本试题 “We the Chinese are not to be ______, ________the situation is.[ ]A. won; however disastrousB. defeated; whatever disastrousC. beaten; whatever disa...” 主要考查您对动词
状语从句
等考点的理解。关于这些考点您可以点击下面的选项卡查看详细档案。
- 动词
- 状语从句
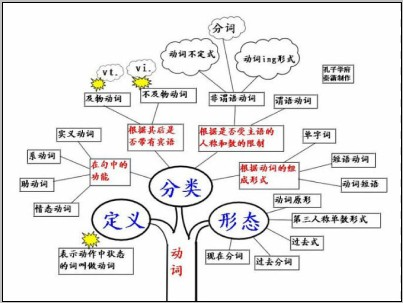
动词的定义:
表示动作中状态的词叫做动词。根据其在句中的功能,动词可分为行为动词、系动词、助动词和情态动词四类,有些动词是兼类词。
例如:We have lunch at 12. (have是行为动词)
We have been to NewYork. (have是助动词)
I am hungry. (am是系动词)
You need not have waited for me. (need是情态动词)
The door needs painting. (need是兼类词)
动词的分类:
1)表示动作中状态的词叫做动词。
2)根据其在句中的功能,动词可分为四类,分别是:
实义动词(Notional Verb)、系动词(Link Verb)、助动词(Auxiliary Verb)、情态动词(Modal Verb)。
说明:有些情况下,有些动词是兼类词。
例如:We are having a meeting. 我们正在开会。(having是实义动词。)
He has gone to NewYork.他已去纽约。(has是助动词。)
3)动词根据其后是否带有宾语,可分为两类,分别是:
及物动词(Transitive Verb)、不及物动词(Intransitive Verb),缩写形式分别为vt.和vi.。
说明:同一动词有时可用作及物动词,有时可用作不及物动词。
例如:She can dance and sing. 她能唱歌又能跳舞。(sing在此用作不及物动词。)
She can sing many English songs. 她能唱好多首英文歌曲。(sing用作及物动词。)
4)根据是否受主语的人称和数的限制,可分两类,分别是:
限定动词(Finite Verb)、非限定动词(Non-finite Verb)。
例如:She sings very well. 她唱得很好。(sing受主语she的限制,故用第三人称单数形式sings。)
She wants to learn English well. 她想学好英语。(to learn不受主语she的限制,没有词形变化,是非限定动词。
说明:英语中共有三种非限定动词,分别是:动词不定式(Infinitive)、动名词(Gerund)、分词(Participle)。
5)根据动词的组成形式,可分为三类,分别是:
单字词(One-Word Verb)、短语动词(Phrasal Verb)、动词短语(Verbal Phrase)
例如:The English language contains many phrasal verbs and verbal phrases. 英语里有许多短语动词和动词短语。(contains是单字动词。)
Students should learn to look up new words in dictionaries. 学生们学会查字典。(look up是短语动词。)
The young ought to take care of the old. 年轻人应照料老人。(takecareof是动词短语。)
6)动词有五种形态,分别是:
原形(OriginalForm)、第三人称单数形式(Singular From in Third Personal)、过去式(Past Form)、过去分词(Past Participle)、现在分词(Present Participle)。
动词知识体系:
状语从句的概念:
状语从句指句子用作状语时,起副词作用的句子。它可以修饰谓语、非谓语动词、定语、状语或整个句子。根据其作用可分为时间、地点、原因、条件、目的、结果、让步、方式和比较等从句。状语从句一般由连词(从属连词)引导,也可以由词组引起。从句位于句首或句中时通常用逗号与主句隔开,位于句尾时可以不用逗号隔开。
比较while/as/when:
1、as/when引导短暂性动作的动词例句:
如:Just as/Just when/When I stopped my car, a man came up to me.
2、当从句的动作发生于主句动作之前,只能用when引导这个从句,不可用as或while。
如:When you have finished your work, you may have a rest.
3、从句表示“随时间推移”连词能用as,不用when或while。
如:As the day went on, the weather got worse.
比较untill/till:
两个连词意义相同,肯定形式表示的意思是“做某事直至某时”,动词必须是延续性的。否定形式表达的意思是“直至某时才做某事”,动词为延续性或非延续性都可以。
正确使用这两个连词的关键之一就在于判断句中的动词该用肯定式还是否定式。
肯定句例句:I slept until midnight. 我一直睡到半夜时醒了。
Wait till I call you. 等着我叫你。
注意:在肯定句中可用before代替:Let's get in the wheat before the sunsets.
否定句例句:She didn't arrive until 6o'clock.
I didn't manage to do it until you had explained how.
1、Until可用于句首,而till通常不用于句首。
例句:Until you told me, I had heard nothing of what happened.
2、Untilwhen疑问句中,until要放在句首。
例句:Until when are you staying? 你呆到什么时候?
注意:否定句可用另外两种句式表示。
1)Not until…在句首,主句用倒装。
例句:Not until the early years of the19th century did man know what heat is.
2)It is not until…that…
状语从句的用种类:
1、时间状语从句:
表示时间的状语从句可由when, as, while, whenever, after, before, till(until), since, once, as soon as(或the moment), by the time, no sooner…than, hardly(scarcely)… when, everytime等引导。
e.g. When I came into the office, the teachers were having a meeting.
