本试题 “It is ten years _____ I lived in Nanjing, so I know ____ about what it is like today.[ ]A. since; nothingB. that; everythingC. before; somethingD. ...” 主要考查您对不定代词
从属连词
等考点的理解。关于这些考点您可以点击下面的选项卡查看详细档案。
- 不定代词
- 从属连词
不定代词概说:
英语的不定代词有all, each, both, either, neither, one, none, little, few, many, much, other, another, some, any, no, few, little, both, enough, every等,以及由some,any,no和every构成的合成代词(即somebody, anyone, nothing等)。在这些不定代词中,多数都能作主语、宾语、表语或定语,但是代词none以及由some, any, no和every构成的合成代词只能作主语、宾语或表语,不能作定语,而no和every则只用作定语。
不定代词用法对比:
1、so little与such little的区别:
用so little还是such little取决于little的意思:若表示数量方面的“少”,则用so little;若表示形状体积的“小”,则用such little:
如:He has so little time for reading. 他读书的时间少得可怜。
I've never seen such little boxes. 我从未见过那样小的盒子。
2、some与any的用法区别:
一般说来,some用于肯定句中,any用于否定句和疑问句中。但是,在表示请求、邀请或征求意见的句子中,通常要用some而不用any:
如:Would you like some cake? 吃点蛋糕吗?
Why not buy some bread? 为什么不买些面包呢?
Shall I get some chalk for you? 要我帮你拿些粉笔来吗?
注:any有时也用于肯定句中,此时表示“任何”:
如:Any colour will do. 任何颜色都行。
Come any day you like. 随便哪天来都可以。
3、many与much的用法区别:
两者都表示“许多”,但many修饰或代替可数名词(复数),与few(少数)相对;
而much用来修饰或代替不可数名词(单数),与little(少量)相对。在口语中两者主要用于非肯定句中:
如:Did you see many people there? 你在那儿看见许多人了吗?
We don't have much time. 我们没有许多时间。
在肯定句中,一般用a lot of, lots of, plenty of 等代之。但在正式文体中有时也用于肯定句中;
另外,若用作主语或主语的定语,或其前有how, too, as, so, a good, a great等修饰,也可用于肯定句中:
如:Many of us left early. 我们有许多人离开得很早。
Much work has been done. 许多工作都已经做了。
You've given me too much. 你已给我太多了。
Take as many(much) as you want. 你要多少拿多少。
I asked her a great many questions. 我问了她许多问题。
4、few, a few与little, a little的用法区别:
(1)few和a few后接可数名词的复数形式。few表示数量很少或几乎没有,强调“少”,含有否定意义;
a few表示数量虽然少但毕竟还有,强调“有”,含有肯定意义:
如:It is very difficult, and few people understand it. 它很难,没有几个人能懂。
It is very difficult, but a few people understand it. 他虽难,但是有些人懂。
(2)little和alittle之后接不可数名词,其区别跟few和a few之间的区别相似:
如:Unfortunately, I had little money on me. 很不巧,我身上没带什么钱。
Fortunately, I had a little money on me. 幸好我身上带着一点钱。
5、other, the other, another与others的用法区别:
这些不定代词不仅在含义上有单复数之分,而且在用法上有泛指(无the)和特指(有the)之别。其用法区别可归纳如下:
(1)指单数时,若泛指用another,若特指用the other:
如:Give me another(one). 另外给我一个。
Shut the other eye, please. 请把另一只眼睛也闭上。
(2)指复数时,若泛指用other(后接复数名词),若特指用the other(后接复数名词):
如:There are other ways of doing it. 做这事还有其他的办法。
Where have the other students gone? 其他学生都到哪里去了?
