
He said that I was going to be sent to meet her at the railway station.他说将要派我去火车站接她
(3)was/were to+动词原形:
如:The building was to be completed next month. 这座建筑改在下个月竣工。
Li Lei was to arrive soon. 李蕾很快就要到了。
(4)was/were about to+动词原形:
如:We were about to leave there when it began to rain heavily and suddenly. 就在我们要离开时,天突然下起了大雨。
He was about to have lunch when the bell rang. 就在他要吃中饭的时候,门铃响起来了。
(5)was/were+现在分词:
如:He was leaving the next day. 他第二天要走了。
We were informed that the leaders were coming to our school soon. 我们接到通知说领导们很快要来我们学校。
过去将来时的用法:
(1)过去将来时,一般用于主句为过去时的宾语从句中。
如:He said he would stay with us. 他说他要与我们呆在一起。
He said he would never go there again. 他说他绝不会再去那儿。
(2)过去将来时,用于虚拟语气中。
如:If I were you, I would not do that. 要是我是你的话,我就不会那样做。
If he were here, he would show us how to do it. 如果他在这儿,他就会向我们展示该如何做了。
过去将来时用法拓展:
was/were going to+动词原形;
was/were to+动词原形;
was/were about to+动词原形等结构都可表达当时一种未曾实现的意图或打算。
如:The conference was going to be held the next month. 会议下个月开。
We were to have our class at eight. 八点我们该上课了。
I was about to tell him about it when WuDong go tin. 就在我要告诉他时,吴东进来了。
与“The football match was really _______. No one was sure wh...”考查相似的试题有:
- I've applied for the job but I'm not very ________ about my chance of getting it.[ ]A.optimisticB.comfortableC.tir...
- 37. Alan had taken care with his appearance that evening.A.generalB.simpleC.extraD.Important
- It is not ____ for me to return all the books to the library now because I still need them.[ ]A. matureB. convenientC...
- 114. How ________ you to remember my birthday!A.sweet forB.sweet ofC.kind forD.nice for
- Painting from still images leads to a loss of sensitivity, which is _____ to an artist.[ ]A. absoluteB. urgentC. spec...
- _____ and happy, Tony stood up and accepted the prize.[ ]A. SurprisingB. SurprisedC. Being surprisedD. To be surprised
- Yesterday our head teacher made such an ____ speech that we all felt _____.A.exciting; excitingB.excited; exci...
- They haven't seen each other for ten years, but they still keep in _____ contact with each other.[ ]A. constantB. ins...
- Interest is as ________ to learning as the ability to understand, even more so.A.similarB.vitalC.availableD.specific
- Keeping your body your mental health.A.is benefit withB.was beneficial toC.have beneficial toD.is beneficial to