He started as soon as he received the news.
Once you see him, you will never forget him.
No sooner had I gone to bed than I went to sleep.
2、原因状语从句:
原因状语从句是表示原因或理由的,引导这类从句的最常用的连词是because, since, as, nowthat(既然)等,for表示因果关系时(它引导的不是从句)为并列连词,语气不如because强。 e.g. He is disappointed because he didn't get the position.
As it is raining, I will not go out.
Now that you mention it, I do remember.
3、地点状语从句:
引导地点状语从句的连词是where和wherever等。
e.g. Sit wherever you like.
Make a mark where you have a question.
4、目的状语从句:
引导目的状语从句最常用的词(组)是so, so that(从句谓语常有情态动词), in order that, in case(以防,以免)等。
e.g. Speak clearly, so that they may understand you.
She has bought the book in order that she could follow the TV lessons.
He left early in case he should miss the train.
5、结果状语从句:
结果状语从句是表示事态结果的从句,通常主句是原因,从句是结果。由so that(从句谓语一般没有情态动词),so…that, such…that等引导。
e.g. She was ill, so that she didn't attend the meeting.
He was so excited that he could not say a word.
She is such a good teacher that everyone admires her.
6、条件状语从句:
条件状语从句分真实性(有可能实现的事情)与非真实性(条件与事实相反或者在说话者看来不大可能实现的事情)条件句。
引导条件状语从句的词(组)主要有if, unless, so(as)long as, on condition that, so(as) far as, if only(=if)。
注意:条件从句中的if不能用whether替换。
e.g. If he is not in the office, he must be out for lunch.
You may borrow the book so long as you keep it clean.
So far as I know(据我所知), he will be away for three months.
You can go swimming on condition that(=if) you don't go too far away from the river bank.
If he had come a few minutes earlier, he could have seen her.
7、让步状语从句:
让步状语从句可由although, though, as, even if(though), however, whatever, whether…or, no matter who(when, what,…)等引导。
注意:as引导的让步状语从句一般是倒装的。
e.g. Though he is a child, he knows a lot.
Child a she is, he knows a lot.
Whatever(=No matter what) you say, I'll never change my mind.
8、方式状语从句:
方式状语从句常由as, as if(though), the way, rather than等引导。
e.g.You must do the exercise as I show you.
He acted as if nothing had happened.
9、比较状语从句:
比较状语从句常用than, so(as)…as, the more…the more等引导。
e.g. I have made a lot more mistakes than you have.
He smokes cigarettes as expensive as he can afford.
The busier he is, the happier he feels.
使用状语从句时要注意的几个问题:
1、在时间和条件(有时也在方式、让步等)从句中,主句是一般将来时,从句通常用一般现在时表示将来。
e.g. We'll go outing if it doesn't rain tomorrow.
I'll write to you as soon as I get to Shanghai.
2、有些时间、地点、条件、方式或让步从句,如果从句的主语与主句主语一致(或虽不一致,是it),从句的谓语又包含动词be,就可省略从句中的“主语+be”部分。
e.g. When(hewas) still a boy of ten, he had to work day and night.
If(you are) asked you may come in.
If(it is) necessary I'll explain to you again.
3、注意区分不同从句:引导的是什么从句,不仅要根据连词,还要根据句子结构和句意来判别。以where为例,能引导多种从句。
e.g. You are to find it where you left it.(地点状语从句)
Tell me the address where he lives.(定语从句,句中有先行词)
I don't know where he came from.(宾语从句)
Where he has gone is not known yet.(主语从句)
This place is where they once hid.(表语从句)
注意:表示“一…就…”的结构 hardly/scarcely…when/before/no sooner…than和as soon as都可以表示“一…就…”的意思。
例句:I had hardly/scarcely got home when it began to rain.
I had no sooner got home than it began to rain.
As soon as I got home, it began to rain.
注意:如果hardly/scarcely或nosooner置于句首,句子必须用倒装结构:
例句:Hardly/Scarcely had I got home when it began to rain.
No sooner had I got home than it began to rain.
与“We the Chinese are not to be ______, ________the situatio...”考查相似的试题有:
- It whether you come or not.A.makes no differenceB.takes no differenceC.makes not differenceD.takes not differences
- My computer must be infected with virus (病毒), for it will ________when I________.[ ]A. die; log onB. break; log onC...
- It took me some time to ____ what I had heard.A. digestB. swallowC. eatD. chew
- — How come a simple meal like this costs so much?— We have _____ in your bill the cost of the cup you broke just now....
- On hearing the news of her husband being killed in the battle, the old lady's face ________ pale.[ ]A. gotB. changedC...
- 短文改错。此题要求改正所给短文中的错误。对标有题号的每一行做出判断:如有错误(每行只有一个错误),则按下列情况改正:该行...
- I was expecting him at ten,but he didn’t_________.A.turn onB.turn offC.turn upD.turn over
- . Her letters_____ the beautiful days when they lived in his hometown.A.call upB.call forC.call onD.call at
- The child should be punished. You shouldn’t let him ______ telling lies.A.keep away fromB.keep away withC.get away...
- .Everybody in our country, men and women, old and young_____sports and games.A.are fond ofB.enjoysC.got in forD.t...