(3)others永远表示复数意义(且其后不能再接名词)。其用法大致相当于“other+复数名词”,同样地the others大致相当于“the other+复数名词”:
如:Other people[Others] may not think that way. 别的人可能不这样想。
He is cleverer than the others[the other students] in her class. 他比班上其他学生聪明。
(4)another一般只能表单数,且其后接名词也只能接单数名词。但是若其后有数词或few修饰时,则也可接复数名词:
如:We need another few chairs. 我们还需要几把椅子。
In another two weeks it'll be finished. 再过两个星期就可做完了。
(5)与some对比使用时,用others(此时与some同义):
如:Some say yes, and others say no. 有人说对,有人说不对。
不定代词用法点拨:
1、指两者和三者的不定代词:
有些不定代词用于指两者(如both, either, neither),有的不定代词用于指三者(如all, any, none, every),注意不要弄混:
如:Both of my parents are doctors. 我的父母都是医生。
All of the students are interested in it. 所有的学生对此都很感兴趣。
There are trees on any side of the square. 广场的每一边都种有树。
He has two sons, neither of whom is rich. 他有两个儿子,都不富有。
He has three sons, none of whom is rich. 他有三个儿子,都不富有。
注:each可用于两者、三者或三者以上,而every只用于三者或三者以上,因此用于两者时只能用each,不能用every。
2、复合不定代词的用法特点:
复合不定代词包括something, somebody, someone, anything, anybody, anyone, nothing, nobody, noone, everything, everybody, everyone等。它们在句中可用作主语、宾语或表语,但不能用作定语。something, someone等和anything, anyone等的区别与some和any的区别一样,前者一般用于肯定句,后者一般用于否定句、疑问句或条件句。具体使用时应注意以下几点:
(1)复合不定代词受定语修饰时,定语应放在它们后面:
如:There is nothing wrong with the radio. 这收音机没有毛病。
Have you seen anyone[anybody] famous? 你见过名人吗?
(2)指人的复合不定代词若用作主语,其谓语动词一般用单数,相应的人称代词和物主代词也用单数he, him, his(不一定指男性)。但在非正式文体中常用复数代词they, them, their:
如:Everyone knows this, doesn't he[don't they]? 人人都知道这一点,不是吗?
If anybody[anyone] comes, ask him[them] to wait. 要是有人来,让他等着。
(3)指事物的复合不定代词若用作主语,谓语动词只能用单数,相应的人称代词也只能用it,而不用they:
如:Everything is ready, isn't it? 一切都准备好了,是吗?
(4)anyone, everyone等只能指人,不能指物,且其后一般不接of 短语。若是指物或后接of 短语,可用any one, every one(分开写):
如:any one of the boys(books) 孩子们(书)当中的任何一个(本)
every one of the students(schools) 每一个学生(一所学校)
3、是any not还是not any:
按英语习惯,any以及含有any的复合不定代词用于否定句时,它只能出现在否定词之后,而不能在否定词之前:
误:Anyone doesn't know how to do it.
正:No one knows how to do it.任何人都不知道如何做它。
误:Anybody[Anyone] can not do it.
正:Nobody[Noone] can do it.这事谁也干不了。
误:Anything can not prevent me from going.
正:Nothing can prevent me from going. 什么也不能阻挡我去。
4、不定代词与部分否定:
不定代词all, both, every等与not连用时构成部分否定;若要表示完全否定,则需换用none, neither, no one等。
比较:All of the students like the novel. 所有这些学生都喜欢这本小说。
Not all of the students like the novel. 并不是所有这些学生都喜欢这本小说。
All of the students don't like the novel. 并不是所有这些学生都喜欢这本小说。
None of the students like the novel. 这些学生当中没有一个喜欢这本小说。
5、all, both, each等用作同位语:
若用作主语同位语,主语可以是名词或代词;若用作宾语等其他成分的同位语,则宾语等成分必须是人称代词,而不能是名词:
如:We have all read it. 我们都读过他。(all修饰的主语是代词)
The villages have all been destroyed. 村庄都被毁了。(all修饰的主语是名词)
They told us all to wait there. 他叫我们都在那儿等。(all修饰的宾语是代词)
但不能说:They told the men all to wait there. (all修饰的宾语是名词不是代词)
不定代词知识体系:

不定代词与语境考题:
不定代词是高考的常考考点,有的不定代词考题出得比较灵活,不能死套规则,要注意结合语境来理解:
例1:—Is____here?
—No, Bob and Tim have asked for leave.
A. anybody
B. everybody
C. somebody
D. nobody
解析:
若只是从表面来看,填空句是个疑问句,可能会误选A。但其实此题最佳答案应选B,因为下文的答句说“只有Bob和Tim请假了”,这说明问句是在查人数,故用Is everybody here? (大家都到齐了吗?)
例2:I agree with most of what you said, but I don't agree with_____.
A. everything
B. anything
C. something
D. nothing
解析:
此句若从表面看,有可能误选B,因为填空句为否定句。但实际上最佳答案为A,因为上文说“我同意他说的大部分内容”,这与下文的but I don't agree with everything (但并不是同意他说的所有内容)完全相符。
例3:—Doyouhave_____athomenow,Mary?
—No, we still have to get some fruit and tea.
A. something
B. anything
C. everything
D. nothing
解析:答案:C,句意为“玛丽,现在家里东西都准备齐了吗?”“还没有,我们还要买些水果和茶。”
例4:—If you want a necklace, I'll buy one for you at once.
—Oh, no. A necklace is not_____that I need most.
A. anything
B. something
C. nothing
D. everything
解析:
此题容易误选A,机械地认为:something用于肯定句,anything用于否定句或疑问句。但是,此题的最佳答案是B,something在此的意思不是“某种东西”,而是指“那种东西”或“这种东西”,即心中最想要的那种东西(相当于the thing)。
从属连词的概念:
连词用于引导从句以形成句子的一部分或修饰句子的构成要素的叫作从属连词。
英语从属连词用法分类详解:
1、引导时间状语从句的从属连词:
(1)表示“当…时候”或“每当”的时间连词。主要的when, while, as, whenever:
如:He jumped up when the phone rang. 电话铃响时他吓了一跳。
We listened while the teacher read. 老师朗读时我们听着。
The phone rang just as I was leaving. 我正要离开,电话铃就响了起来。
(2)表示“在…之前(或之后)”的时间连词。主要的有before, after:
如:Turn the lights off before you leave. 离开前请关灯。
He started the job soon after he left the university. 他大学毕业后就开始做这份工作。
(3)表示“自从”或“直到”的时间连词。主要的有since, until, till:
如:He has lived here since he got married. 他结婚后就一直住在这儿。
Most men worked until[till] they're 65. 大多数男人工作到65岁。
(4)表示“一…就”的时间连词。主要的有as soon as, the moment, the minute, the second, the instant, immediately, directly, instantly, once, no sooner…than, hardly…when等:
如:Tell him the news as soon as you see him. 你一见到他就把这消息告诉他。
I recognized her the moment(that) I saw her. 我一看到她就认出她来了。
I want to see him the minute(that) he arrives. 他一到来我就要见他。
I went home directly I had finished work. 我一干完活就回家了。
Once he arrives, we can start. 他一来我们就可以开始。
(5)表示“上次”、“下次”、“每次”等的时间连词。主要的有every time(每次),each time(每次),(the) next time(下次),any time(随时),(the) last time(上次),the first time(第一次):
如:Last time I saw him, he looked ill. 上次我见到他的时候,他好像有病。
Next time you're in London come and visit us. 你下次来伦敦过来探望我们。
Do look me up next time you're in London. 你下次到伦敦来,一定来找我。
Every time I call on him, he is out. 我每次去访问他,他都不在。
You can call me any time you want to. 你随时都可以给我打电话。
【注】every time,each time,any time前不用冠词,(the)next time, (the)last time中的冠词可以省略,而the first time中的冠词通常不能省略。
2、引导条件状语从句的从属连词:
这类连词主要有if, unless, as[so] long as, incase等:
如:If anyone calls tell them I'm not at home. 要是有人打电话来,就说我不在家。
You will fail unless you work hard. 你若不努力就会失败。
As[So] long as you need me, I'll stay. 只要你需要我,我就留下。
In case I forget, please remind me about it. 万一我忘记,请提醒我一下。
【注】在条件状语从句中,通常要用一般现在时表示将来意义,而不能直接使用将来时态。不过,有时表示条件的if之后可能用will,但那不是将来时态,而是表示意愿或委婉的请求(will为情态动词):
如:If you will wait a moment, I'll fetch the money. 请等一下,我就去拿钱。
3、引导目的状语从句的从属连词:
主要有in order that, so that, in case, for fear等:
如:We used the computer in order that we might save time. 我们使用计算机是为了节约时间。
Speak clearly so that they may understand you. 说清楚,以便让他们能明白你的意思。
Be quiet in case you should wake the baby. 安静些,免得把婴儿吵醒。
He is working hard for fear he should fail. 他努力工作以免会失败。
4、引导结果状语从句的从属连词:
主要的有so that, so…that, such…that等:
如:We're all here now, so that the meeting can begin at last. 我们现在都到齐了,终于能开会了。
It's so difficult a question that none of us can answer it. 那是一个很难的问题,我们没有一个人能回答。
He shut the window with such force that the glass broke. 他关窗户用力很大,结果玻璃震破了。
【注】so that中的that在口语中通常可以省略。
5、引导原因状语从句的从属连词:
主要的有because, as, since, seeing(that), now(that), considering(that)等:
如:He couldn't got to school because he had a cold. 他因患感冒而未能去上学。
Since everybody is here, let's begin our discussion. 大家都到了,我们就开始吧。
Seeing that it is 8o'clock, we'll wait no longer. 由于时间已到8点,我们将不再等了。
Now that you are here, you'd better stay. 你既然来了,最好还是留下吧。
6、引导让步状语从句的从属连词:
主要有although, though, eventhough, even if, while, however, whatever, whoever, whenever, wherever等:
如:Although[Though] he is poor, he is well contented. 他虽穷却能知足常乐。
Though[Even though] it's hard work, I enjoy it. 尽管是苦活,但我乐意干。
Even if you don't like wine, try a glass of this. 即使你不喜欢喝酒,也尝尝这杯吧。
7、引导方式状语从句的从属连词:
主要有as, like, as if, as though, the way等:
如:Do it as[like] he does. 像他那样做。
He behaved as if nothing had happened. 他装作若无其事的样子。
They treat me as though I were a stranger. 他们待我如陌生人。
Nobody else loves you the way(=as) I do.没有人像我这样爱你。
8、引导地点状语从句的从属连词:
主要有where, wherever, everywhere等:
如:There were lots of parks where I lived. 我住的地方有许多公园。
Sit wherever you like. 你想坐在那儿就坐在那儿。
Everywhere they went, they were warmly welcomed. 他们每到一个地方都受到热烈欢迎。
9、引导比较状语从句的从属连词:
主要有than和as…as:
如:It's easier than I thought. 这比我想像的要容易。
They are as often wrong as they are right. 他们错对各半。
10、引导名词性从句的从属连词:
主要有that, if, whether:
如:It is clear enough what he meant. 他是什么意思很清楚。
Your greatest fault is that you are careless. 你最大的缺点是粗心大意。
Whether it will do us harm remains to be seen.是否对我们有害还要看一看。
She didn't say if he was still alive. 她没说他是否还活着。
从属连词知识体系:
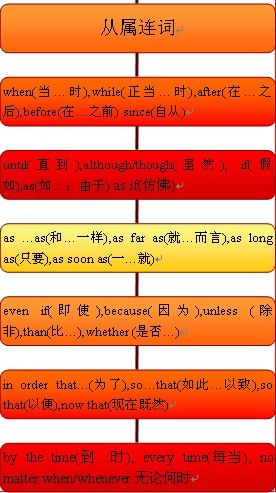
用作从属连词的六类名词结构:
英语中有些名词结构可用作从属连词,用以引导状语从句,且主要是时间状语从句。这类结构归纳起来有以下六类:
一、the+瞬间名词:
其中的瞬间名词主要包括moment, minute, instant, second等,其意为“一……就……”,相当于as soon as。
如:The minute he saw her he fell in love. 他对她一见倾心。
Telephone me the moment(that) you get the results. 你一有结果,马上给我打电话。
I was so tired that I fell asleep the instant I closed my eyes. 我很累,一合上眼就睡着了。
Sheputdownthereceiverthesecondsherecognizedmyvoice.她一听出是我的声音,马上就放下电话听筒。
注:其中的瞬间名词后可接that,也可省略。另外,有的个别副词(如directly/immediately等)也可表示类似意思。
如: Immediately the meal was over,he switchedon the radio.饭一吃完他就把收音机打开。
二、the+季节名词:
其中的季节名词包括spring,summer,autumn,winter,其意为“在……的那年春天、夏天、秋天、冬天。
如:His wife left him thes pring he went abroad.在他出国的那年春天,他的妻子离开了他。
He sold his house and went to the souththe summer he lost hisjob.在他失业的那年夏天,他卖掉房子去了南方。
He was sentto prison the winter his third daughter was born.在他第三个女儿出生的那年冬天,他被关进了监狱。
She got married the autumn she graduated from college.她大学毕业的那年秋天就结婚了。
三、the+时间名词:
其中的时间名词主要包括hour,day,night,week,month,season,year等,其意为“在……的时候、那天、那个晚上、那周、那个月、那个季节、那年”。
如: The hour he wa sin her office,he felt very sad.当他在她办公室的时候,他感到很伤心。
The day here turned home,his father was already dead.他回家的那一天,他的父亲已经死了。
The night I wenttoseeher,shehadleftforBeijingtoattendanimportantmeeting.就我去看她的那个晚上,她到北京去开一个重要的会议了。
Mr Smith didn't go to work the week his wife was ill.史密斯先生在他妻子生病的那个星期没去上班。
They ear helivedinthecountry,he learned alot.他在乡下呆的那一年,他学到了不少东西。
四、the+序数词+time
其中的序数词包括first,second,third,fourth等,其意为“当第几次……的时候”。
如: My girlfriend beat me at pokert he first time weplayed.我头一次和女朋友打扑克,她就把我赢了。
These cond time I saw her,she looked like an old woman.我第二次见到她时,她看上去像一个老太婆。
The third time I went there,I found all of them had left and the offices were all empty.我第三次去那儿时,我发现他们都离开了,所有的办公室都是空的。
注:
1.next,last也具有类似序数词的性质,因此也具有以上用法。
如: Nexttimeyoucomein,pleaseclosethedoor.下次你进来,请关门。
Thelasttimewetalkedhesaidheneededanothertwodays.上次我们谈话时他说他还需要两天。
2.thefirsttime,thesecondtime,thethirdtime等用作连词引导时间状语从句时,其前通常要有定冠词,而(the)nexttime,(the)lasttime引导状语从句时,其中的冠词可以省略,如下面这道上海高考题,其答案是C,不是A:
I though ther nice and honest______Imether.
A.first time B.fo rthe first time C.the first timeD.by the first time
五、不定代词+time
其中的不定代词主要包括each,every,any等。
如:Every time I ringher,the phone is engaged.我每次给她打电话,电话都占线。
Every time I see him he either wants to tell me his trouble or borrow some money.每次我见到他,他不是向我诉苦,就是要向我借钱。
He felt nervous each times he spoke to him.每次她和他讲话,他都感到紧张。
AnytimeyoucometoLondondolookmeup.你无论什么时候到伦敦来,一定要来看我。
注意:everytime,eachtime,anytime用作连词引导状语从句时其前习惯上不用冠词,它与the first time,these cond time,the third time等引导时间状语从句时其前必须要用定冠词不同。
六、其他名词结构
以上归纳的名词结构均用于引导时间状语从句,有些其他结构还可引导其他性质的状语从句,如the way可用于引导方式状语从句,表示“像……一样”。如:
The didn’t do it the way we do now.那时他们不像我们现在这样行事。
Joyce looked at me the way alotof girls did.乔伊丝像许多姑娘那样瞧着我。
注:这样用的theway与as用法相似。
如:Hold itin both hands,the way(=as)Mummy does.用两只手捧住,像妈妈那样。
与“It is ten years _____ I lived in Nanjing, so I know ____ ...”考查相似的试题有:
- — Is this book interesting?— Yes, but I'm sure it won't interest________.[ ]A. everybodyB. anybodyC. nobodyD. somebody
- Mrs. White managed to settle the quarrel between Lei and Rain without hurting the feelings of______.[ ]A. eitherB. no...
- 一 Excuse me. I want to buy some stamps, but I can't find a post office.一 I know _____ nearby. Come on, I'll show yo...
- 短文改错。To everyone in the world, money was a sensitive topic.No one can live with money in modern society. People ...
- When they retire, many people over 60 prefer the houses in the country to spend their remaining years to __________ i...
- 34.About seven years ago she felt she had to ask herself____she really wanted to spend her life farming. Now she has...
- Granny read newspaper every day in her sixties _____ she could keep herself informed of the latest news.A.so thatB....
- The open-air celebration has been put off ____ the bad weather.[ ]A. in case ofB. in spite ofC. instead ofD. because of
- The villagers thought highly of the way we treated the beggar.A.whichB.whereC.whyD.that
- What surprised me was not what he said but ______ he said it.A.the wayB.in way thatC.in the wayD.in the way that